Abstract
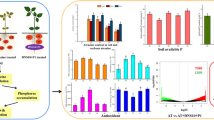
This study investigated the regulatory role of Rhodopseudomonas palustris RP11 in alleviating TBBPA-induced harmful effects in soybean seedlings. In this study, the characteristics of growth promotion by strain RP11 were studied by analysing 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) production, as well as phosphorus-solubilizing and potassium-solubilizing ability. In the pot culture conditions, we tested whether strain RP11 improved soybean seedlings tolerance against TBBPA by measuring the root length and physiological parameters of the seedlings treated with strain RP11 and different concentration of TBBPA (0, 5, 50, 100, and 1000 mg/kg) together. The results showed that strain RP11 secreted IAA and ALA, and solubilized phosphate and potassium. In pot trials, strain RP11 increased the root length, chlorophyll content, carotenoid content, soluble sugar and protein content of soybean seedlings treated with TBBPA, in comparison with the seedlings treated only with TBBPA. Furthermore, strain RP11 induced the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD), decreased the malondialdehyde (MDA) content in soybean seedlings under TBBPA stress. It was concluded that strain RP11 alleviated TBBPA-induced harmful effects in soybean seedlings by the secretion of IAA and ALA, the accumulation of carotenoid, soluble sugar and soluble protein, and the induction of SOD, CAT and POD as well as nutrient adjustment of phosphorus and potassium levels.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 February 2020
The original article has published with the incorrect article title.
References
Abdallah MAE (2016) Environmental occurrence, analysis and human exposure to the flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBP-A)—a review. Environ Int 94:235–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.05.026
Ahemad M, Kibret M (2014) Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: current perspective. J King Saud Univ Sci 26:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2013.05.001
Akram NA, Ashraf M (2013) Regulation in plant stress tolerance by a potential plant growth regulator, 5-aminolevulinic acid. J Plant Growth Regul 32:663–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-013-9325-9
Bailly C, Benamar A, Corbineau F, Come D (1996) Changes in malondialdehyde content and in superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione reductase activities in sunflower seeds as related to deterioration during accelerated aging. Physiol Plant 97:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1996.tb00485.x
Batool K, Tuz Zahra F, Rehman Y (2017) Arsenic-redox transformation and plant growth promotion by purple nonsulfur bacteria Rhodopseudomonas palustris CS2 and Rhodopseudomonas faecalis SS5. BioMed Res Int 2017:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6250327
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Cha-um S, Charoenpanich A, Roytrakul S, Kirdmanee C (2009) Sugar accumulation, photosynthesis and growth of two indica rice varieties in response to salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 31:477–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-008-0256-1
Couée I, Sulmon C, Gouesbet G, El Amrani A (2006) Involvement of soluble sugars in reactive oxygen species balance and responses to oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot 57:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj027
Cui M, Lin Y, Zu Y, Efferth T, Li D, Tang Z (2015) Ethylene increases accumulation of compatible solutes and decreases oxidative stress to improve plant tolerance to water stress in Arabidopsis. J Plant Biol 58:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-014-0302-z
Dogan M, Yumrutas O, Saygideger SD, Korkunc M (2010) Effects of bisphenol A and tetrabromobisphenol A on chickpea roots in germination stage. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 9:186–192
Dunnick JK, Sanders JM, Kissling GE, Johnson CL, Boyle MH, Elmore SA (2015) Environmental chemical exposure may contribute to uterine cancer development: studies with tetrabromobisphenol A. Toxicol Pathol 43:464–473. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623314557335
Ge HL, Zhang FL (2017) Effects of tetrabromobisphenol A stress on growth and physiological characteristics of soybean seedlings. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1974-5
Gill PK, Sharma AD, Singh P, Bhullar SS (2003) Changes in germination, growth and soluble sugar contents of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench seeds under various abiotic stresses. Plant Growth Regul 40:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024252222376
Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical examination of the specificity of the Salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 619:793–796
Hotta Y, Tanaka T, Takaoka H, Takeuchi Y, Konnai M (1997) Promotive effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid on the yield of several crops. Plant Growth Regul 22:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005883930727
Jan S, Parween T, Siddiqi TO, Mahmooduzzafar X (2012) Effect of gamma radiation on morphological, biochemical and physiological aspects of plants and plant products. Environ Rev 20:17–39. https://doi.org/10.1139/a11-021
Kantha T, Kantachote D, Klongdee N (2015) Potential of biofertilizers from selected Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains to assist rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp. indica) growth under salt stress and to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Ann Microbiol 65:2109–2118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1049-6
Li Y, Zhou Q, Li F, Liu X, Luo Y (2008) Effects of tetrabromobisphenol A as an emerging pollutant on wheat (Triticum aestivum) at biochemical levels. Chemosphere 74:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.08.024
Liu P, Li MG, Li CW (2007) Experiment technology of plant physiology. Science Press, Beijing
Liu H, Ma Z, Zhang T, Yu N, Su G, Giesy JP, Yu H (2018) Pharmacokinetics and effects of tetrabromobisphenol a (TBBPA) to early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 190:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.137
Lu Z, Letcher RJ, Chu S, Ciborowski JJH, Haffner GD, Drouillard KG, Macleod SL, Marvin CH (2015) Spatial distributions of polychlorinated biphenyls, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, tetrabromobisphenol A and bisphenol A in Lake Erie sediment. J Great Lakes Res 41:808–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2015.04.007
Mauzerall D, Granick S (1956) The occurrence and determination of δ-aminolevulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem 219:435–446
Mohammad Y, Hossin B, Abas GM (2011) Investigation the effect of biofertilizers, phosphate solubilization microorganisms (PSM) and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on improvement of quality and quantity in corn (Zea mayz L.). Adv Environ Biol 5:2182–2185
Mohite B (2013) Isolation and characterization of indole acetic acid (IAA) producing bacteria from rhizospheric soil and its effect on plant growth. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 13:638–649. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162013005000051
Moustakas M, Sperdouli I, Kouna T, Antonopoulou CI, Therios I (2011) Exogenous proline induces soluble sugar accumulation and alleviates drought stress effects on photosystem II functioning of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant Growth Regul. 65:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-011-9604-z
Naeem MS, Rasheed M, Liu D, Jin ZL, Ming DF, Yoneyama K, Zhou WJ (2011) 5-Aminolevulinic acid ameliorates salinity-induced metabolic, water-related and biochemical changes in Brassica napus L. Acta Physiol Plant 33:517–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0575-x
Nunkaew T, Kantachote D, Kanzaki H, Nitoda T, Ritchie RJ (2014) Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)-containing supernatants from selected Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains on rice growth under NaCl stress, with mediating effects on chlorophyll, photosynthetic electron transport and antioxidative enzymes. Electron J Biotechnol 17:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt2013.12.004
Papaioannou EH, Stoforos NG, Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M (2011) Substrate contribution on free radical scavenging capacity of carotenoid extracts produced from Blakeslea trispora cultures. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:851–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0527-z
Reistad T, Mariussen E, Fonnum F (2005) The effect of a brominated flame retardant, tetrabromobisphenol-A, on free radical formation in human neutrophil granulocytes: the involvement of the MAP kinase pathway and protein kinase C. Toxicol Sci 83:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfh298
Ronisz D, Finne EF, Karlsson H, Förlin L (2004) Effects of the brominated flame retardants hexabromocyclododecane(HBCDD), and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), on hepatic enzymes and other biomarkers in juvenile rainbow trout and feral eelpout. Aquat Toxicol 69:229–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.05.007
Sakpirom J, Kantachote D, Nunkaew T, Khan E (2017) Characterizations of purple non-sulfur bacteria isolated from paddy fields, and identification of strains with potential for plant growth-promotion, greenhouse gas mitigation and heavy metal bioremediation. Res Microbiol 168:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2016.12.001
Sasaki K, Watanabe M, Suda Y, Ishizuka A, Noparatnaraporn N (2005) Applications of photosynthetic bacteria for medical fields. J Biosci Bioeng 100:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.100.481
Shi H, Wang X, Luo Y, Su Y (2005) Electron paramagnetic resonance evidence of hydroxyl radical generation and oxidative damage induced by tetrabromobisphenol A in Carassius auratus. Aquat Toxicol 74:365–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.06.009
Taurian T, Anzuay MS, Ludueña LM, Angelini JG, Muñoz V, Valetti L, Fabra A (2013) Effects of single and co-inoculation with native phosphate solubilising strain Pantoea sp J49 and the symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacterium Bradyrhizobium sp. SEMIA 6144 on peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) growth. Symbiosis 59:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s.13199-012-0193-z
Tereshina VM, Memorskaya AS, Feofilova EP (2003) Zygote formation in Blakeslea trispora: morphological peculiarities and relationship with caroteniod synthesis. Microbiology 72:448–454. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025096723803
Wei DD, Cheng D, Liu WB, Liu T, Yang XH, Zheng YH (2015) Adequate potassium application enhances salt tolerance of moderate-halophyte Sophora alopecuroides. Plant Soil Environ 61:364–370. https://doi.org/10.17221/232/2015-PSE
Xu J, Feng Y, Wang Y, Luo X, Tang J, Lin X (2016) The foliar spray of Rhodopseuomonas palustris grown under Stevia residue extract promotes plant growth via changing soil microbial community. J Soil Sediment 16:916–923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1269-1
Young AJ, Lowe GM (2001) Antioxidants and prooxidants properties of carotenoids. Arch Biochem Biophys 385:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.2000.2149
Zerrouk IZ, Benchabane M, Khelif L, Yokawa K, Ludwig-Müller J, Baluska F (2016) A Pseudomonas strain isolated from date-palm rhizospheres improves root growth and promotes root formation in maize exposed to salt and aluminum stress. J Plant Physiol 191:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2015.12.009
Zhang C, Kong F (2014) Isolation and identification of potassium-solubilizing bacteria from tobacco rhizospheric soil and their effect on tobacco plants. Appl Soil Ecol 82:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.05.002
Zhao K, Penttinen P, Zhang X, Ao X, Liu M, Yu X, Chen Q (2014) Maize rhizosphere in Sichuan, China, hosts plant growth promoting Burkholderia cepacia with phosphate solubilizing and antifungal abilities. Microbiol Res 169:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.07.003
Zou Q (2000) Instruction of plant physiology experiment. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Provincial Science and Technology Department of China (182102110290).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, H., Liu, Z. Alleviation of tetrabromobisphenol A toxicity in soybean seedlings by Rhodopseudomonas palustris RP1n1. Arch Microbiol 202, 895–903 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01797-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01797-8