Abstract
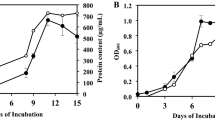
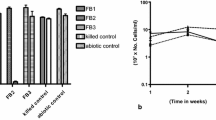
Acinetobacter pittii strain ABC was isolated from oily sludge sediments and characterized with regard to utilization/degradation of hydrocarbons and competitive persistence in hydrocarbon-amended media. The isolate grew in both aliphatic- and aromatic hydrocarbon-amended Bushnell–Haas medium (BHM). When incubated in 1% (v/v) Assam crude oil-amended BHM for 5 and 10 days, this strain was able to degrade 88% and 99.8% of the n-hexane extractable crude oil components, respectively. The isolate showed appreciable emulsification index (E24 65.26 ± 1.2%), hydrophobicity (60.88 ± 3.5%) and produced lipopeptide biosurfactant (0.57 g L−1). The isolate was able to tolerate heavy metal salts at concentrations reported in crude oil-polluted sediments from Assam. A 16S rDNA DGGE-based screening showed the persistence of A. pittii strain ABC in hydrocarbon-amended microcosms co-inoculated with other hydrocarbonoclastic bacterial strains (Pseudomonas aeruginosa AKS1, Bacillus sp. AKS2, Arthrobacter sp. BC1, and Novosphingobium panipatense P5:ABC), each isolated from the same oily sludge sediment. These findings indicate A. pittii strain ABC as a potential agent for the bioremediation of crude oil-polluted environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao M, Pi Y, Wang L, Sun P, Li Y, Cao L (2014) Lipopeptide biosurfactant production bacteria Acinetobacter sp. D3-2 and its biodegradation of crude oil. Environ Sci Process Impacts 16(4):897–903
Berg G, Seech AG, Lee H, Trevors JT (1990) Identification and characterization of a soil bacterium with extracellular emulsifying activity. J Environ Sci Health A 25(7):753–764
Chettri B, Mukherjee A, Langpoklakpam JS, Chattopadhyay D, Singh AK (2016) Kinetics of nutrient enhanced crude oil degradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa AKS1 and Bacillus sp. AKS2 isolated from Guwahati refinery, India. Environ Pollut 216:548–558
Dal S, Steiner I, Gerischer U (2002) Multiple operons connected with catabolism of aromatic compounds in Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 are under carbon catabolite repression. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4:389–404
Das K, Mukherjee AK (2007) Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a petroleum-oil contaminated soil from North-East India. Bioresour Technol 98(7):1339–1345
Das D, Baruah R, Sarma RA, Singh AK, Deka Boruah HP, Kalita J, Bora TC (2015) Complete genome sequence analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa N002 reveals its genetic adaptation for crude oil degradation. Genomics 105(3):182–190
Dikshit KR, Dikshit JK (2014) Industries and associated economic activities. In: North-East India: land, people and economy. Advances in Asian Human-Environmental Research, Springer Dordrecht
Head IM, Jones DM, Roling WF (2006) Marine microorganisms make a meal of oil. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(3):173–182
Hibbing ME, Fuqua C, Parsek MR, Peterson SB (2010) Bacterial competition: surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(1):15–25
Islam MA, Al-mamun A, Hossain F, Quraish SB, Naher K, Khan R, Das S, Tamim U, Hossain SM, Nahid F (2017) Contamination and ecological risk assessment of trace elements in sediments of the rivers of Sundarban mangrove forest, Bangladesh. Mar Pollut Bull 124:356–366
Jadeja NB, Moharir P, Kapley A (2019) Genome sequencing and analysis of strains Bacillus sp. AKBS9 and Acinetobacter sp. AKBS16 for biosurfactant production and bioremediation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 187(2):518–530
Kingston PF (2002) Long-term environmental impact of oil spills. Spill Sci Technol Bull 7(1–2):53–61
Kriipsalu M, Marques M, Maastik A (2008) Characterization of oily sludge from a wastewater treatment plant flocculation-flotation unit in a petroleum refinery and its treatment implications. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 10(1):79–86
Lal B, Khanna S (1996) Degradation of crude oil by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Alcaligenes odorans. J Appl Bacteriol 81(4):355–362
Long H, Wang Y, Chang S, Liu G, Chen T, Huo G, Zhang W, Wu X, Tai X, Sun L, Zhang B (2017) Diversity of crude oil-degrading bacteria and alkane hydroxylase (alkB) genes from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environ Monit Assess 189(3):116
Mazzoli R, Pessione E, Giuffrida MG, Fattori P, Barello C, Giunta C, Lindley ND (2007) Degradation of aromatic compounds by Acinetobacter radioresistens S13: growth characteristics on single substrates and mixtures. Arch Microbiol 188(1):55–68
Mindlin S, Petrenko A, Kurakov A, Beletsky A, Mardanov A, Petrova M (2016) Resistance of permafrost and modern Acinetobacter lwoffii strains to heavy metals and arsenic revealed by genome analysis. Biomed Res Int 2016:3970831
Mishra S, Jyot J, Kuhad RC, Lal B (2001) In situ bioremediation potential of an oily sludge-degrading bacterial consortium. Curr Microbiol 43(5):328–335
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
Office of the Federal Registration (OFR) (1982) Appendix A: priority pollutants. Fed Reg 47:52309
Peterson CH (2001) The “Exxon Valdez” oil spill in Alaska: acute, indirect and chronic effects on the ecosystem. Adv Mar Biol 39:1–103
Ratajczak A, Geissdorfer W, Hillen W (1998) Expression of alkane hydroxylase from Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 is induced by a broad range of n-alkanes and requires the transcriptional activator AlkR. J Bacteriol 180(22):5822–5827
Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E (1980) Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 9:29–33
Roy AS, Baruah R, Borah M, Singh AK, Boruah HPD, Saikia N, Deka M, Dutta N, Bora TC (2014) Bioremediation potential of native hydrocarbon degrading bacterial strains in crude oil contaminated soil under microcosm study. Int Biodeter Biodegr 94:79–89
Sakai Y, Maeng JH, Tani Y, Kato N (1994) Use of long-chain n-alkanes (C13–C44) by an isolate, Acinetobacter sp. M-1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58(11):2128–2130
Sarkar J, Kazy SK, Gupta A, Dutta A, Mohapatra B, Roy A, Bera P, Mitra A, Sar P (2016) Biostimulation of indigenous microbial community for bioremediation of petroleum refinery sludge. Front Microbiol 7:1407
Silliman BR, van de Koppel J, McCoy MW, Diller J, Kasozi GN, Earl K, Adams PN, Zimmerman AR (2012) Degradation and resilience in Louisiana salt marshes after the BP–Deepwater Horizon oil spill. PNAS 109(28):11234–11239
Singh AK, Chettri B, Ghosh A, Chikara SK, Tripathi T (2017) Draft genome sequence of the hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Acinetobacter pittii strain ABC isolated from Noonmati Refinery, Assam. India. Genome Announc 5(44):e01264-17
Teal JM (1984) Oil spill studies: a review of ecological effects. Environ Manag 8(1):27–44
Thangaraj K, Kapley A, Purohit HJ (2008) Characterization of diverse Acinetobacter isolates for utilization of multiple aromatic compounds. Bioresour Technol 99(7):2488–2494
Throne-Holst M, Wentzel A, Ellingsen TE, Kotlar HK, Zotchev SB (2007) Identification of novel genes involved in long-chain n-alkane degradation by Acinetobacter sp. strain DSM 17874. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(10):3327–3332
Tissot BP, Welte DH (1984) Petroleum formation and occurrence. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, New York
Wolfe DA, Hameedi MJ, Galt JA, Watabayashi G, Short J, O’Claire C, Rice S, Michel J, Payne JR, Braddock J, Hanna S, Sale D (1994) The fate of the oil spilled from the Exxon Valdez. Environ Sci Technol 28(13):560–568
Yuan H, Yao J, Masakorala K, Wang F, Cai M, Yu C (2014) Isolation and characterization of a newly isolated pyrene-degrading Acinetobacter strain USTB-X. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(4):2724–2732
Zakaria ZA, Zakaria Z, Surif S, Ahmad WA (2007) Hexavalent chromium reduction by Acinetobacter haemolyticus isolated from heavy-metal contaminated wastewater. J Hazard Mater 146(1–2):30–38
Zibilski LM (1994) Carbon mineralization. In: Weaver RW, Angle S, Bottomley P (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2, microbiological and biochemical properties. Soil Science Society of America, Madison
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from DBT, Govt. of India (BT/306/NE/TBP/2012). Fellowship grant from Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India to BC (IF10272) is gratefully acknowledged. AM was supported by the CSIR/UGC-NET Fellowship from the University Grants Commission, Govt. of India (201112-NETJRF-10217-100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chettri, B., Singha, N.A., Mukherjee, A. et al. Hydrocarbon degradation potential and competitive persistence of hydrocarbonoclastic bacterium Acinetobacter pittii strain ABC. Arch Microbiol 201, 1129–1140 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01687-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01687-z