Abstract
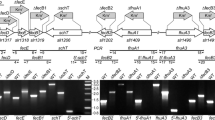
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus SW1, under nitrogen limitation, assimilates the nitrogen moiety of taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonate) inducibly and excretes sulfoacetaldehyde, a product of taurine dehydrogenase (TauXY). BLAST searches of newly available genome sequences using the TauXY sequences revealed a 5-gene cluster, tauRXYPI, in Acinetobacter radioresistens SH164. We hypothesized that tauXYPI (HMPREF0018_00717–HMPREF0018_00720) encodes proteins that are orthologs of the undefined pathway from strain SW1, and that tauR (HMPREF0018_00716) encodes the relevant transcriptional regulator. Strain SH164 excreted sulfoacetaldehyde from taurine during growth. TauXY activity was expressed inducibly. Reverse transcription PCR showed that the tauRXYPI genes were transcribed inducibly. This allowed the conclusions that (i) TauP (currently annotated as permease GabP [TC 2.A.3]) is a taurine permease, and (ii) TauI (currently annotated as DUF6 drug/metabolite exporter [TC 2.A.7]) is a sulfoacetaldehyde exporter. The presumably equifunctional cluster tauRXYPI was then found in strain SW1. TauP is the third recognized taurine uptake system, and TauI is the third postulated class of sulfonate exporters, in bacteria.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription PCR
- TauABC:
-
ABC transporter for taurine
- tauI :
-
Encodes sulfoacetaldehyde exporter
- tauP :
-
Encodes taurine permease
- tauR :
-
Encodes transcriptional regulator of taurine genes
- tauXY :
-
Encode taurine dehydrogenase
References
Allen JA, Garrett MR (1971) Taurine in marine invertebrates. Adv Mar Biol 9:205–253
Belitsky BR, Sonenshein AL (2002) GabR, a member of a novel protein family, regulates the utilization of gamma-aminobutyrate in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 45:569–583
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Bergmeyer HU, Beutler H-O (1984) Ammonia. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 454–461
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brüggemann C, Denger K, Cook AM, Ruff J (2004) Enzymes and genes of taurine and isethionate dissimilation in Paracoccus denitrificans. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 150:805–816
Cook AM (1987) Biodegradation of s-triazine xenobiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 46:93–116
Cook AM, Hütter R (1981) s-Triazines as nitrogen sources for bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 29:1135–1143
Cunningham C, Tipton KF, Dixon HBF (1998) Conversion of taurine into N-chlorotaurine (taurine chloramine) and sulphoacetaldehyde in response to oxidative stress. Biochem J 330:939–945
Denger K, Laue H, Cook AM (1997) Anaerobic taurine oxidation: a novel reaction by a nitrate-reducing Alcaligenes sp. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 143:1919–1924
Denger K, Ruff J, Rein U, Cook AM (2001) Sulfoacetaldehyde sulfo-lyase [EC 4.4.1.12] from Desulfonispora thiosulfatigenes: purification, properties and primary sequence. Biochem J 357:581–586
Denger K, Ruff J, Schleheck D, Cook AM (2004a) Rhodococcus opacus expresses the xsc gene to utilize taurine as a carbon source or as a nitrogen source but not as a sulfur source. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 150:1859–1867
Denger K, Weinitschke S, Hollemeyer K, Cook AM (2004b) Sulfoacetate generated by Rhodopseudomonas palustris from taurine. Arch Microbiol 182:254–258
Denger K, Smits THM, Cook AM (2006a) Genome-enabled analysis of the utilization of taurine as sole source of carbon or nitrogen by Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 152:3167–3174
Denger K, Smits THM, Cook AM (2006b) L-Cysteate sulfo-lyase, a widespread, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-coupled desulfonative enzyme purified from Silicibacter pomeroyi DSS-3T. Biochem J 394:657–664
Denger K, Weinitschke S, Smits THM, Schleheck D, Cook AM (2008) Bacterial sulfite dehydrogenases in organotrophic metabolism: separation and identification in Cupriavidus necator H16 and in Delftia acidovorans SPH-1. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 154:256–263
Denger K, Mayer J, Buhmann M, Weinitschke S, Smits THM, Cook AM (2009) Bifurcated degradative pathway of 3-sulfolactate in Roseovarius nubinhibens ISM via sulfoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase and (S)-cysteate sulfo-lyase. J Bacteriol 191:5648–5656
Desomer J, Crespi M, Van Montagu M (1991) Illegitimate integration of non-replicative vectors in the genome of Rhodococcus fascians upon electrotransformation as an insertional mutagenesis system. Mol Microbiol 5:2115–2124
Eichhorn E, van der Ploeg JR, Kertesz MA, Leisinger T (1997) Characterization of α-ketoglutarate-dependent taurine dioxygenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 272:23031–23036
Eichhorn E, van der Ploeg JR, Leisinger T (2000) Deletion analysis of the Escherichia coli taurine and alkanesulfonate transport systems. J Bacteriol 182:2687–2795
González JM et al (2003) Silicibacter pomeroyi sp. nov. and Roseovarius nubinhibens sp. nov., dimethylsulfoniopropionate-demethylating bacteria from marine environments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1261–1269
Graham DE, Xu H, White RH (2002) Identification of coenzyme M biosynthetic phosphosulfolactate synthase: a new family of sulfonate biosynthesizing enzymes. J Biol Chem 277:13421–13429
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Ito K, Miyazawa K, Matsumoto F (1977) Amino acid composition of the ethanolic extractives from 31 species of marine red algae. Hiroshima Daigaku Suichikusangakubu Kiyo 16:77–90
Jack DL, Yang NM, Saier MH Jr (2001) The drug/metabolite transporter superfamily. Eur J Biochem 268:3620–3639
Jones NR (1953) Taurine in fresh and iced skeletal muscle of codling (Gadus callarias). Biochem J 56:xxii
Kappler U, Bennett B, Rethmeier J, Schwarz G, Deutzmann R, McEwan AG, Dahl C (2000) Sulfite:cytochrome c oxidoreductase from Thiobacillus novellus. Purification, characterization, and molecular biology of a heterodimeric member of the sulfite oxidase family. J Biol Chem 275:13202–13212
Kondo H, Anada H, Ohsawa K, Ishimoto M (1971) Formation of sulfoacetaldehyde from taurine in bacterial extracts. J Biochem 69:621–623
Krejčík Z, Denger K, Weinitschke S, Hollemeyer K, Pačes V, Cook AM, Smits THM (2008) Sulfoacetate released during the assimilation of taurine-nitrogen by Neptuniibacter caesariensis: purification of sulfoacetaldehyde dehydrogenase. Arch Microbiol 190:159–168
Krejčík Z, Hollemeyer K, Smits THM, Cook AM (2010) Isethionate formation from taurine in Chromohalobacter salexigens: purification of sulfoacetaldehyde reductase. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 156:1547–1555
Mampel J, Maier E, Tralau T, Ruff J, Benz R, Cook AM (2004) A novel outer-membrane anion channel (porin) as part of the putatively two-component transport system for p-toluenesulfonate in Comamonas testosteroni T-2. Biochem J 383:91–99
Mayer J, Cook AM (2009) Homotaurine metabolized to 3-sulfopropanoate in Cupriavidus necator H16: enzymes and genes in a patchwork pathway. J Bacteriol 191:6052–6058
Niegemann E, Schulz A, Bartsch K (1993) Molecular organization of the Escherichia coli gab cluster: nucleotide sequence of the structural genes gabD and gabP and expression of the GABA permease gene. Arch Microbiol 160:454–460
Rösch V, Denger K, Schleheck D, Smits THM, Cook AM (2008) Different bacterial strategies to degrade taurocholate. Arch Microbiol 190:11–18
Ruff J, Denger K, Cook AM (2003) Sulphoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase yields acetyl phosphate: purification from Alcaligenes defragrans and gene clusters in taurine degradation. Biochem J 369:275–285
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour
Sörbo B (1987) Sulfate: turbidimetric and nephelometric methods. Methods Enzymol 143:3–6
Styp von Rekowski K, Denger K, Cook AM (2005) Isethionate as a product from taurine during nitrogen-limited growth of Klebsiella oxytoca Tau-N1. Arch Microbiol 183:325–330
Weinitschke S, Styp von Rekowski K, Denger K, Cook AM (2005) Sulfoacetaldehyde is excreted quantitatively by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus SW1 during growth with taurine as sole source of nitrogen. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 151:1285–1290
Weinitschke S, Denger K, Cook AM, Smits THM (2007) The DUF81 protein TauE in Cupriavidus necator H16, a sulfite exporter in the metabolism of C2-sulfonates. Microbiology (Reading, UK) 153:3055–3060
Weinitschke S, Hollemeyer K, Kusian B, Bowien B, Smits THM, Cook AM (2010) Sulfoacetate is degraded via a novel pathway involving sulfoacetyl-CoA and sulfoacetaldehyde in Cupriavidus necator H16. J Biol Chem 285:35249–35254
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Wiethaus J, Schubert B, Pfander Y, Narberhaus F, Masepohl B (2008) The GntR-like regulator TauR activates expression of taurine utilization genes in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol 190:487–493
Wilson JJ, Kappler U (2009) Sulfite oxidation in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:1516–1525
Yin M, Palmer HR, Fyfe-Johnson AL, Bedford JJ, Smith RA, Yancey PH (2000) Hypotaurine, N-methyltaurine, taurine, and glycine betaine as dominant osmolytes of vestimentiferan tubeworms from hydrothermal vents and cold seeps. Physiol Biochem Zool 73:629–637
Acknowledgments
The project was funded by the University of Konstanz and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Co 206/6-1). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. We are grateful to Bodo Philipp for permission to use his ‘L2’ laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Ursula Priefer.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krejčík, Z., Schleheck, D., Hollemeyer, K. et al. A five-gene cluster involved in utilization of taurine-nitrogen and excretion of sulfoacetaldehyde by Acinetobacter radioresistens SH164. Arch Microbiol 194, 857–863 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-012-0806-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-012-0806-1