Abstract
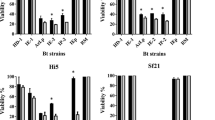
BLB1 is a new Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki strain, isolated from a Tunisian soil sample. Assay of toxicity of BLB1 crystal proteins resulted in an LC50 of 70.32 ng of toxin per mg of flour against third instar Ephestia kuehniella with confidence limits of (31.6–109.04 ng). This LC50 is less than that of the commercial strains HD1 used as a reference. The characterization of this strain by scanning transmission electron microscopy, analysis of its cry genes content by PCR-sequencing, and analysis of its δ-endotoxin patterns demonstrate that it belongs to the same subgroup than HD1, but ruled out the involvement of cry gene content or protoxin activation in the hypertoxicity of this strain. Taking into account the δ-endotoxin/spore ratio for each strain, and by allowing the estimation of the production level per spore, it might be concluded that BLB1 production is the highest, when compared with that of HD1. On the basis of its toxicity, BLB1 could be considered as a strain of great interest and would allow the production of quantities of bioinsecticides at low cost.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechtel DB, Bulla LA Jr (1976) Electron microscope study of sporulation and parasporal crystal formation in Bacillus thuringiensis. J Bacteriol 127:1472–1481
Bobrowski VL, Pscali G, Bodanese-zanetti MH, Fiuza LM (2002) Characterization of two Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from south Brasil and their toxicity against Anticarsia gemmatalis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biol Control 25:129–135
Bravo A, Sarabia S, Lopez L, Ontiveros H, Abarca C, Ortiz A, Ortiz M, Lina L, Villalobos FJ, Pena G, Nunez-Valdez ME, Soberon M, quintero R (1998) Characterization of cry genes in a Mexican Bacillus thuringiensis strain collection. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4965–4972
Carozzi NB, Kramer VC, Warren GW, Evola S, Koziel M (1991) Prediction of insecticidal activity Bacillus thuringiensis strain by polymerase chain reaction product profiles. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:353–356
Christeller JT, Laing WA, Markwick NP, Burgess EPJ (1992) Midgut protease activities in 12 phytophagous lepidopteran larvae: dietary and protease inhibitor interactions. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 22:735–746
Ferré J, Escriche B, Bel Y, Van Rie J (1995) Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal proteins. FEMS Microbiol Lett 132:1–7
Geiser M, Schweitzer S, Grimm C (1986) The hypervariable region in the genes coding for entomopathogenic crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis: nucleotide sequence of the kur Hdl gene of subsp Kurstaki HD-1. Gene 48:109–118
Ghribi D, Zouari N, Trigui W, Jaoua S (2007) Use of sea water as salts source in starch- and soya bean-based media, for the production of Bacillus thuringiensis bioinsecticides. Process Biochem 42:374–378
Herrel LJ, Anderson GL, Wilson KH (1995) Genetic variability of Bacillus thuringiensis and related species. J Clin. Microbiol 33:1847–1850
Höfte H, Whiteley HR (1989) Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Rev 53:242–255
Ibarra JE, Del Rincón MC, Ordúz S, Noriega D, Benintende G, Monnerat R, Regis L, de Oliveira CMF, Lanz H, Rodriguez MH, Sánchez J, Peña G, Bravo A (2003) Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis strains from Latin America with insecticidal activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5269–5274
Jaoua S, Zouari N, Tounsi S, Ellouz R (1996) Study of the δ-endotoxins produced by three recently isolated strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 145:349–354
Knowles BH (1994) Mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal delta-endotoxins. In: Evans PD (ed) Advances in insect physiology, vol 24. Academic Press, London, pp 275–308
Lee IH, Je YH, Chang JH (2001) Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki strain toxic to Spodoptera exigua and Culex pipiens. Curr Microbiol 43:284–287
Liu PYF, Wu WL (1997) Use of different PCR-based DNA fingerprinting techniques and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to investigate the epidemiology of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus–Acinetobacter baumannii complex. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 28:19–28
Marchetti S, Chiaba C, Chiesa F, Bandiera A, Pitotti A (1998) Isolation and partial characterization of two trypsins from the larval midgut of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisduval). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 28:449–458
Martínez C, Jorge E, Ibarra C, Primitivo C (2005) Association analysis between serotype, cry gene content, and toxicity to Helicoverpa armigera larvae among Bacillus thuringiensis isolates native to Spain. J Invertebr Pathol 90:91–97
Masson L, Mazza A, Gringorten L, Baines D, Aneliunas V, Brousseau R (1994) Specificity domain localization of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxins is highly dependent on the bioassay system. Mol Microbiol 14:851–860
Mohan M, Gujar GT (2002) Geographical variation in larval susceptibility of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) to Bacillus thuringiensis spore-crystal mixtures and purified crystal proteins, and associated resistance development in India. Bull Ent Res 92:489–498
Monnerat RG, Batista AC, Telles de Medeiros P, Martins ES, Melatti VM, Praça LB, Dumas VF, Morinaga C, Demo C, Gomes ACM, Falcão R, Siqueira CB, Silva-Werneck JO, Berry C (2007) Screening of Brazilian Bacillus thuringiensis isolates active against Spodoptera frugiperda, Plutella xylostella and Anticarsia gemmatalis. Biol Control 41:291–295
Pang ASD, Gringorten JL (1998) Degradation of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin in host insect gut juice. FEMS Microbiol Lett 167:281–285
Rouis S, Chakroun M, Saadaoui I, Jaoua S (2007) Proteolysis, histopathological effects, and immunohistopathological localization of delta-endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki in the midgut of lepidopteran olive tree pathogenic insect Prays oleae. Mol Biotechnol 35:141–148
Rouis S, Chakroun M, Jaou S (2008) Comparative study of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Aa and Cry1Ac δ-endotoxin activation, inactivation and in situ histopathological effect in Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Mol Biotechnol 38:233–239
Sambrook J, Frisch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schwartz JL, Juteau M, Grochulski P, Cygler M, Préfontaine G, Brousseau R, Masson L (1997) Restriction of intramolecular movements within the Cry1Aa toxin molecule of Bacillus thuringiensis through disulphide bond engineering. FEBS Lett 410:397–402
Shao Z, Cui Y, Liu X, Yi H, Ji J, Yu Z (1998) Processing of δ-endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD-1 in Heliothis armigera midgut juice and the effects of protease inhibitors. J Invertebr Pathol 72:73–81
Shin BS, Park SH, Choi SK, Koo BT, Lee ST, Kim JI (1995) Distribution of cryV-type insecticidal protein genes in Bacillus thuringiensis and cloning of cryV-type genes from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. entomocidus. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2402–2407
Theunis W, Aguda RM, Cruz WT, Decock C, Peferoen M, Lambert B, Bottrell DG, Gould FL, Litsinger JA, Cohen MB (1998) Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from the Philippines: habitat distribution, delta-endotoxin diversity, and toxicity to rice stem borers (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Bull Entomol Res 88:335–342
Tounsi S, Dammak M, Rebaî A, Jaoua S (2005) Response of larval Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) to individual Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki toxins and toxin mixtures. Biol Control 35:27–31
Travers RS, Martin PAW, Reichelderfer CF (1987) Selective process for efficient isolation of soil Bacillus species. App Environ Microbiol 53:1263–1266
Venables WN, Smith DM (2004) The R. development core team. An introduction to R. version 1.9.1. http://www..r-project.org/
Yang XW, Walker MJ, Hornitzky M, Chin J (2006) Development of a group-specific PCR combined with ARDRA for the identification of Bacillus species of environmental significance. J Microbiol Methods 64:107–119
Zouari N, Jaoua S (1999) The effect of complex carbon and nitrogen, salt, Tween-80 and acetate on delta-endotoxin production by a Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:497–502
Zouari N, Dhouib A, Ellouz R, Jaoua S (1998) Nutritional requirement of a strain of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Kurstaki and use of gruel hydrolysate, for the formulation of a new medium for delta-endotoxin production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 69:41–52
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the “Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology” and the AUF “Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie”. We thank Dr. Patrick Schultz, Institute of Genetics and Molecular and Cellular Biology, for his help in electron microscopy experiments and Pr. Ahmed Rebai, Centre of Biotechnology of Sfax, for his help in statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saadaoui, I., Rouis, S. & Jaoua, S. A new Tunisian strain of Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki having high insecticidal activity and δ-endotoxin yield. Arch Microbiol 191, 341–348 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0458-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0458-y