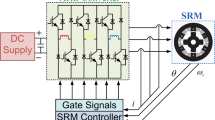
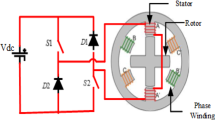
Abstract
To improve the state-of-the-art control of a switched reluctance motor (SRM) drive, this research paper proposes and applies a novel approach for tweaking the parameters of the proportional-integral (PI) current controller using a multivariable sliding-mode extremum-seeking (MSES). The proposed MSES-PI current control approach uses a sliding-mode extremum-seeking optimizer to fine-tune the PI control gains to minimize a cost function defined by the feedback error term. As a result, the PI current controller exhibits robustness against disturbances and insensitivity to changes in SRM parameters, while remaining sensitive to tracking reference current inputs. In addition, this study proposes an innovative speed control strategy for SRM drives using an adaptive extremum-seeking PI speed controller (AES-PI). The proposed speed control utilizes a PI controller and a separate version of the extremum-seeking controller to enhance the step responsiveness of SRM drives. In particular, AES minimizes a cost function analogous to the one used to quantify the performance of the PI speed controller. Both simulation and experimental verification show that MSES-PI and AES-PI outperform traditional PI controllers. Through the utilization of ES to fine-tune the PI controller’s settings, dynamic performance is enhanced, and torque ripple and speed oscillation are significantly suppressed.







































Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
de Paula MV, dos Santos Barros TA (2020) New flux linkage estimation with drift cancellation technique for switched reluctance machines. Electronics 9(3):405
Wei Y, Qishuang M, Poming Z, Yangyang G (2016) Torque ripple reduction in switched reluctance motor using a novel torque sharing function. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference on aircraft utility systems, Beijing, pp 177–182
Ye J, Bilgin B, Emadi A (2015) An offline torque sharing function for torque ripple reduction in switched reluctance motor drives. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 30(2):726–735
Li H, Bilgin B, Emadi A (2019) An improved torque sharing function for torque ripple reduction in switched reluctance machines. IEEE Trans Power Electron 34(2):1635–1644
Fang G, Scalcon FP, Xiao D, Vieira RP, Gründling HA, Emadi A (2021) Advanced control of switched reluctance motors (SRMs): a review on current regulation, torque control and vibration suppression. IEEE Open J Ind Electron Soc 2(4):280–301
Reddy PK, Ronanki D, Parthiban P (2019) Direct torque and flux control of switched reluctance motor with enhanced torque per ampere ratio and torque ripple reduction. Electron Lett 55(8):477–478
Xu A, Zhang W, Ren P (2018) Comparison of torque ripple reduction for switched reluctance motor based on DTC and DITC. In: Proceedings of 13th IEEE conference on industrial electronics and applications, pp 1727–1732
Xu A, Shang C, Chen J, Zhu J, Han L (2019) A new control method based on DTC and MPC to reduce torque ripple in SRM. IEEE Access 7:68584–68593
Ding W, Li J, Yuan J (2022) An improved model predictive torque control for switched reluctance motors with candidate voltage vectors optimization. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 70(5):4595–4607
Ahmad SS, Narayanan G (2018) Predictive control based constant current injection scheme for characterization of switched reluctance machine. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 54(4):3383–3392
Mehta S, Kabir MA, Husain I (2018) Speed current profiling algorithm for low torque ripple SRM using model predictive control. In: Proceedings IEEE energy conversion congress and exposition, Portland, pp 4558–4563
Divandari M, Brazamini R, Dadpour A, Jazaeri M (2009) A novel dynamic observer and torque ripple minimization via fuzzy logic for SRM drives. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, Seoul, pp 847–852
Divandari M, Koochaki A, Maghsoodloo A, Rastegar H, Noparast J (2007) High-performance SRM drive with hybrid observer and fuzzy logic torque ripple minimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, Vigo, pp 1230–1235
Kim D, Jeong H, Lee K (2013) Torque ripple minimization of switched reluctance motors based on fuzzy logic and sliding mode control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, Taipei, pp 1–6
De Paula MV, dos Santos Barros TA (2021) A sliding mode DITC cruise control for SRM with steepest descent minimum torque ripple point tracking. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 69(1):151–159
Sial MR, Sahoo NC (2023) Torque ripple minimization in SRM drive using second-order-generalized-integrator-based FLL equivalent PR current controller. Electr Eng 1–21
Sial MR, Sahoo NC (2023) SOGI-FLL-2DOF PID-A combined second-order-generalized-integrator based FLL and two-degree-of-freedom PID current control for switched reluctance motor drives. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Ind Electron
Feng L, Sun X, Yang Z, Diao K (2023) Optimal torque sharing function control for switched reluctance motors based on active disturbance rejection controller. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron
Feng L, Sun X, Tian X, Diao K (2022) Direct torque control with variable flux for an SRM based on hybrid optimization algorithm. IEEE Trans Power Electron 37(6):6688–6697
Valencia DF, Tarvirdilu-Asl R, Garcia C, Rodriguez J, Emadi A (2020) A review of predictive control techniques for switched reluctance machine drives. Part I: fundamentals and current control. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 36(2):1313–1322
Valencia DF, Tarvirdilu-Asl R, Garcia C, Rodriguez J, Emadi A (2020) A review of predictive control techniques for switched reluctance machine drives. Part II: torque control, assessment and challenges. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 36(2):1323–1335
Li S, Zhang S, Jiang C, Mayor JR, Habetler TG, Harley RG (2017) A fast control-integrated and multiphysics-based multi-objective design optimization of switched reluctance machines. In: Proceedings of IEEE energy conversion congress and exposition, Cincinnati, pp 730–737
Lee D, Pham TH, Ahn J (2013) Design and operation characteristics of four-two pole high-speed SRM for torque ripple reduction. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(9):3637–3643
Hu Y, Gan C, Cao W, Zhang J, Li W, Finney SJ (2016) Flexible fault-tolerant topology for switched reluctance motor drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(6):4654–4668
Deng X, Mecrow B, Wu H, Martin R (2018) Design and development of low torque ripple variable-speed drive system with six-phase switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 33(1):420–429
Killingsworth N, Krstic M (2005) Auto-tuning of PID controllers via extremum seeking. In: Proceedings of the American control conference, Portland, pp 2251–2256
Killingsworth NJ, Krstic M (2006) PID tuning using extremum seeking: online, model-free performance optimization. IEEE Control Syst 26(1):70–79
Chen Q, Tan Y, Li J et al (2018) Decentralized PID control design for magnetic levitation systems using extremum seeking. IEEE Access 6:3059–3067
Tan Y, Moase WH, Manzie C, Nešić D, Mareels IMY (2010) Extremum seeking from 1922 to 2010. In: Proceedings of the the 29th Chinese control and decision conference (CCC), pp 14–26
Krstić M, Wang H-H (2000) Stability of extremum seeking feedback for general nonlinear dynamic systems. Automatica 36(4):595–601
Tan Y, Nešić D, Mareels I (2006) ‘On non-local stability properties of extremum seeking control.’ Automatica 42(6):889–903
Killingsworth N, Krstić M (2005) Auto-tuning of PID controllers via extremum seeking. In: Proceedings of the American control conference, pp 2251–2256
Killingsworth NJ, Krstić M (2006) ‘PID tuning using extremum seeking: online, model-free performance optimization.’ IEEE Control Syst Mag 26(1):70–79
Hjalmarsson H, Gevers M, Gunnarsson S, Lequin O (1998) Iterative feedback tuning: theory and applications. IEEE Contr Syst Mag 18(4):26–41
Lequin O, Gevers M, Triest T (1999) Optimizing the settling time with iterative feedback tuning. In: Proceedings of the 14th IFAC world congress, Beijing, pp 433–437
Lequin O, Gevers M, Mossberg M, Bosmans E, Triest L (2003) Iterative feedback tuning of PID parameters: comparison with classical tuning rules. Control Eng Pract 11(9):1023–1033
Sial MR, Sahoo NC (2022) A combined second-order-generalized-integrator based FLL and two-degree-of-freedom PID current control scheme with quintic torque sharing function for torque ripple minimization in SRM drives. In: 2022 IEEE 1st industrial electronics society annual on-line conference (ONCON), IEEE, pp 1–6
Gobbi R, Sahoo NC, Vejian R (2008) Experimental investigations on computer-based methods for determination of static electromagnetic characteristics of switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 57(10):2196–2211
Tsai MF, Quy TP, Wu BF, Tseng CS (2011) Model construction and verification of a BLDC motor using MATLAB/SIMULINK and FPGA control. In: 2011 6th IEEE conference on industrial electronics and applications, IEEE, pp 1797–1802
Hjalmarsson H, Gevers M, Gunnarsson S, Lequin O (1998) Iterative feedback tuning: theory and applications. IEEE Control Syst Mag 18(4):26–41
Lequin O, Gevers M, Triest T (1999) Optimizing the settling time with iterative feedback tuning. In: Proceeedings of the 14th IFAC world congress, Beijing, pp 433–437
Lequin O, Bosmans E, Triest T (2003) Iterative feedback tuning of PID parameters: comparision with classical tuning rules. Control Eng Practice 11(9):1023–1033
Funding
The authors have not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Manas Ranjan Sial conceptualized, implemented, analyzed results, and wrote the manuscript. N. C. Sahoo contributed to the development of concepts, critically analyzed results, and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sial, M.R., Sahoo, N.C. Torque ripple minimization and speed control of switched reluctance motor drives using extremum-seeking PI controller. Electr Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-024-02427-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-024-02427-3