Abstract
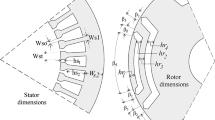
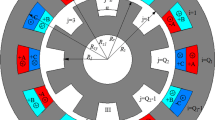
In the present paper, a simple model based on magnetic equivalent circuit (MEC) method is introduced for the switched reluctance machine to predict the phase flux linkage characteristic. All equations required to build up the model are given, and therefore, someone can use it easily for different types of the switched reluctance machines. Because of large speed of the suggested model, it can be utilized properly for quick prediction of machine performance. The suggested MEC model is applied to a typical 8/6 switched reluctance motor (SRM), and simulation results including flux linked by a phase, phase current and instantaneous torque are presented. In order to validate the suggested MEC model, the obtained simulation results are compared to those derived from finite element method (FEM) and experimental results.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller TJE (1993) Switched reluctance motor and their control. Clarendon, Oxford U.K
Krishnan R (2001) Switched reluctance motor drives modeling, simulation, analysis, design and applications. CRC Press, FL, USA
Hu Y et al (2015) Winding-centre-tapped switched reluctance motor drive for multi-source charging in electric vehicle applications. IET Power Electron 8(11):2067–2075
Todd R et al (2014) Behavioural modelling of a switched reluctance motor drive for aircraft power systems. IET Electr Syst Transp 4(4):107–113
Choi D, Byun S, Cho Y (2014) A study on the maximum power control method of switched reluctance generator for wind turbine. IEEE Trans Magn 50(1):1–4
Miller TJE, McGilp M (1990) Nonlinear theory of the switched reluctance motor for rapid computer-aided design. IEE Proc 137(6):337–347
Farshad M, Faiz J, Lucas C (2005) Development of analytical models of switched reluctance motor in two-phase excitation mode: extended miller model. IEEE Trans Magn 41(6):2145–2155
Radun A (2000) Analytically computing the flux linked by a switched reluctance motor phase when the stator and rotor poles overlap. IEEE Trans Magn 36(4):1996–2003
Uddin W, Sozer Y (2017) Analytical modeling of mutually coupled switched reluctance machines under saturation based on design geometry. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 53(5):4431–4440
Preston MA, Lyons JP (1991) A switched reluctance motor model with mutual coupling and multi-phase excitation. IEEE Trans Magn 27(6):5423–5425
Moallem M, Dawson GE (1998) An improved magnetic equivalent circuit method for predicting the characteristic of highly saturated electromagnetic devices. IEEE Trans Magn 34(5):3632–3635
Sheth NK, Rajagopal KR (2005) Calculation of the flux-linkage characteristics of a switched reluctance motor by flux tube method. IEEE Trans Magn 41(10):4069–4071
Deihimi A, Farhangi S, Henneberger G (2002) A general nonlinear model of switched reluctance motor with mutual coupling and multiphase excitation. Electr Eng 84:143–158
Vujicic V, Vukosavic SN (2000) A simple nonlinear model of the switched reluctance motor. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 15(4):395–400
Radimov N, Ben-Hail N, Rabinovici R (2004) Simple model of switched-reluctance machine based only on aligned and unaligned position data. IEEE Trans Magn 40(3):1562–1572
Lin D (2009) An analytical circuit model of switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans Magn 45(12):5368–5375
Mao SH, Dorrell D, Tsai MC (2009) Fast analytical determination of aligned and unaligned flux linkage in switched reluctance motors based on a magnetic circuit model. IEEE Trans Magn 45(7):2935–2942
Ding W, Liang D, Tang R (2011) A fast nonlinear variable structure equivalent magnetic circuit modeling for dual-channel switched reluctance machine. Energy Convers Manage 52(1):308–320
Ding W et al (2014) Magnetic circuit model and finite-element analysis of a modular switched reluctance machine with E-core stators and multi-layer common rotors. IET Electr Power Appl 8(8):296–309
Chen H, Yan W, Wang Q (2016) Electromagnetic analysis of flux characteristics of double-sided switched reluctance linear machine. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 26(4):1–7
W. Peng, J. Gyselinck (2016) Magnetic-equivalent-circuit modelling of switched reluctance machines with mutual coupling effects, International Conference on Electrical Machines ICEM. Lausanne, Switzerland
Yu Q, Wang X, Cheng Y (2016) Magnetic modeling of saliency effect for saturated electrical machines with a new calculation method. IEEE Trans Magn 52(6):1–6
Yan W, Chen H, Wang K, Chen L (2018) Dynamic circuit model considering core losses and phase interaction for switched reluctance machines. IET Electr Power Appl 12(6):826–836
MatLab: ‘User’s manual’, The Mathworks, available at www.mathworks.com.
Faiz J, Ganji B, Carstensen CE, De Doncker RW (2009) Loss prediction in switched reluctance machines using finite element method. J Eur Trans Electr Power 19:731–748
Faiz J, Ganji B, De Doncker R, Fiedler J (2006) Electromagnetic modeling of switched reluctance motor using FEM, The 32nd annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society, IECON’06. Paris, France, pp 1557–1562
Zhang J, Radun AV (2006) A new method to measure the switched reluctance motor’s flux. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 42(5):1171–1176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vahedi, P., Ganji, B. A simple magnetic equivalent circuit model for switched reluctance machine. Electr Eng 103, 1307–1320 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-01146-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-01146-9