Abstract
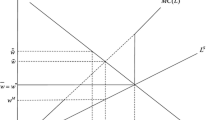
Two firms choose locations (non-wage job characteristics) on the interval [0, 1] prior to announcing wages at which they employ workers who are uniformly distributed; the (constant) marginal revenue products of workers may differ. Subgame perfect equilibria of the two-stage location-wage game are studied under laissez-faire and under a minimum wage regime. Up to a restriction for the existence of pure strategy equilibria, the imposition of a minimum wage is always welfare-improving because of its effect on non-wage job characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghion P., Espinosa M., Jullien B.: Dynamic duopoly with learning through market experimentation. Econ Theory 3, 517–539 (1993). doi:10.1007/BF01209700
Bhaskar V., To T.: Minimum wages for Ronald McDonald monopsonies; a theory of monopsonistic competition. Econ J 109, 190–203 (1999). doi:10.1111/1468-0297.00427
Bhaskar V., To T.: Oligopsony and the distribution of wages. Eur Econ Rev 47, 371–399 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0014-2921(01)00180-5
d’Aspremont C., Gabszewicz J.-J., Thisse J.-F.: On Hotelling’s stability in competition. Econometrica 47, 1145–1150 (1979)
de Fraja G.: Minimum wage legislation, productivity and employment. Economica 66, 473–488 (1999)
Delfgaauw J.: The effect of job satisfaction on job search; not just whether, but also where. Labour Econ 14, 299–317 (2007)
Kaas L., Madden P.: Hold-up in oligopsonistic labour markets—a new role for the minimum wage. Labour Econ 15, 334–349 (2008)
Lederer P.J., Hurter A.P.: Competition of firms; discriminatory pricing and location. Econometrica 53(3), 623–640 (1986)
Manning A.: Monopsony in Motion. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2003)
Meagher K.J., Zauner K.G.: Product differentiation and location decisions under demand uncertainty. J Econ Theory 117, 147–161 (2004)
Meagher K.J., Zauner K.G.: Location then price competition with uncertain consumer tastes. Econ Theory 25, 799–818 (2005)
Walsh F.: Comment on minimum wages for Ronald McDonald monopsonies; a theory of monopsonistic competition. Econ J 113, 718–722 (2003)
Ziss S.: Entry deterrence, cost advantage and horizontal product differentiation. Reg Sci Urban Econ 23, 523–543 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We thank the editors and a referee, who made a number of very helpful comments and suggestions.
Electronic supplementary material
The Below is the Electronic Supplementary Material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaas, L., Madden, P. Minimum wages and welfare in a Hotelling duopsony. Econ Theory 43, 167–188 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00199-008-0412-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00199-008-0412-2