Abstract:
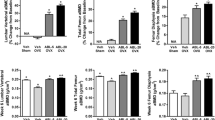
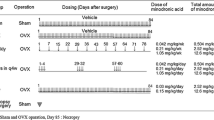
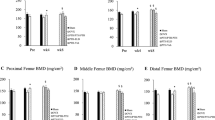
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) can prevent the bone loss induced by ovariectomy (OVX), but it is not established whether they can increase bone mass and strength in a curative protocol in ovariectomized osteopenic animals. We investigated the influence of a SERM of the new generation, MDL 103,323, on areal bone mineral density (BMD), as measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, bone strength and remodeling in OVX osteopenic rats. Nine weeks after OVX, 8-month-old rats were divided into six groups of 10 animals. MDL 103,323 was given by gavage at doses of 0.01, 0.1 or 0.6 mg/kg body weight, 5 days a week. The effect of MDL 103,323 was compared with that of the bisphosphonate pamidronate (APD), which was injected subcutaneously at a dose of 1.6 mmol/kg body weight for 5 days every 4 weeks. Lumbar spine (LS), femoral neck (FN), proximal tibia (PT) and midshaft tibia (MT) BMD, bone strength, and proximal tibia histomorphometry, serum osteocalcin, urinary total deoxypyridinoline and serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) were measured. After 16 weeks of treatment, BMD changes (means ± SEM) were −11.4 ± 2.2, +4.0 ± 2.1 and +6.4 ± 1.0% respectively in OVX controls, in rats treated with 0.1 mg/kg MDL 103,323 (p<0.05) and in APD-treated rats (p<0.02) at the level of LS; −0.4 ± 1.1, +6.7 ± 1.4, +7.2 ± 1.8% (p<0.01 and NS) at the level of FN; and −2.6 ± 1.2%, +5.8 ± 1.2, +6.9 ± 1.4% (p<0.03 and 0.01) at the level of PT. MDL 103,323-treated animals had a higher trabecular bone volume, a higher number of trabeculae and smaller intertrabecular spaces compared with OVX controls. Vertebral body ultimate strength was 186 ± 13, 292 ± 16, 249 ± 23 N (p<0.05) in OVX controls, MDL 103,323-treated rats and APD-treated rats, respectively. The administration of 0.6 mg/kg of MDL 103,323 did not further increase BMD or bone strength, indicating a bell-shaped dose–response curve. MDL 103,323 lowered plasma osteocalcin concentration and urinary deoxypyridinoline excretion. In rats treated with 0.1 mg/kg MDL 103,323, plasma IGF-I was increased as compared with OVX controls (664 ± 36 ng/ml vs 527 ± 39 ng/ml, p<0.05). In conclusion, these results indicate that this new SERM positively influences BMD and lumbar spine bone strength in estrogen-deficient rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 October 1998 / Accepted: 12 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ammann, P., Bourrin, S., Bonjour, JP. et al. The New Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator MDL 103,323 Increases Bone Mineral Density and Bone Strength in Adult Ovariectomized Rats . Osteoporos Int 10, 369–376 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980050242
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980050242