Abstract
Summary
Lower vitamin D and higher parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels are associated with higher volumetric BMD and bone strength at the lumbar spine as measured by central quantitative computed tomography in primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT), but there are no differences in bone microarchitecture as measured by trabecular bone score (TBS).
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) and volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD) and the TBS at the lumbar spine (LS) in PHPT.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional analysis of PHPT patients with and without low 25OHD. We measured vBMD with quantitative computed tomography (cQCT) and TBS by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) at the LS in 52 and 88 participants, respectively.
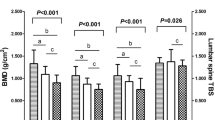
Results
In the cQCT cohort, those with lower vitamin D (<20 vs. 20-29 vs. ≥30 ng/ml) tended to be younger (p = 0.05), were less likely to use vitamin D supplementation (p < 0.01), and had better renal function (p = 0.03). Those with 25OHD <20 ng/ml had 80 and 126 % higher serum PTH levels respectively vs. those with 25OHD 20–29 ng/ml (p = 0.002) and 25OHD ≥30 ng/ml (p < 0.0001). Covariate-adjusted integral and trabecular vBMD were higher in those with 25OHD 20–29 vs. those with 25OHD ≥30 ng/ml, but those with 25OHD <20 did not differ. Because there were few participants with 25OHD deficiency, we also compared those with vitamin D <30 vs. ≥30 ng/ml. Covariate-adjusted integral and trabecular vBMD were 23 and 30 % higher respectively (both p < 0.05) in those with vitamin D <30 vs. ≥30 ng/ml. TBS was in the partially degraded range but did not differ by vitamin D status.
Conclusion
In mild PHPT, lower 25OHD is associated with higher PTH, but vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency using current clinical thresholds did not adversely affect lumbar spine skeletal health in PHPT. Further work is needed to determine if higher vBMD in those with lower vitamin D is due to an anabolic effect of PTH.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silverberg SJ, Shane E, de la Cruz L, Dempster DW, Feldman F, Seldin D, Jacobs TP, Siris ES, Cafferty M, Parisien MV et al (1989) Skeletal disease in primary hyperparathyroidism. J Bone Miner Res 4:283–291
Parisien M, Silverberg SJ, Shane E, Dempster DW, Bilezikian JP (1990) Bone disease in primary hyperparathyroidism. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 19:19–34
Rao DS, Honasoge M, Divine GW, Phillips ER, Lee MW, Ansari MR, Talpos GB, Parfitt AM (2000) Effect of vitamin D nutrition on parathyroid adenoma weight: pathogenetic and clinical implications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:1054–1058
Rao DS, Agarwal G, Talpos GB, Phillips ER, Bandeira F, Mishra SK, Mithal A (2002) Role of vitamin D and calcium nutrition in disease expression and parathyroid tumor growth in primary hyperparathyroidism: a global perspective. J Bone Miner Res 17(Suppl 2):N75–N80
Moosgaard B, Vestergaard P, Heickendorff L, Melsen F, Christiansen P, Mosekilde L (2005) Vitamin D status, seasonal variations, parathyroid adenoma weight and bone mineral density in primary hyperparathyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 63:506–513
Silverberg SJ, Shane E, Dempster DW, Bilezikian JP (1999) The effects of vitamin D insufficiency in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Am J Med 107:561–567
Ozbey N, Erbil Y, Ademoglu E, Ozarmagan S, Barbaros U, Bozbora A (2006) Correlations between vitamin D status and biochemical/clinical and pathological parameters in primary hyperparathyroidism. World J Surg 30:321–326
Beyer TD, Chen EL, Nilubol N, Prinz RA, Solorzano CC (2007) Short-term outcomes of parathyroidectomy in patients with or without 25-hydroxy vitamin D insufficiency. J Surg Res 143:145–150
Moosgaard B, Christensen SE, Vestergaard P, Heickendorff L, Christiansen P, Mosekilde L (2008) Vitamin D metabolites and skeletal consequences in primary hyperparathyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 68:707–715
Yamashita H, Noguchi S, Uchino S, Watanabe S, Koike E, Murakami T, Fujihira T, Koga Y, Masatsugu T, Yamashita H (2002) Vitamin D status in Japanese patients with hyperparathyroidism: seasonal changes and effect on clinical presentation. World J Surg 26:937–941
Walker MD, Cong E, Lee JA, Kepley A, Zhang C, McMahon DJ, Silverberg SJ (2015) Vitamin D in primary hyperparathyroidism: effects on clinical, biochemical, and densitometric presentation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:3443–3451
Stein EM, Dempster DW, Udesky J, Zhou H, Bilezikian JP, Shane E, Silverberg SJ (2011) Vitamin D deficiency influences histomorphometric features of bone in primary hyperparathyroidism. Bone 48:557–561
Walker MD, Nishiyama KK, Zhou B, Cong E, Wang J, Lee JA, Kepley A, Zhang C, Guo XE, Silverberg SJ (2016) Effect of low vitamin D on volumetric bone mineral density, bone microarchitecture, and stiffness in primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:905–913
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH, Weaver CM (2011) Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1911–1930
Hertzler A, Frary R (1994) A dietary rapid assessment method (RAM). Top Clin Nutr 9:76–85
Stein EM, Strain G, Sinha N, Ortiz D, Pomp A, Dakin G, McMahon DJ, Bockman R, Silverberg SJ (2009) Vitamin D insufficiency prior to bariatric surgery: risk factors and a pilot treatment study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 71:176–183
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Bonnick SL, Johnston CC Jr, Kleerekoper M, Lindsay R, Miller P, Sherwood L, Siris E (2001) Importance of precision in bone density measurements. J Clin Densitom 4:105–110
Cheng X, Li J, Lu Y, Keyak J, Lang T (2007) Proximal femoral density and geometry measurements by quantitative computed tomography: association with hip fracture. Bone 40:169–174
Lang T, LeBlanc A, Evans H, Lu Y, Genant H, Yu A (2004) Cortical and trabecular bone mineral loss from the spine and hip in long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res 19:1006–1012
Lang TF, Leblanc AD, Evans HJ, Lu Y (2006) Adaptation of the proximal femur to skeletal reloading after long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res 21:1224–1230
Hans D, Barthe N, Boutroy S, Pothuaud L, Winzenrieth R, Krieg MA (2011) Correlations between trabecular bone score, measured using anteroposterior dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry acquisition, and 3-dimensional parameters of bone microarchitecture: an experimental study on human cadaver vertebrae. J Clin Densitom 14:302–312
Dufour R, Winzenrieth R, Heraud A, Hans D, Mehsen N (2013) Generation and validation of a normative, age-specific reference curve for lumbar spine trabecular bone score (TBS) in French women. Osteoporos Int 24:2837–2846
Popp AW, Guler S, Lamy O, Senn C, Buffat H, Perrelet R, Hans D, Lippuner K (2013) Effects of zoledronate versus placebo on spine bone mineral density and microarchitecture assessed by the trabecular bone score in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a three-year study. J Bone Miner Res 28:449–454
McCloskey EV, Oden A, Harvey NC, Leslie WD, Hans D, Johansson H, Barkmann R, Boutroy S, Brown J, Chapurlat R, Elders PJ, Fujita Y, Gluer CC, Goltzman D, Iki M, Karlsson M, Kindmark A, Kotowicz M, Kurumatani N, Kwok T, Lamy O, Leung J, Lippuner K, Ljunggren O, Lorentzon M, Mellstrom D, Merlijn T, Oei L, Ohlsson C, Pasco JA, Rivadeneira F, Rosengren B, Sornay-Rendu E, Szulc P, Tamaki J, Kanis JA (2015) A meta-analysis of trabecular bone score in fracture risk prediction and its relationship to FRAX. J Bone Miner Res 2015
Roux JP, Wegrzyn J, Boutroy S, Bouxsein ML, Hans D, Chapurlat R (2013) The predictive value of trabecular bone score (TBS) on whole lumbar vertebrae mechanics: an ex vivo study. Osteoporos Int 24:2455–2460
Muschitz C, Kocijan R, Haschka J, Pahr D, Kaider A, Pietschmann P, Hans D, Muschitz GK, Fahrleitner-Pammer A, Resch H (2015) TBS reflects trabecular microarchitecture in premenopausal women and men with idiopathic osteoporosis and low-traumatic fractures. Bone 79:259–266
Silva BC, Leslie WD, Resch H, Lamy O, Lesnyak O, Binkley N, McCloskey EV, Kanis JA, Bilezikian JP (2014) Trabecular bone score: a noninvasive analytical method based upon the DXA image. J Bone Miner Res 29:518–530
Ulivieri FM, Silva BC, Sardanelli F, Hans D, Bilezikian JP, Caudarella R (2014) Utility of the trabecular bone score (TBS) in secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine 47:435–448
Khosla S, Melton LJ 3rd, Wermers RA, Crowson CS, O’Fallon W, Riggs B (1999) Primary hyperparathyroidism and the risk of fracture: a population-based study. J Bone Miner Res 14:1700–1707
Vestergaard P, Mollerup CL, Frokjaer VG, Christiansen P, Blichert-Toft M, Mosekilde L (2000) Cohort study of risk of fracture before and after surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism. BMJ 321:598–602
De Geronimo S, Romagnoli E, Diacinti D, D’Erasmo E, Minisola S (2006) The risk of fractures in postmenopausal women with primary hyperparathyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol 155:415–420
Vignali E, Viccica G, Diacinti D, Cetani F, Cianferotti L, Ambrogini E, Banti C, Del Fiacco R, Bilezikian JP, Pinchera A, Marcocci C (2009) Morphometric vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2306–2312
Lundstam K, Heck A, Mollerup C, Godang K, Baranowski M, Pernow Y, Varhaug JE, Hessman O, Rosen T, Nordenstrom J, Jansson S, Hellstrom M, Bollerslev J, Group SS (2015) Effects of parathyroidectomy versus observation on the development of vertebral fractures in mild primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:1359–1367
Silva BC, Boutroy S, Zhang C, McMahon DJ, Zhou B, Wang J, Udesky J, Cremers S, Sarquis M, Guo XD, Hans D, Bilezikian JP (2013) Trabecular bone score (TBS)—a novel method to evaluate bone microarchitectural texture in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1963–1970
Rolighed L, Rejnmark L, Sikjaer T, Heickendorff L, Vestergaard P, Mosekilde L, Christiansen P (2014) Vitamin D treatment in primary hyperparathyroidism: a randomized placebo controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:1072–1080
Martin EN, Haney EM, Shannon J, Cauley JA, Ensrud KE, Keaveny TM, Zmuda JM, Orwoll ES, Harrison SL, Marshall LM (2015) Femoral volumetric bone density, geometry, and strength in relation to 25-hydroxy vitamin D in older men. J Bone Miner Res 30:562–569
Shawwa K, Arabi A, Nabulsi M, Maalouf J, Salamoun M, Choucair M, Hans D, El-Hajj FG (2016) Predictors of trabecular bone score in school children. Osteoporos Int 27:703–710
Aloia JF, Mikhail M, Usera G, Dhaliwal R, Islam S (2015) Trabecular bone score (TBS) in postmenopausal African American women. Osteoporos Int 26:1155–1161
Walker MD, Cong E, Lee JA, Kepley A, Zhang C, McMahon DJ, Bilezikian JP, Silverberg SJ (2015) Low vitamin D levels have become less common in primary hyperparathyroidism. Osteoporos Int 26:2837–2843
Acknowledgments
Marcella D. Walker—acquisition of data, data analysis and interpretation, drafting of manuscript
Isra Saeed—acquisition of data, manuscript revision
James Lee—acquisition of data, manuscript revision
Chengchen Zhang—analysis of data, manuscript revision
Didier Hans—acquisition of data, manuscript revision
Thomas Lang—acquisition of data, manuscript revision
Shonni J. Silverberg—design, acquisition of data, interpretation of data, manuscript drafting
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding sources
This work was supported by NIH grants R01 DK084986 and K24 DK074457 as well as the Joseph Weintraub Family Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
Didier Hans is a co-owner of the patent for TBS and has corresponding ownership shares in Medimaps. Marcella D. Walker, Isra Saeed, James Lee, Chengchen Zhang, Thomas Lang, and Shonni Silverberg declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walker, M.D., Saeed, I., Lee, J.A. et al. Effect of concomitant vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency on lumbar spine volumetric bone mineral density and trabecular bone score in primary hyperparathyroidism. Osteoporos Int 27, 3063–3071 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3637-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3637-0