Abstract
Summary
The skeletal renin-angiotensin system contributes to the development of osteoporosis. The renin inhibitor aliskiren exhibited beneficial effects on trabecular bone of osteoporotic mice, and this action might be mediated through angiotensin and bradykinin receptor pathways. This study implies the potential application of renin inhibitor in the management for postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Introduction
The skeletal renin-angiotensin system plays key role in the pathological process of osteoporosis. The present study is designed to elucidate the effect of renin inhibitor aliskiren on trabecular bone and its potential action mechanism in ovariectomized (OVX) mice.
Methods
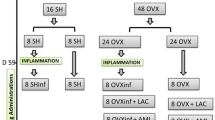
The OVX mice were treated with low dose (5 mg/kg) or high dose (25 mg/kg) of aliskiren or its vehicle for 8 weeks. The bone turnover markers were measured by ELISA. The structural parameters of trabecular bone at lumbar vertebra (LV) and distal femoral metaphysis were measured by micro-CT. The expression of messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein was studied by RT-PCR and immunoblotting, respectively.
Results
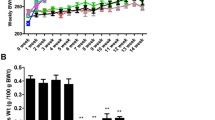
Aliskiren treatment reduced urinary excretion of calcium and serum level of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in OVX mice. The treatment with aliskiren significantly increased bone volume (BV/TV) and connectivity density (Conn.D) of trabecular bone at LV-2 and LV-5 as well as dramatically enhanced BV/TV, Conn.D, bone mineral density (BMD/BV) and decreased bone surface (BS/BV) at the distal femoral end. Aliskiren significantly down-regulated the expression of angiotensinogen, angiotensin II (Ang II), Ang II type 1 receptor, bradykinin receptor (BR)-1, and osteocytic-specific gene sclerostin as well as the osteoclast-specific genes, including carbonic anhydrase II, matrix metalloproteinase-9, and cathepsin K.
Conclusions
This study revealed that renin inhibitor aliskiren exhibited the beneficial effects on trabecular bone of ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic mice, and the underlying mechanism for this action might be mediated through Ang II and BR signaling pathways in bone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Namazi S, Ardeshir-Rouhani-Fard S, Abedtash H (2011) The effect of renin angiotensin system on tamoxifen resistance. Med Hypotheses 77:152–155
Skov J, Persson F, Frøkiær J, Christiansen JS (2014) Tissue renin-angiotensin systems: a unifying hypothesis of metabolic disease. Front Endocrinol 5:23
Lau T, Carlsson PO, Leung PS (2004) Evidence for a local angiotensin-generating system and dose-dependent inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin release by angiotensin II in isolated pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 47:240–248
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Ning G, Deb DK, Kong J, Li YC (2008) Combination therapy with AT1 receptor blocker and vitamin D analog markedly ameliorates diabetic nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:15896–15901
Zhang Y, Deb DK, Kong J, Ning G, Wang Y, Li G, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Strugnell S, Sabbagh Y, Arbeeny C, Li YC (2009) Long-term therapeutic effect of vitamin D analog doxercalciferol on diabetic nephropathy: strong synergism with AT1 receptor antagonist. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F791–F801
Koïtka A, Cao Z, Koh P, Watson AMD, Sourris KC, Loufrani L, Soro-Paavonen A, Walther T, Woollard KJ, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Cooper ME, Allen TJ (2010) Angiotensin II subtype 2 receptor blockade and deficiency attenuate the development of atherosclerosis in an apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 53:584–592
Inaba S, Iwai M, Furuno M, Kanno H, Senba I, Okayama H, Mogi M, Higaki J, Horiuchi M (2011) Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in cardiac hypertrophy induced by nitric oxide synthase inhibition. J Hypertens 29:2236–2245
Naffah-Mazzacoratti Mda G, Gouveia TL, Simões PS, Perosa SR (2014) What have we learned about the kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems in neurological disorders? World J Biol Chem 5:130–140
Herr D, Bekes I, Wulff C (2013) Local renin-angiotensin system in the reproductive system. Front Endocrinol 4:150
Asaba Y, Ito M, Fumoto T, Watanabe K, Fukuhara R, Takeshita S, Nimura Y, Ishida J, Fukamizu A, Ikeda K (2009) Activation of renin-angiotensin system induces osteoporosis independently of hypertension. J Bone Miner Res 24:241–250
Izu Y, Mizoguchi F, Kawamata A, Hayata T, Nakamoto T, Nakashima K, Inagami T, Ezura Y, Noda M (2009) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor blockade increases bone mass. J Biol Chem 284:4857–4864
Lamparter S, Kling L, Schrader M, Ziegler R, Pfeilschifter J (1998) Effects of angiotensin II on bone cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol 175:89–98
Kumar R, Boim MA (2009) Diversity of pathways for intracellular angiotensin II synthesis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 18:33–39
Shimizu H, Nakagami H, Osako MK, Hanayama R, Kunugiza Y, Kizawa T, Tomita T, Yoshikawa H, Ogihara T, Morishita R (2008) Angiotensin II accelerates osteoporosis by activating osteoclasts. FASEB J 22:2465–2475
Hiruma Y, Inoue A, Hirose S, Hagiwara H (1997) Angiotensin II stimulates the proliferation of osteoblast-rich populations of cells from rat calvariae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 230:176–178
Kaneko K, Ito M, Fumoto T, Fukuhara R, Ishida J, Fukamizu A, Ikeda K (2011) Physiological function of the angiotensin AT1a receptor in bone remodeling. J Bone Miner Res 26:2959–2966
Gu SS, Zhang Y, Li XL, Wu SY, Diao TY, Hai R, Deng H (2012) Involvement of the skeletal renin-angiotensin system in age-related osteoporosis of ageing mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:1367–1371
Gu SS, Zhang Y, Wu SY, Diao TY, Gebru YA, Deng H (2012) Early molecular responses of bone to obstructive nephropathy induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction in mice. Nephrology 17:767–773
Diao TY, Pan H, Gu SS, Chen X, Zhang FY, Wong MS, Zhang Y (2014) Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, captopril, on bone of mice with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes. J Bone Miner Metab 32:261–270
Garcia P, Schwenzer S, Slotta JE, Scheuer C, Tami AE, Holstein JH, Histing T, Burkhardt M, Pohlemann T, Menger MD (2010) Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme stimulates fracture healing and periosteal callus formation—role of a local renin-angiotensin system. Br J Pharmacol 159:1672–1680
Zhang Y, Wang K, Song Q, Liu R, Ji W, Ji L, Wang C (2014) Role of the local bone renin-angiotensin system in steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Mol Med Rep 9:1128–1134
Liu YY, Yao WM, Wu T, Xu BL, Chen F, Cui L (2011) Captopril improves osteopenia in ovariectomized rats and promotes bone formation in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Metab 29:149–158
Yamamoto S, Kido R, Onishi Y, Fukuma S, Akizawa T, Fukagawa M, Kazama JJ, Narita I, Fukuhara S (2015) Use of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors is associated with reduction of fracture risk in hemodialysis patients. PLoS One 10:e0122691
Shimizu H, Nakagami H, Osako MK, Nakagami F, Kunugiza Y, Tomita T, Yoshikawa H, Rakugi H, Ogihara T, Morishita R (2009) Prevention of osteoporosis by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 32:786–790
Donmez BO, Ozdemir S, Sarikanat M, Yaras N, Koc P, Demir N, Karayalcin B, Oguz N (2012) Effect of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker on osteoporotic rat femurs. Pharmacol Rep 64:878–888
Kang KY, Kang Y, Kim M, Kim Y, Yi H, Kim J, Jung HR, Park SH, Kim HY, Ju JH, Hong YS (2013) The effects of antihypertensive drugs on bone mineral density in ovariectomized mice. J Korean Med Sci 28:1139–1144
Reginster JY, Burlet N (2006) Osteoporosis: a still increasing prevalence. Bone 38:S4–S9
Ghosh M, Majumdar SR (2014) Antihypertensive medications, bone mineral density, and fractures: a review of old cardiac drugs that provides new insights into osteoporosis. Endocrine 46:397–405
Zhang Y, Dong XL, Leung PC, Wong MS (2009) Differential mRNA expression profiles in proximal tibia of aged rats in response to ovariectomy and low-Ca diet. Bone 44:46–52
Wood JM, Maibaum J, Rahuel J, Grütter MG, Cohen NC, Rasetti V, Rüger H, Göschke R, Stutz S, Fuhrer W, Schilling W, Rigollier P, Yamaguchi Y, Cumin F, Baum HP, Schnell CR, Herold P, Mah R, Jensen C, O’Brien E, Stanton A, Bedigian MP (2003) Structure-based design of aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308:698–705
Persson F, Rossing P, Parving HH (2013) Direct renin inhibition in chronic kidney disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol 76:580–586
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Chen Y, Deb DK, Sun T, Zhao Q, Li YC (2012) Inhibition of renin activity by aliskiren ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mouse model. J Diabetes Mellitus 2:353–360
Riccioni G (2013) The role of direct renin inhibitors in the treatment of the hypertensive diabetic patient. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab 4:139–145
Gandhi S, Srinivasan B, Akarte AS (2013) Aliskiren improves insulin resistance and ameliorates diabetic renal vascular complications in STZ-induced diabetic rats. J Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 14:3–13
Nussberger J, Wuerzner G, Jensen C, Brunner HR (2002) Angiotensin II suppression in humans by the orally active renin inhibitor aliskiren (SPP100): comparison with enalapril. Hypertension 39:E1–E8
Koid SS, Ziogas J, Campbell DJ (2014) Aliskiren reduces myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by a bradykinin B2 receptor- and angiotensin AT2 receptor-mediated mechanism. Hypertension 63:768–773
Desjarlais M, Dussault S, Dhahri W, Mathieu R, Rivard A (2015) Direct renin inhibition with aliskiren improves ischemia-induced neovascularization: blood pressure-independent effect. Atherosclerosis 242:450–460
Yong QC, Thomas CM, Seqqat R, Chandel N, Baker KM, Kumar R (2013) Angiotensin type 1a receptor-deficient mice develop diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction, which is prevented by renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. Cardiovasc Diabetol 12:169
Moriya H, Kobayashi S, Ohtake T, Tutumi D, Mochida Y, Ishioka K, Oka M, Maesato K, Hidaka S, Nomura S (2013) Aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, improves vascular endothelial function in patients on hemodialysis independent of antihypertensive effect—a pilot study. Kidney Blood Press Res 37:190–198
Li YC (2007) Inhibition of renin: an updated review of the development of renin inhibitors. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 8:750–757
Zhang YF, Qin L, Leung PC, Kwok TC (2012) The effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use on bone loss in elderly Chinese. J Bone Miner Metab 30:666–673
Zhang Y, Diao TY, Gu SS, Wu SY, Gebru YA, Chen X, Wang JY, Ran S, Wong MS (2014) Effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker on bones in mice with type 1 diabetes induced by streptozotocin. J Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 15:218–227
Stimpel M, Jee WS, Ma Y, Yamamoto N, Chen Y (1995) Impact of antihypertensive therapy on postmenopausal osteoporosis: effects of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor Moexipril, 17beta-estradiol and their combination on the ovariectomy-induced cancellous bone loss in young rats. J Hypertens 13:1852–1856
Kwok T, Leung J, Zhang YF, Bauer D, Ensrud KE, Barrett-Connor E, Leung PC, Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Research Group (2012) Does the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers affect bone loss in older men? Osteoporos Int 23:2159–2167
Masunari N, Fujiwara S, Nakata Y, Furukawa K, Kasagi F (2008) Effect of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor and benzodiazepine intake on bone loss in older Japanese. Hiroshima J Med Sci 57:17–25
Kim KR, Kim HJ, Lee SK, Ma GT, Park KK, Chung WY (2015) 15-deoxy-δ12,14-prostaglandin j2 inhibits Osteolytic breast cancer bone metastasis and estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss. PLoS One 10:e0122764
Li Y, Shen GS, Yu C, Li GF, Shen JK, Xu YJ, Gong JP (2015) Local bone interaction between renin-angiotensin system and kallikrein-kinin system in diabetic rat. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:1604–1612
Roux S (2010) New treatment targets in osteoporosis. Joint Bone Spine 77:222–228
Yayama K, Okamoto H (2008) Angiotensin II-induced vasodilation via type 2 receptor: role of bradykinin and nitric oxide. Int Immunopharmacol 8:312–318
Horiuchi M, Iwanami J, Mogi M (2012) Regulation of angiotensin II receptors beyond the classical pathway. Clin Sci (Lond) 123:193–203
Namsolleck P, Recarti C, Foulquier S, Steckelings UM, Unger T (2014) AT (2) receptor and tissue injury: therapeutic implications. Curr Hypertens Rep 16:416
Souza PP, Brechter AB, Reis RI, Costa CA, Lundberg P, Lerner UH (2013) IL-4 and IL-13 inhibit IL-1β and TNF-α induced kinin B1 and B2 receptors through a STAT6-dependent mechanism. Br J Pharmacol 169:400–412
Srivastava S, Sharma K, Kumar N, Roy P (2014) Bradykinin regulates osteoblast differentiation by Akt/ERK/NFκB signaling axis. J Cell Physiol 229:2088–2105
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81202894).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Y. Zhang and L. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Song, Y. et al. Renin inhibitor aliskiren exerts beneficial effect on trabecular bone by regulating skeletal renin-angiotensin system and kallikrein-kinin system in ovariectomized mice. Osteoporos Int 27, 1083–1092 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3348-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3348-y