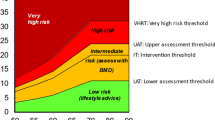
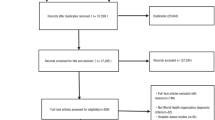
Abstract
Participants in the conference selected to attend two different working group sessions. The working groups discussed different perspectives of system-based approaches to osteoporosis and fracture care. The group on postfracture case management recommended that nurse case managers be used to improve communication among patients, orthopaedic surgeons, and those providing ongoing clinical care. The hospital working group discussed the impact of and barriers to improved postfracture management in the hospital setting. The health systems group emphasized the difference between a closed system in which long-term benefits of interventions were more likely to be appreciated than in fee for service systems. The health information technology group discussed the advantages and challenges of electronic health records. The working group on consumer and provider education discussed interventions for both primary and secondary prevention of fractures. Recommendations were produced by most groups for improving postfracture care.
Similar content being viewed by others
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adler, R.A., Bates, D.W., Dell, R.M. et al. Systems-based approaches to osteoporosis and fracture care: policy and research recommendations from the workgroups. Osteoporos Int 22 (Suppl 3), 495 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1708-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1708-9