Abstract
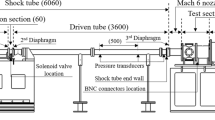
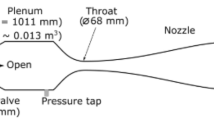
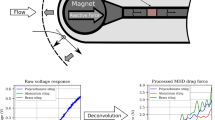
Shock tunnels are important ground test facilities that can generate high-enthalpy flow. Flight velocity at a high Mach number can be simulated for aerodynamic testing of chemically reacting flows. However, the application of these tunnels is limited due to the only milliseconds-long test duration, especially for aerodynamic force measurement using traditional strain gauge balances. This study presents an impulse force-measurement system, which was used for a large-scale test model to measure its drag in a high-enthalpy shock tunnel with an approximately 3–7-ms test time. Force tests were conducted for a cone in the JF-10 high-enthalpy shock tunnel in the Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. An integrated design of the impulse force-measurement system was proposed for load measurement over a short duration, for which a recommended design criterion is that the measurement period be a minimum of twice the period corresponding to the lowest natural frequency of the measurement system. The current measurement technique breaks the limitations of the application of the conventional strain gauge balance. As an integrated measuring system, the impulse force-measurement system expands the structural design concept of strain gauge balances. The impulse force-measurement system performed well in the present tests. The test results show differences from the numerical simulations and some data obtained in a conventional wind tunnel. A preliminary analysis was performed on the real gas effects on the aerodynamic force.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrington, P.J., Joiner, R.J., Henderson, A.J.: Longitudinal characteristics of several configurations at hypersonic mach numbers in conical and contoured nozzles. NASA TN D-2489 (1954)
Bernstein, L.: Force measurement in short-duration hypersonic facilities. AGARDograph No. 214 (1975)
Naumann, K., Ende, H., Mathieu, G., George, A.: Millisecond aerodynamic force measurement with side-jet model in the ISL shock tunnel. AIAA J. 31, 1068–1074 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.11730
Naumann, K., Ende, H.: A novel technique for aerodynamic force measurement in shock tubes. International Congress on Instrumentation in Aerospace Simulation Facilities, Gottingen, West Germany, pp. 535–544 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIASF.1989.77710
Joarder, R., Jagadeesh, G.: A new free floating accelerometer balance system for force measurements in shock tunnels. Shock Waves 13, 409–412 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-003-0225-y
Saravanan, S., Jagadeesh, G., Reddy, K.P.J.: Aerodynamic force measurement using 3-component accelerometer force balance system in a hypersonic shock tunnel. Shock Waves 18, 425–435 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-008-0172-8
Sahoo, N., Mahapatra, D.R., Jagadeesh, G., Gopalakrishnan, S., Reddy, K.P.J.: An accelerometer balance system for measurement of aerodynamic force coefficients over blunt bodies in a hypersonic shock tunnel. Meas. Sci. Technol. 14, 260–272 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/14/3/303
Robinson, M.J., Schramm, J.M., Hannemann, K.: Design and implementation of an internal stress wave force balance in a shock tunnel. CEAS Space J. 1, 45–57 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-010-0003-5
Sanderson, S.R., Simmons, J.M., Tuttle, S.L.: A drag measurement technique for free-piston shock tunnels. 29th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV, U.S.A., AIAA Paper 91-0549 (1991). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1991-549
Mee, D.J., Daniel, W.J.T., Simmons, J.M.: Three-component force balance for flows of millisecond duration. AIAA J. 34(3), 590–595 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.13108
Seiler, F., Mathieu, G., George, A., Srulijes, J., Havermann, M.: Development of a free flight force measuring technique (FFM) at the ISL shock tube laboratory. 25th International Symposium on Shock Wave, Bangalore, India (2005)
Wey, P., Bastide, M., Martinez, B., Srulijes, J., Gnemmi, P.: Determination of aerodynamic coefficients from shock tunnel free-flight trajectories. 28th Aerodynamic Measurement Technology, Ground Testing, and Flight Testing Conference, New Orleans, USA, AIAA Paper 2012-3321 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2012-3321
Martinez, B., Bastide, M., Wey, P.: Free-flight measurement technique in shock tunnel. Proceedings of the 30th Aerodynamic Measurement Technology and Ground Testing Conference, Atlanta, USA, AIAA Paper 2014–2523 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2014-2523
Tanno, H., Komuro, T., Sato, K., Fujita, K., Laurence, S.J.: Free-flight measurement technique in the free-piston shock tunnel hiest. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85, 045112 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4870920
Tanno, H., Komuro, T., Sato, K., Itoh, K., Yamada, T.: Free-flight tests of reentry capsule models in free-piston shock tunnel. 43rd Fluid Dynamics Conference, San Diego, CA, AIAA Paper 2013-2979 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2013-2979
Laurence, S.J., Karl, S.: An improved visualization-based force-measurement technique for short-duration hypersonic facilities. Exp. Fluids 48, 949–965 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-009-0780-9
Marineau, E., MacLean, M., Mundy, E., Holden, M.: Force measurements in hypervelocity flows with an acceleration compensated strain gage balance. J. Spacecr. Rockets 49(3), 474–482 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A32041
Wang, Y.P., Liu, Y.F., Luo, C.T., Jiang, Z.L.: Force measurement using strain-gauge balance in a shock tunnel with long test duration. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87, 055108 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4950781
Wang, Y.P., Liu, Y.F., Jiang, Z.L.: Design of a pulse-type strain gauge balance for a long-test-duration hypersonic shock tunnel. Shock Waves 26(6), 835–844 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-015-0616-x
Jiang, Z., Yu, H.: Theories and technologies for duplicating hypersonic flight conditions for ground testing. Natl. Sci. Rev. 4, 290–296 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwx007
Jiang, Z., Zhao, W., Wang, C., Takayama, K.: Forward-running detonation drivers for high-enthalpy shock tunnels. AIAA J. 40, 2009–2016 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2514/2.1533
Jiang, Z., Chang, L., Zhang, F.: Dynamic characteristics of spherically converging detonation waves. Combust. Flame 16, 253–267 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-006-0066-6
Stalker, R.: Modern developments in hypersonic wind tunnels. Aeronaut. J. 110(1103), 21–39 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000004346
Holden, M.: Design, development and calibration of the lens facility. AFOSR-TR 94–0161 (1994)
Holden, M.: Recent advances in hypersonic test facilities and experimental research. AIAA/DGLR 5th International Aerospace Planes and Hypersonics Technologies Conference, Munich, Germany, AIAA Paper 93-5005 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1993-5005
Rose, P.H.: Development of the calorimeter heat transfer gauge for use in shock tubes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 29(7), 557–564 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1716258
Stalker, R.: A study of the free-piston shock tunnel. AIAA J. 5(12), 2160–2165 (1967). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.4402
Stalker, R.J.: Shock tunnel for real gas hypersonics. Aerodynamics of Hypersonic Lifting Vehicles, AGARD Conference Proceedings No. 428, Bangalore, India (1987)
Yu, H.R., Esser, B., Lenartz, M., Gronig, H.: Gaseous detonation driver for a shock tunnel. Shock Waves 2, 245–254 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414760
Zhao, W., Jiang, Z.L., Saito, T., Lin, J., Yu, H., Takayama, K.: Performance of a detonation driven shock tunnel. Shock Waves 14(1–2), 53–59 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-004-0238-1
Jiang, Z., Lin, J., Zhao, W.: Performance tests of JF-10 high-enthalpy shock tunnel with a FDC driver. Int. J. Hypersonics 2(1), 29–36 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1260/1759-3107.2.1.29
Grabau, M., Smithson, H.K., Little, W.J.: A data reduction program for hotshot tunnels based on the Fay–Riddell heat transfer rate using nitrogen at stagnation temperatures from 1500 to 5000 K. Technical report AEDC- TDR-64-50 (1964)
Simeonides, G.: Hypersonic shock wave boundary layer interactions over compression corners. PhD thesis, von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics, University of Bristol (1992). https://doi.org/10.12681/eadd/28688
Hirschfelder, J.O., Buehler, R.J., McGee, H.A., Sutton, J.R.: Generalized equation of state for gases and liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. 50, 375–385 (1958)
Culotta, S., Enkenhus, K.R.: Analytical expressions for the thermo-dynamic properties of dense nitrogen. Technical note VKI-TN-50 (1968)
Jiang, Z., Takayama, K., Chen, Y.: Dispersion conditions for non-oscillatory shock capturing schemes and its applications. Comput. Fluid Dyn. J. 4, 137–150 (1995)
Jiang, Z.: On dispersion-controlled principles for non-oscillatory shock-capturing schemes. Acta Mech. Sin. 20, 1–15 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02484239
Jiang, Z., Han, G., Wang, C., Zhang, F.: Self-organized generation of transverse waves in diverging cylindrical detonations. Combust. Flame 156, 1653–1661 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2009.02.012
Jiang, Z., Takayama, K.: An investigation into the validation of numerical solutions of complex flow fields. J. Comput. Phys. 151, 479–497 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1999.6186
Spalart, P.R., Allmaras, S.R.: A one-equation turbulence model for aerodynamic flows. 30th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, U.S.A., AIAA Paper 92-0439 (1992). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1992-439
Luo, C.T., Wang, Y.P., Wang, C., Jiang, Z.L.: Wave system fitting: a new method for force measurements in shock tunnels with long test duration. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 62–63, 296–304 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.02.024
Penland, J.A.: Aerodynamic force characteristics of a series of lifting cone and cone-cylinder configurations at M = 6.83 and angles of attack up to 130\(^{\circ }\). NASA TN D-840 (1961)
Ladson, C., Blackstock, T.: Air-helium simulation of the aerodynamic force coefficients of cones at hypersonic speeds. NASA TN D-1473 (1962)
Zhang, H.: Hypersonic Aerodynamic Test. National Defense Industry Press, Beijing (2004)
Cheng, H.K.: Hypersonic shock-layer theory of a yawed cone and other three-dimensional pointed bodies. WADC TN 59–335 (1959)
Cheng, H.K.: Hypersonic flows past a yawed circular cone and other pointed bodies. J. Fluid Mech. 12(2), 169–191 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022112062000142
Ma, J., Tang, Z., Zhang, X.: Free flight method in hypersonic impulse type tunnels for static and dynamic stability study. Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 4, 82–90 (1983). (in Chinese)
Fluid Dynamics Panel Working Group 15. Quality assessment for wind tunnel testing. AGARD-AR-304 (1994)
AIAA Standard: Assessment of experimental uncertainty with application to wind tunnel testing (AIAA S-071A-1999). American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, VA, USA (1999). https://doi.org/10.2514/4.476648.001
AIAA Guide: Assessing experimental uncertainty-supplement to AIAA S-071A-1999 (AIAA G-045-2003). American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, VA, USA (2003). https://doi.org/10.2514/4.476648.001
Anderson, J.D.: Hypersonic and High-Temperature Gas Dynamics, 2nd edn. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Reston (2006). https://doi.org/10.2514/4.861956
MacWherter, M., Noack, R.W., Oberkampf, W.L.: Evaluation of boundary-layer and parabolized Navier–Stokes solutions for re-entry vehicles. J. Spacecr. Rockets 23(1), 70–78 (1986). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.25085
Yang, Y., Wang, F., Guo, D.: Force measurement of the cone with 10\(^{\circ }\) semivertex angle using a six-component balance system in the hypersonic impulse wind tunnel. Aerodyn. Exp. Meas. Control 2(1), 60–64 (1988). (in Chinese)
Koppenwallner, G.: Fundamentals of hypersonics: aerodynamics and heat transfer. VKI Short Course notes Hypersonic Aerothermodynamics (1984)
Gray, J.D.: Summary report on aerodynamic characteristics of standard models hb-1 and hb-2. AEDC-TDR-64-137 (1964)
Hirschel, E.H.: Basics of Aerothermodynamics. Springer, Berlin (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/b137734
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11672357).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Seiler.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Jiang, Z. Impulse force-measurement system. Shock Waves 30, 603–613 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-020-00971-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-020-00971-y