Abstract.
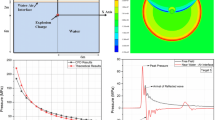
The attenuation of an underwater shock wave by a thin porous layer is studied both experimentally and numerically. The shock waves are generated by exploding 10 mg silver azide pellets and the pressures at different distances from the explosion center are measured. Measurements are also carried out with a gauze layer placed between the explosion source and the pressure gauge. The results with and without the gauze layer are compared evaluating the shock wave attenuation. Numerical simulations of the phenomenon are also carried out for a simple wave attenuation model. The results are compared with the experimental data. Despite the simple mathematical model of wave attenuation, the agreement between the experimental and numerical results is reasonable.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Grönig
Received: 22 October 2002, Accepted: 17 June 2003, Published online: 5 August 2003
PACS:
47.11.+j, 47.40.Nm, 47.55.Mh
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, T., Marumoto, M., Yamashita, H. et al. Experimental and numerical studies of underwater shock wave attenuation. Shock Waves 13, 139–148 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-003-0201-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-003-0201-6