Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of external anal sphincter repair on fecal incontinence symptoms, quality of life, and anal sphincter squeeze pressures.
Methods
The fecal incontinence symptoms and impact on quality of life, patient satisfaction, and anorectal manometry were assessed pre- and post-operatively.
Results
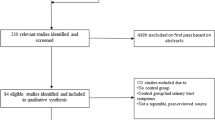
One hundred four women were eligible and 74/104 (71%) returned post-operative questionnaires. Fifty-four of 74 (73%) had pre- and post-operative questionnaires. Twenty-five of 74 (34%) had pre- and post-operative anorectal manometry measures. Mean length of follow-up for participants (n = 54) was 32 ± 19 months. Modified Manchester Health Questionnaire scores decreased from 47.3 ± 21.9 to 28.4 ± 24.3 (p < 0.01) and Fecal Incontinence Severity Index scores from 30.6 ± 13.0 to 21.6 ± 15.5 (p < 0.01). Seventy-seven percent of the participants was satisfied. Sphincter squeeze pressures increased from 53.4 ± 25.0 to 71.8 ± 29.1 mmHg (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
External anal sphincter repair resulted in sustained improvements in fecal incontinence severity and quality of life along with improved anal sphincter squeeze pressures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitehead WE, Borrud L, Goode PS, Meikle S, Mueller ER, Tuteja A, Weidner A, Weinstein M, Ye W, Pelvic Floor Disorders Network (2009) Fecal incontinence in US adults: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterology 137:512–517
Nygaard I, Barber MD, Burgio KL, Kenton K, Meikle S, Schaffer J, Spino C, Whitehead WE, Wu J, Brody DJ, Pelvic Floor Disorders Network (2008) Prevalence of symptomatic pelvic floor disorders in US women. JAMA 300:1311–1316
Melville JL, Fan MY, Newton K, Fenner D (2005) Fecal incontinence in US women: a population-based study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:2071–2076
Goode PS, Burgio KL, Halli AD, Jones RW, Richter HE, Redden DT, Baker PS, Allman RM (2005) Prevalence and correlates of fecal incontinence in community-dwelling older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 53:629–635
Varma M, Brown JS, Creasman JM, Thom DH, Van Den Eeden SK, Beattie MS, Subak LL, Reproductive risks for incontinence study at Kaiser (RRISK) research group (2006) Fecal incontinence in females older than aged 40 years: who is at risk? Dis Colon Rectum 49:841–851
Bharucha AE, Zinsmeister AR, Locke GR, Schleck C, McKeon K, Melton LJ (2006) Symptoms and quality of life in community women with fecal incontinence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:1004–1009
Macmillan AK, Merrie AEH, Marshall RJ, Parry BR (2004) The prevalence of fecal incontinence in community dwelling adults: a systematic review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum 47:1004–1009
Kamm MA (1998) Faecal incontinence. BMJ 316:528–532
Abramov Y, Sand PK, Botros SM, Gandhi S, Miller JJR, Nickolov A, Goldberg RP (2005) Risk factors for female anal incontinence: new insight through the Evanston Northwestern Twin Sisters Study. Obstet Gynecol 106:726–732
Malouf AJ, Norton CS, Engel AF, Nicholls RJ, Kamm MA (2000) Long-term results of overlapping anterior anal-sphincter repair for obstetric trauma. Lancet 355:260–265
Young CJ, Mathur MN, Eyers AA, Solomon MJ (1998) Successful overlapping anal sphincter repair: relationship to patient age, neuropathy, and colostomy formation. Dis Colon Rectum 41:344–349
Halverson AL, Hull TL (2002) Long-term outcome of overlapping anal sphincter repair. Dis Colon Rectum 45:345–348
Bravo Gutierrez A, Madoff RD, Lowry AC, Parker SC, Buie WD, Baxter NN (2004) Long-term results of anterior sphincteroplasty. Dis Colon Rectum 47:727–732
Zorcolo L, Covotta L, Bartolo DC (2005) Outcome of anterior sphincter repair for obstetric injury: comparison of early and late results. Dis Colon Rectum 48:524–531
Maslekar S, Gardiner AB, Duthie GS (2007) Anterior anal sphincter repair for fecal incontinence: good longterm results are possible. J Am Coll Surg 204:40–46
Karoui S, Leroi A, Koning E, Menard J, Michot F, Denis P (2000) Results of sphincteroplasty in 86 patients with anal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum 43:813–820
Brown SR, Washawan H, Nelson RL (2007) Surgery for faecal incontinence in adults. Cocnhrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD001757
Gearhart S, Hull T, Floruta C (2005) Anal manoetric parameters: predictors of outcome following anal sphincter repair? J Gastro Surg 9:115–120
Zutshi M, Salcedo L, Hammel J, Hull T (2010) Anal physiology testing in fecal incontinence: is it of any value? Int J Colorectal Dis 25:277–282
Evans C, Davis K, Kumar D (2006) Overlapping anal sphincter repair and anterior levatorplasty: effect of patient’s age and duration of follow-up. Dis Colon Rectum 21:795–801
Kwon S, Visco AG, Fitzgerald MP, Ye W, Whitehead WE, Pelvic Floor Disorders Network (2005) Validity and reliability of the Modified Manchester Health Questionnaire in assessing patients with fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum 48:323–331
Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D, Lawrence K, Petersen S, Paice C, Stradling J (1997) A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? J Public Health Med 19:179–186
Yalcin I, Viktrup L (2007) Comparison of physician and patient assessments of incontinence severity and improvement. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 18:1291–1295
Srikrishna S, Robinson D, Cardozo L (2010) Validation of the patient global impression of improvement (PGI-I) for urogenital prolapse. Int Urogynecol J 21:523–528
Jelovsek JE, Chen Z, Markland AD, Brubaker L, Dyer KY, Meikle S, Rahn DD, Siddiqui NY, Tuteja A, Barber MD (2010) Minimum important differences for scales assessing symptom severity and quality of life in patients with fecal incontinence. Supplement to Fem Pelv Med Recon Surg S66
Markland AD, Richter HE, Burgio KL, Wheeler TL, Redden DT, Goode PS (2008) Outcomes of combination treatment of fecal incontinence in women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 199:699e1–699e7
Davis KJ, Kumar D, Poloniecki J (2004) Adjuvant biofeedback following anal sphincter repair: a randomized study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20:539–549
Acknowledgments
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) ARRA Administrative Supplement 3K24DK068389-05S1 and 2DK24-DK068389 granted financial support to HER.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Oral presentation of this study was made at the 37th Annual Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons at San Antonio, TX, on April 11–13, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gleason, J.L., Markland, A., Greer, W.J. et al. Anal sphincter repair for fecal incontinence: effect on symptom severity, quality of life, and anal sphincter squeeze pressures. Int Urogynecol J 22, 1587–1592 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-011-1551-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-011-1551-8