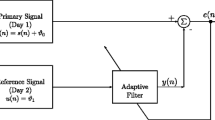
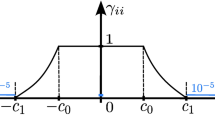
Abstract
Based on a least-squares model for double-difference GPS pseudoranges and carrier-phases, measurement residuals expressed in time series during an observation session are positively correlated between one sidereal day and the preceding days. As a result of the satellite’s period, the phenomenon, which takes place at a user receiving site, is attributed to multipath interference. Examples from a weekly measurement dataset of control baselines are shown, where the known end-point coordinates also serve as a benchmark for assessing positioning accuracy. The system of error equations for mixed-model adjustment is divided into two subsystems. One set of the error equations is related to the real range measurements, while the other involves the pseudo-observation with an empirical sample variance. According to the existing correlation between day-to-day residual estimates, a multipath-mitigating algorithm is proven to improve the accuracy of the GPS height determination by at least 40%. It is also found that the algorithm depends on a variance-component estimator that adaptively scales an error covariance matrix for both the real range and empirical delay measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew DC, Larson KM (2007) Finding the repeat times of the GPS constellation. GPS Solutions 11(1): 71–76. doi:10.1007/s10291-006-0038-4
Ahn YW, Lachapelle G, Skone S, Gutman S, Sahm S (2006) Analysis of GPS RTK performance using external NOAA tropospheric corrections integrated with a multiple reference station approach. GPS Solutions 10(3): 171–186. doi:10.1007/s10291-005-0017-1
Amiri-Simkooei AR, Tiberius CCJM (2007) Assessing receiver noise using GPS short baseline time series. GPS Solutions 11(1): 21–35. doi:10.1007/s10291-006-0026-8
Beran T, Langley RB, Bisnath SB, Serrano L (2007) High-accuracy point positioning with low-cost GPS receivers. Navigation 54(1): 53–63
Bevis M, Businger S, Herring TA, Rocken C, Anthes RA, Ware RH (1992) GPS meteorology: remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the global positioning system. J Geophys Res 97(D14): 15787–15801
Braasch MS (1996) Multipath effects. In: Parkinson BW, Spilker JJ Jr (eds) Global positioning system: theory and applications, progress in astronautics and aeronautics, vol 163. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Washington DC, pp 547–568
Choi K, Bilich A, Larson KM, Axelrad P (2004) Modified sidereal filtering: implications for high-rate GPS positioning. Geophys Res Lett 31: L22608. doi:10.1029/2004GL021621
Crocetto N, Gatti M, Russo P (2000) Simplified formulae for the BIQUE estimation of variance components in disjunctive observation groups. J Geod 74(6): 447–457. doi:10.1007/s001900000109
Dach R, Beutler G, Hugentobler U, Schaer S, Schildknecht T, Springer T, Dudle G, Prost L (2003) Time transfer using GPS carrier phase: error propagation and results. J Geod 77(1–2): 1–14. doi:10.1007/s00190-002-0296-z
Dow JM, Noll RE (2009) The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J Geod 83(3–4): 191–198. doi:10.1007/s00190-008-0300-3
Genrich JF, Bock Y (1992) Rapid resolution of crustal motion at short ranges with the Global Positioning System. J Geophys Res 97(B3): 3261–3269
Georgiadou Y, Kleusberg A (1988) On carrier signal multipath effects in relative GPS positioning. Manus Geod 13(3): 172–179
Goad CC, Yang M (1997) A new approach to precision airborne GPS positioning for photogrammetry. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 63(9): 1067–1077
Hardwick CD, Liu J (1996) Characterization of phase and multipath errors for an aircraft GPS antenna. Navigation 43(1): 41–54
Hassibi A, Boyd S (1998) Integer parameter estimation in linear models with applications to GPS. IEEE Trans Signal Process 46(11): 2938–2952
Hofmann-Wellenhof B, Lichtenegger H, Collins J (1997) Global positioning system theory and practice, 4th edn. Springer, Wien
Horemuž M, Sjöberg LE (2002) Rapid GPS ambiguity resolution for short and long baselines. J Geod 76(6–7): 381–391. doi:10.1007/s00190-002-0259-4
Hu G, Abbey DA, Castleden N, Featherstone WE, Earls C, Ovstedal O, Weihing D (2005) An approach for instantaneous ambiguity resolution for medium- to long-range multiple reference station networks. GPS Solutions 9(1): 1–11. doi:10.1007/s10291-004-0120-8
Klobuchar JA (1996) Ionospheric effects on GPS. In: Parkinson BW, Spilker JJ Jr (eds) Global positioning system: theory and applications, progress in astronautics and aeronautics, vol 163. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Washington DC, pp 485–515
Koch KR (1999) In: (eds) Parameter estimation and hypothesis testing in linear models, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Kuang D, Schutz BE, Watkins MM (1996) On the structure of geometric positioning information in GPS measurements. J Geod 71(1): 35–43. doi:10.1007/s001900050073
Lachapelle G, Cannon ME, Lu G (1992) High-precision GPS navigation with emphasis on carrier-phase ambiguity resolution. Marine Geod 15(4): 253–269
Lau L, Cross P (2007) Development and testing of a new ray-tracing approach to GNSS carrier-phase multipath modelling. J Geod 81(11): 713–732. doi:10.1007/s00190-007-0139-z
Leick A (2004) GPS satellite surveying, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Marshall J, Schenewerk M, Snay R (2001) The effect of the MAPS weather model on GPS-determined ellipsoidal heights. GPS Solutions 5(1): 1–14. doi:10.1007/PL00012871
Milbert D (2005) Influence of pseudorange accuracy on phase ambiguity resolution in various GPS modernization scenarios. Navigation 52(1): 29–38
Mohamed AH, Schwarz KP (1998) A simple and economical algorithm for GPS ambiguity resolution on the fly using a whitening filter. Navigation 45(3): 221–231
Park KD, Nerem RS, Schenewerk MS, Davis JL (2004) Site-specific multipath characteristics of global IGS and CORS GPS sites. J Geod 77(12): 799–803. doi:10.1007/s00190-003-0359-9
Ragheb AE, Clarke PJ, Edwards SJ (2007) GPS sidereal filtering: coordinate- and carrier-phase-level strategies. J Geod 81(5): 325–335. doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0113-1
Reichert AK, Axelrad P (2001) Carrier-phase multipath corrections for GPS-based satellite attitude determination. Navigation 48(2): 77–88
Santerre R, Beutler G (1993) A proposed GPS method with multi-antennae and single receiver. Bull Géod 67(4): 210–223
Stoew B, Nilsson T, Elgered G, Jarlemark POJ (2007) Temporal correlations of atmospheric mapping function errors in GPS estimation. J Geod 81(5): 311–323. doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0114-0
Teunissen PJG, de Jonge PJ, Tiberius CCJM (1997) Performance of the LAMBDA method for fast GPS ambiguity resolution. Navigation 44(3): 373–383
Tiberius C, Kenselaar F (2003) Variance component estimation and precise GPS positioning: case study. J Surv Eng 129(1): 11–18. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9453(2003)129:1(11)
Wang J, Stewart MP, Tsakiri M (1998) Stochastic modeling for static GPS baseline data processing. J Surv Eng 124(4): 171–181. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9453(1998)124:4(171)
Wielgosz P, Kashani I, Grejner-Brzezinska D (2005) Analysis of long-range network RTK during a severe ionospheric storm. J Geod 79(9): 524–531. doi:10.1007/s00190-005-0003-y
Wu J, Yeh TF (2005) Single-epoch weighting adjustment of GPS phase observables. Navigation 52(1): 39–47
Xu PL (2001) Random simulation and GPS decorrelation. J Geod 75(7–8): 408–423. doi:10.1007/s001900100192
Zheng Y, Feng YM (2005) Interpolating residual zenith tropospheric delays for improved regional area differential GPS positioning. Navigation 52(3): 179–187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Hsieh, CH. Statistical modeling for the mitigation of GPS multipath delays from day-to-day range measurements. J Geod 84, 223–232 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0358-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0358-6