Abstract
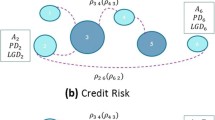
This paper introduces a novel framework to study default dependence and systemic risk in a financial network that evolves over time. We analyse several indicators of risk, and develop a new latent space model to assess the health of key European banks before, during and after the recent financial crises. We propose a new statistical model that permits a latent space visualisation of the financial system. This provides a clear and interpretable model-based summary of the interaction data, and it gives a new perspective on the topology structure of the network. Crucially, the methodology provides a new approach to assess and understand the systemic risk associated with a financial system, and to study how debt may spread between institutions. Our dynamic framework provides an interpretable map that illustrates the default dependencies between institutions, highlighting the possible patterns of contagion and the institutions that may pose systemic threats.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
These are the extreme values observed across all time frames.
Results available upon request.
Results are available upon request.
Results are available upon request.
LogLoss function computes cross-entropy loss between forecasting and true values of out-of-sample. It is available in R package MLmetrics (Yan 2016).
References
Acemoglu D, Ozdaglar A, Tahbaz-Salehi A (2015) Systemic risk and stability in financial networks. Am Econ Rev 105(2):564–608
Acharya V, Drechsler I, Schnabl P (2014) A pyrrhic victory? Bank bailouts and sovereign credit risk. J Finance 69(6):2689–2739
Acharya V, Engle R, Richardson M (2012) Capital shortfall: a new approach to ranking and regulating systemic risks. Am Econ Rev 102(3):59–64
Agosto A, Ahelegbey DF, Giudici P (2020) Tree networks to assess financial contagion. Econ Model 85:349–366
Aiyar S (2012) From financial crisis to great recession: the role of globalized banks. Am Econ Rev 102(3):225–30
Allen F, Babus A, (2009) Networks in finance. The network challenge: strategy, profit, and risk in an interlinked world 367
Andrieu C, De Freitas N, Doucet A, Jordan MI (2003) An introduction to MCMC for machine learning. Mach Learn 50(1–2):5–43
Bartram SM, Brown GW, Hund JE (2007) Estimating systemic risk in the international financial system. J Financ Econ 86(3):835–869
Battiston S, Puliga M, Kaushik R, Tasca P, Caldarelli G (2012) Debtrank: too central to fail? Financial networks, the fed and systemic risk. Sci Rep 2:541
Beirne J, Fratzscher M (2013) The pricing of sovereign risk and contagion during the european sovereign debt crisis. J Int Money Finance 34:60–82
Benoit S, Colliard J-E, Hurlin C, Prignon C (2017) Where the risks lie: a survey on systemic risk. Rev Finance 21(1):109–152
Billio M, Caporin M, Frattarolo L, Pelizzon L (2018) Networks in risk spillovers: a multivariate garch perspective
Billio M, Getmansky M, Lo AW, Pelizzon L (2012) Econometric measures of connectedness and systemic risk in the finance and insurance sectors. J Financ Econ 104(3):535–559
Birch J, Pantelous AA, Soramäki K (2016) Analysis of correlation based networks representing dax 30 stock price returns. Comput Econ 47(4):501–525
Brida JG, Risso WA (2010) Dynamics and structure of the 30 largest north american companies. Comput Econ 35(1):85
Cai J, Eidam F, Saunders A, Steffen S (2018) Syndication, interconnectedness, and systemic risk. J Financ Stabil 34:105–120
Chi KT, Liu J, Lau FC (2010) A network perspective of the stock market. J Empir Finance 17(4):659–667
Cook DO, Spellman LJ (1996) Firm and guarantor risk, risk contagion, and the interfirm spread among insured deposits. J Financ Quant Anal 31(2):265–281
Das SR (2016) Matrix metrics: network-based systemic risk scoring. J Altern Invest 18(4):33–51
De Haas R, Van Horen N (2012) International shock transmission after the Lehman brothers collapse: evidence from syndicated lending. Am Econ Rev 102(3):231–37
Delpini D, Battiston S, Caldarelli G, Riccaboni M (2019) Systemic risk from investment similarities. PLoS ONE 14(5):e0217141
Diebold FX, Yılmaz K (2014) On the network topology of variance decompositions: measuring the connectedness of financial firms. J Econom 182(1):119–134
Durante D, Dunson DB, Vogelstein JT (2017) Nonparametric bayes modeling of populations of networks. J Am Stat Assoc 112(520):1516–1530
Edwards S (2000) Contagion. In: World Economy. Citeseer
Eichengreen B, Mody A, Nedeljkovic M, Sarno L (2012) How the subprime crisis went global: evidence from bank credit default swap spreads. J Int Money Finance 31(5):1299–1318
Elliott M, Golub B, Jackson MO (2014) Financial networks and contagion. Am Econ Rev 104(10):3115–53
Engle R, Jondeau E, Rockinger M (2014) Systemic risk in Europe. Rev. Finance 19(1):145–190
Flavin TJ, Hurley MJ, Rousseau F (2002) Explaining stock market correlation: a gravity model approach. Manchest Schl 70(S1):87–106
Foglia M, Angelini E (2020) From me to you: measuring connectedness between eurozone financial institutions. Res Int Bus Finance 54:101238
Friel N, Rastelli R, Wyse J, Raftery AE (2016) Interlocking directorates in Irish companies using a latent space model for bipartite networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(24):6629–6634
Friel N, Wyse J (2012) Estimating the evidence—a review. Stat Neerland 66(3):288–308
Giner J, Mendoza Aguilar J, Morini-Marrero S (2018) Correlation as probability: applications of Sheppard’s formula to financial assets. Quant Finance 18(5):777–787
Giudici P, Parisi L (2016) Corisk: measuring systemic risk through default probability contagion. DEM Working Papers Series 116, University of Pavia, Department of Economics and Management
Giudici P, Parisi L (2018) Corisk: credit risk contagion with correlation network models. Risks 6(3):95
Giudici P, Sarlin P, Spelta A (2020) The interconnected nature of financial systems: direct and common exposures. J Bank Finance 112:105149
Grassi R, Stefani S, Torriero A (2010) Centrality in organizational networks. Int J Intell Syst 25(3):253–265
Grinis I (2015) Credit risk spillovers, systemic importance and vulnerability in financial networks
Handcock MS, Raftery AE, Tantrum JM (2007) Model-based clustering for social networks. J R Stat Soc Ser A (Stat Soc) 170(2):301–354
Hasse J-B (2020a) Systemic risk: a network approach
Hasse J-B (2020b) SystemicR: monitoring systemic risk. R package version 0.1.0
Hasse J-B, Lajaunie Q (2020) Does the yield curve signal recessions? new evidence from an international panel data analysis
Hasse J-B, Lajaunie Q, Lajaunie MQ (2021) Package EWS
He B-J, Zhao D-X, Zhu J, Darko A, Gou Z-H (2018) Promoting and implementing urban sustainability in china: an integration of sustainable initiatives at different urban scales. Habit Int 82:83–93
Hledik J, Rastelli R (2018) A dynamic network model to measure exposure diversification in the Austrian interbank market. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.01367
Hoff PD, Raftery AE, Handcock MS (2002) Latent space approaches to social network analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 97(460):1090–1098
Hué S, Lucotte Y, Tokpavi S (2019) Measuring network systemic risk contributions: a leave-one-out approach. J Econ Dyn Control 100:86–114
Hyndman R, Koehler AB, Ord JK, Snyder RD (2008) Forecasting with exponential smoothing: the state space approach. Springer, Berlin
Hyndman RJ, Athanasopoulos G, Bergmeir C, Caceres G, Chhay L, O’Hara-Wild M, Petropoulos F, Razbash S, Wang E (2020) Package ‘forecast’. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/forecast/forecast.pdf
Ibragimov R, Jaffee D, Walden J (2011) Diversification disasters. J Financ Econ 99(2):333–348
Jiang B, Rigobon R, Dahleh MA (2020) Contingent linear financial networks. Tech. rep, National Bureau of Economic Research
Jin X, De Simone FN (2020) Monetary policy and systemic risk-taking in the euro area investment fund industry: a structural factor-augmented vector autoregression analysis. J Financ Stab 49:100749
Kenett DY, Huang X, Vodenska I, Havlin S, Stanley HE (2015) Partial correlation analysis: applications for financial markets. Quant Finance 15(4):569–578
Lesnoff M, Lancelot R, Lancelot MR, Suggests M (2010) Package ‘aod’. Maran, N., Crispim, B., Iahnn, S., Araújo, R., Grisolia, A., & Oliveira, K.(2016). Depth and well type related to groundwater microbiological contamination 13(10):1036
Mantegna RN, Stanley HE (1999) Introduction to econophysics: correlations and complexity in finance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Matesanz D, Ortega GJ (2014) Network analysis of exchange data: interdependence drives crisis contagion. Qual Quant 48(4):1835–1851
Møller J, Pettitt AN, Reeves R, Berthelsen KK (2006) An efficient Markov chain Monte Carlo method for distributions with intractable normalising constants. Biometrika 93(2):451–458
Murray I, Ghahramani Z, MacKay D (2012) Mcmc for doubly-intractable distributions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1206.6848
Naceur SB, Candelon B, Lajaunie Q (2019) Taming financial development to reduce crises. Emerg Mark Rev 40:100618
Nolde N, Zhang J (2020) Conditional extremes in asymmetric financial markets. J Bus Econ Stat 38(1):201–213
Pais A, Stork PA (2011) Contagion risk in the Australian banking and property sectors. J Bank Finance 35(3):681–697
Poledna S, Martinez-Jaramillo S, Caccioli F, Thurner S (2021) Quantification of systemic risk from overlapping portfolios in the financial system. J Financ Stab 52:100808
Pourkhanali A, Kim J-M, Tafakori L, Fard FA (2016) Measuring systemic risk using vine-copula. Econ Model 53:63–74
Qi, X., D. R. C. K. F. E. S. A. W. Q. W. Y. T. W., Zhang C (2013) Terrorist networks, network energy and node removal: a new measure of centrality based on Laplacian energy
Raftery AE, Niu X, Hoff PD, Yeung KY (2012) Fast inference for the latent space network model using a case-control approximate likelihood. J Comput Graph Stat 21(4):901–919
Rastelli R (2021) lpm4i repository. https://github.com/riccardorastelli/lpm4i
Rastelli R, Friel N, Raftery AE (2016) Properties of latent variable network models. Netw Sci 4(4):407–432
Rastelli R, Maire F, Friel N (2018) Computationally efficient inference for latent position network models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02274
Sander H, Kleimeier S (2003) Contagion and causality: an empirical investigation of four Asian crisis episodes. J Int Financ Mark Inst Money 13(2):171–186
Scardoni G, Laudanna C (2012) Centralities based analysis of complex networks. New Front Graph Theory 2012:323–348
Schweitzer F, Fagiolo G, Sornette D, Vega-Redondo F, Vespignani A, White DR (2009) Economic networks: the new challenges. Science 325(5939):422–425
Sebestyén T, Iloskics Z (2020) Do economic shocks spread randomly? A topological study of the global contagion network. PLoS ONE 15(9):e0238626
Selover DD (2004) International co-movements and business cycle transmission between Korea and Japan. J Jpn Int Econ 18(1):57–83
Shortreed S, Handcock MS, Hoff P (2006) Positional estimation within a latent space model for networks. Methodology 2(1):24–33
Tobias A, Brunnermeier MK (2016) Covar. Am Econ Rev 106(7):1705
Tumminello M, Lillo F, Mantegna RN (2010) Correlation, hierarchies, and networks in financial markets. J Econ Behav Organ 75(1):40–58
Wagner W (2010) Diversification at financial institutions and systemic crises. J Financ Intermed 19(3):373–386
Wang G-J, Xie C, Stanley HE (2018) Correlation structure and evolution of world stock markets: evidence from Pearson and partial correlation-based networks. Comput Econ 51(3):607–635
Wen F, Yang X, Zhou W-X (2019) Tail dependence networks of global stock markets. Int J Finance Econ 24(1):558–567
Winkler G (2012) Image analysis, random fields and Markov chain Monte Carlo methods: a mathematical introduction, vol 27. Springer, Berlin
Xu G, Gao W (2019) Financial risk contagion in stock markets: causality and measurement aspects. Sustainability 11(5):1402
Yan Y (2016) Mlmetrics: machine learning evaluation metrics. R package version 1(1):1
Zheng Z, Podobnik B, Feng L, Li B (2012) Changes in cross-correlations as an indicator for systemic risk. Sci Rep 2(1):1–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendices
Appendix A: Proof of Proposition 1
Proof
We wish to study the density \(\pi \left( y_i^{(t)} \big | \mathbf{y }_{-(i,t)}, \mathbf{Z }, \mathbf{X } \right) \), up to a proportionality constant that does not depend on \(y_i^{(t)}\):
where
Then:
which is proportional to a Gaussian density with the following mean and variance:
\(\square \)
Appendix B: Summary of default probabilities by bank
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tafakori, L., Pourkhanali, A. & Rastelli, R. Measuring systemic risk and contagion in the European financial network. Empir Econ 63, 345–389 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-021-02135-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-021-02135-y