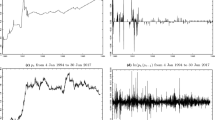
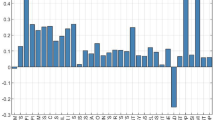
Abstract
In this paper, score-driven time series models are used, in order to provide robust estimates of the seasonal components of Russian rouble (RUB) currency exchange rates for the period of 1999 to 2020. This paper is the first empirical application of score-driven models to the RUB to US dollar (USD) and RUB to Euro (EUR) currency exchange rates in the literature. The model includes score-driven local level, seasonality, and volatility components for a variety of probability distributions: Student’s t distribution, skewed generalized t (Skew-Gen-t) distribution, exponential generalized beta distribution of the second kind (EGB2), normal-inverse Gaussian (NIG) distribution, and Meixner (MXN) distribution. The use of the MXN distribution is new in the literature of score-driven seasonality models. We show that the score-driven models of this paper are robust to changes in the currency exchange rate regimes of the Bank of Russia. We find that the annual seasonality of the RUB is significant, and it is in the range of \(\pm 4\%\). We review the determinants of the RUB seasonality using data on exports, imports, and primary income from the current account of the Russian Federation. The statistical performances of all score-driven models are superior to the statistical performance of the classical multiplicative seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model. Our results may motivate the practical use of score-driven models of the RUB exchange rate seasonality for financing, investment, or policy decisions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data source is reported in the paper, and data are available from the authors upon request.
Code availability
Codes are available from the authors upon request.
References
Alekhin BI (2016) Oil and the Russian ruble: two Links of the same chain. Fin Anal Sci Exper 16:2–19. http://213.226.126.9/fa/2016/fa16/fa1616-2.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Algieri B (2013) Determinants of the real effective exchange rate in the Russian Federation. J Int Trade Econ Dev 22:1013–1037. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638199.2011.631216
Ayala A, Blazsek S (2018a) Score-driven copula models for portfolios of two risky assets. Eur J Financ 24:1861–1884. https://doi.org/10.1080/1351847X.2018.1464488
Ayala A, Blazsek S (2018b) Equity market neutral hedge funds and the stock market: an application of score-driven copula models. Appl Econ 50:4005–4023. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2018.1440062
Ayala A, Blazsek S (2019a) Score-driven models of stochastic seasonality in location and scale: an application case study of the Indian rupee to USD exchange rate. Appl Econ 51:4083–4103. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2019.1588952
Ayala A, Blazsek S (2019b) Score-driven currency exchange rate seasonality as applied to the Guatemalan quetzal/US dollar. SERIEs 10:65–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13209-018-0186-0
Baliño TJT, Horder J, Hoelscher DS (1997) Evolution of monetary policy instruments in Russia. Working paper, December 1997, International Monetary Fund, Monetary and Exchange Affairs Department. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2016/12/30/Evolution-of-Monetary-Policy-Instruments-in-Russia-2452. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Bank of Russia (2009) Guidelines for the single state monetary policy in 2010 and for 2011 and 2012. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation, November 2009.https://www.cbr.ru/Content/Document/File/48485/on_10-eng.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Bank of Russia (2013) The history of the Bank of Russia’s exchange rate policy. Bank for International Settlements, working paper no. 73, October 2013, pp 293–299. https://www.bis.org/publ/bppdf/bispap73u.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Bank of Russia (2017) Statement by Elvira Nabiullina, Bank of Russia Governor, in follow-up to Board of Directors meeting 15 September 2017. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation, 15 September 2017. https://www.cbr.ru/eng/press/event/?id=1340#highlight=seasonality%7Cexchange%7Crate. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Bank of Russia (2020) The history of the Bank of Russia FX policy. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation, 13 March 2020. http://cbr.ru/eng/dkp/about_inflation/history/. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Blasques F, Koopman SJ, Lucas A (2015) Information-theoretic optimality of observation-driven time series models for continuous responses. Biometrika 102:325–343. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/asu076
Blasques F, Koopman SJ, Lucas A (2017) Maximum likelihood estimation for score-driven models. TI 2014-029/III Tinbergen Institute Discussion Paper. https://papers.tinbergen.nl/14029.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Blasques F, Lucas A, van Vlodrop A (2020) Finite sample optimality of score-driven volatility models: some Monte Carlo evidence. Econom Stat 19:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecosta.2020.03.010
Blazsek S, Escribano A, Licht A (2021) Multivariate Markov-switching score-driven models: an application to the global crude oil market. Stud Nonlinear Dyn Econom. https://doi.org/10.1515/snde-2020-0099
Blazsek S, Haddad M (2020) Estimation and statistical performance of Markov-switching score-driven volatility models: the case of G20 stock markets. Discussion Paper 1/2020, Francisco Marroquín University, School of Business. https://en.ufm.edu/gesg/discussion-papers/. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Blazsek S, Ho H-C, Liu S-P (2018) Score-driven Markov-switching EGARCH models: an application to systematic risk analysis. Appl Econ 50:6047–6060. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2018.1488073
Blazsek S, Licht A (2020) Dynamic conditional score models: a review of their applications. Appl Econ 52:1181–1199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2019.1659498
Bollerslev T (1986) Generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity. J Econom 31:307–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4076(86)90063-1
Borochkin AA (2017) Volatility and predictability of the Russian ruble exchange rate. Financ Credit 23:274–291. https://doi.org/10.24891/fc.23.5.274
Bozhechkova A, Knobel A (2021) Trunin P (2017) Russia’s Balance of Payments in Q2 2017: the balance moves negative. Monitoring of Russia’s Economic Outlook 14:11–14. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3025009 (Accessed 24 April)
Bozhechkova A (2021) Trunin P (2018) Russia’s Balance of Payments in Q3 2018: non-residents’ investment continued to fall. Monitoring of Russia’s Economic Outlook 18:16–18. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3290530 (Accessed 24 April)
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1970) Time series analysis, forecasting and control. Holden-Day, San Francisco
Brockwell PJ, Davis RA (1996) An introduction to time series and forecasting. Springer, New York
Caivano M, Harvey A (2014) Time-series models with an EGB2 conditional distribution. J Time Ser Anal 35:558–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsa.12081
Caivano M, Harvey A, Luati A (2016) Robust time series models with trend and seasonal components. SERIEs 7:99–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13209-015-0134-1
Cox DR (1981) Statistical analysis of time series: some recent developments (with discussion and reply). Scand J Stat 8: 93–115. https://www.jstor.org/stable/4615819. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Creal D, Koopman SJ, Lucas A (2008) A general framework for observation driven time-varying parameter models. Tinbergen Institute Discussion Paper 2008-108/4. https://papers.tinbergen.nl/08108.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Creal DD, Koopman SJ, Lucas A (2011) A dynamic multivariate heavy-tailed model for time-varying volatilities and correlations. J Bus Econ Stat 29:552–563. https://doi.org/10.1198/jbes.2011.10070
Davidson R, MacKinnon JG (2004) Econometric theory and methods, international edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Dickey DA, Fuller WA (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J Am Stat Assoc 74:427–431. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1979.10482531
Dreyer I, Popescu N (2014) Do sanctions against Russia work? European Union Institute for Security Studies (EUISS). http://www.jstor.com/stable/resrep06799. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Engle RF (1982) Autoregressive conditional heteroscedasticity with estimates of the variance of United Kingdom inflation. Econometrica 50:987–1007. https://doi.org/10.2307/1912773
Geweke J, Porter-Hudak S (1983) The estimation and application of long memory time series models. J Time Ser Anal 4:221–238. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9892.1983.tb00371.x
Gusev MS, Shirov AA (2009) Foreign trade forecast in the system of midterm forecasting of the Russian economy. Stud Russ Econ Dev 20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1075700709010018
Harvey AC (2013) Dynamic models for volatility and heavy tails. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Harvey AC, Chakravarty T (2008) Beta-t-(E)GARCH. Cambridge working papers in Economics 0840, Faculty of Economics, University of Cambridge, Cambridge. http://www.econ.cam.ac.uk/research-files/repec/cam/pdf/cwpe0840.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Harvey A, Lange RJ (2017) Volatility modeling with a generalized \(t\) distribution. J Time Ser Anal 38:175–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsa.12224
Harvey AC, Lange RJ (2018) Modeling the interactions between volatility and returns using EGARCH-M. J Time Ser Anal 39:909–919. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsa.12419
Harvey AC, Luati A (2014) Filtering with heavy tails. J Am Stat Assoc 109:1112–1122. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2014.887011
Ivanova N (2007) Estimation of the equilibrium real exchange rate in Russia: trade-balance approach. Centre for Economic and Financial Research at New Economic School, Working Paper No 102. https://www.nes.ru/files/Preprints-resh/WP102.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Kutu AA, Ngalawa H (2016) Exchange rate volatility and global shocks in Russia: an application of GARCH and APARCH models. Invest Man Financ Innov 13:203–211. https://doi.org/10.21511/imfi.13(4-1).2016.06
Lucas A, Opschoor A (2019) Fractional integration and fat tails for realized covariance kernels and returns. J Financ Econom 17:66–90. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjfinec/nby029
Menash L, Obi P, Bokpin G (2017) Cointegration test of oil price and US dollar exchange rates for some oil dependent economies. Res Int Bus Financ 42:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ribaf.2017.07.141
Mironov V (2015) Russian devaluation in 2014–2015: falling into the abyss or a window of opportunity? Russ J Econ 1:217–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ruje.2015.12.005
Nelson DB (1991) Conditional heteroskedasticity in asset returns: a new approach. Econometrica 59:347–370. https://doi.org/10.2307/2938260
Rautava J (2004) The role of oil prices and the real exchange rate in Russia’s economy—a cointegration approach. J Comp Econ 32:315–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jce.2004.02.006
Robinson PM (1995) Gaussian semiparametric estimation of long range dependence. Ann Stat 23:1630–1661. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176324317
Rodionov DG, Pshenichnikov VV, Zherebov ED (2015) Currency crisis in Russia on the spun of 2014 and 2015: causes and consequences. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 207:850–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.10.176
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 52:591–611. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/52.3-4.591
Sosounov K, Ushakov N (2009) Determination of the real exchange rate of Rouble and assessment of long-run policy of real exchange rate targeting. J New Econ Assoc 3-4:97–121. http://www.econorus.org/repec/journl/2009-3-4-97-121r.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Sosunov K, Zamulin O (2006) Can oil prices explain the real appreciation of the Russian ruble in 1998-2005? Working Papers w0083, Center for Economic and Financial Research (CEFIR). https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=931905. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Tabata S (2011) Growth in the international reserves of Russia, China, and India: a comparison of underlying mechanisms. Eurasian Geog Econ 52:409–427. https://doi.org/10.2747/1539-7216.52.3.409
Turuntseva M, Astafieva E, Bayeva M, Bozhechkova A, Buzaev A, Kiblitskaya T, Ponomarev Y, Skrobotov A (2018) Model calculations of short-term forecast of Russian economic time series (revised). Gaidar Inst Econ Policy 09/2018. https://www.iep.ru/files/RePEc/gai/mcfren/mcfren-2019-12-1077.pdf. Accessed 24 Apr 2021
Tyll L, Pernica K, Arltová M (2018) The impact of economic sanctions on Russian economy and the RUB/USD exchange rate. J Int Stud 11:21–33. https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-8330.2018/11-1/2
Viktorov I, Abramov A (2020) The 2014–15 financial crisis in Russia and the foundations of weak monetary power autonomy in the international political economy. New Polit Econ 20:487–510. https://doi.org/10.1080/13563467.2019.1613349
Zerihun M, Breitenbach M, Njindan Iyke B (2020) A comparative analysis of currency volatility among BRICS countries. J Afr Bus 21:78–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/15228916.2019.1587805
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Lorenzo Cristofaro, Matthew Copley, Demian Licht, and Jacob Rasmussen for helpful comments and suggestions. All remaining errors are our own. Funding from the School of Business of Universidad Francisco Marroquín is acknowledged. No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors. Data source is reported, and data are available from the authors upon request. Codes are available from the authors upon request. The authors express their consent for publication.
Funding
Funding from the School of Business of Universidad Francisco Marroquín is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Consent for publication
The authors express their consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayala, A., Blazsek, S. & Licht, A. Score-driven stochastic seasonality of the Russian rouble: an application case study for the period of 1999 to 2020. Empir Econ 62, 2179–2203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-021-02103-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-021-02103-6
Keywords
- Russian rouble
- Current account of Russia
- Currency exchange rate regimes of the Bank of Russia
- Score-driven local level
- seasonality
- and volatility
- Dynamic conditional score
- Generalized autoregressive score