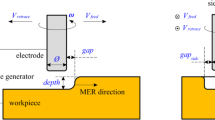
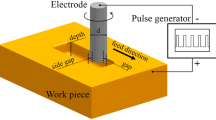
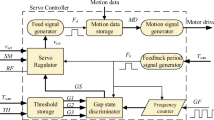
Abstract
Multi-axis electrical discharging machining (EDM) is the most commonly used manufacturing method for shrouded blisks. The discharge points and discharge gap distance are time-varying in a multi-axis EDM process. It is difficult to obtain an optimal servo feedrate. In traditional multi-axis EDM servo control systems, servo sensitivity is usually chosen as a smaller constant to avoid arc discharges. Thus, the servo feedrate is lower than the material removal rate in a machining process. The open circuit rate is high and the machining efficiency is decreased. This paper proposes an adaptive servo sensitivity control algorithm for multi-axis EDM of shrouded blisks. Servo sensitivity is adjusted according to discharge status, so as to decrease the open circuit rate and to improve the machining efficiency. Experiment results show that the proposed adaptive servo sensitivity control algorithm can improve the machining efficiency of shrouded blisks by 28.02% without deteriorating surface integrity.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
This paper uses proprietary software and will not be available.
Abbreviations
- K :
-
Servo adjustment constant
- MRR :
-
Material removal rate
- N de :
-
Number of discharge pulses in 1 s
- N open :
-
Number of open circuit pulses in 1 s
- N short :
-
Number of short circuit pulses in 1 s
- N spark :
-
Number of normal discharge pulses in 1 s
- r open :
-
Open circuit ratio in 1 s
- r open,A :
-
Average open circuit ratio in a machining process
- r open,i :
-
Open circuit discharge ratio in the ith second of a machining process
- r short :
-
Short circuit ratio in 1 s
- r short,A :
-
Average short circuit ratio in a machining process
- r short,i :
-
Short circuit ratio in the ith second of a machining process
- r spark :
-
Normal discharge ratio in 1 s
- r spark,A :
-
Average normal discharge ratio in a machining process
- r spark,i :
-
Normal discharge ratio in the ith second of a machining process
- S :
-
Area of a machining surface
- S F :
-
Servo speed
- S F ’ :
-
Estimated servo feedrate
- S S :
-
Servo sensitivity
- T machine :
-
Total time of a machining process
- U :
-
Gap voltage
- U ref :
-
Servo reference voltage
- θ :
-
Estimated parameter vector of the parameter estimation model
- φ :
-
Observation vector of the parameter estimation model
References
Yuan G, Wang Y (2023) Nonlinear dynamics and vibration localization of shrouded blisk with contact and friction effects. Machines 11(2):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020238
Zhan H, Zhao W, Wang G (2000) Manufacturing turbine blisks. Aircr Eng Aerosp Technol 72(3):247–252
Liu H, Xi X, Chen M, Zhao W, Chen H (2018) Jump motion planning for shrouded blisks multi-axis EDM with short line segments. Procedia CIRP 68:399–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.102
Li L, Wang Y (2020) Discharge gap and relative discharge ratio in dry electrical discharge machining. Procedia CIRP 95:482–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2020.03.145
Kumar D, Sisodiya MS, Bajpai V (2023) A novel servo-stabilized electromagnetic levitation for micro-EDM processing and its feasibility analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part B: J Eng Manuf 237(6–7):862–872. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544054221124473
Fu X, Zhang Q, Gao L et al (2016) A novel micro-EDM-piezoelectric self-adaptive micro-EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85:817–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7939-8
Hayakawa S, Takahashi M, Itoigawa F, Nakamura T (2004) Study on EDM phenomena with in-process measurement of gap distance. J Mater Process Technol 149(1–3):250–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2003.11.057
Xin B, Li S, Yin X, Lu X (2018) Dynamic observer modeling and minimum-variance self-tuning control of EDM interelectrode gap. Appl Sci 8(9):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091443
Kang X, Yang Y, Tao X, Zhao W (2018) Integral shrouded blisk EDM pre-rough machining by using simplified electrode. Procedia CIRP 68:411–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.104
Liu X, Kang X, Zhao W, Liang W (2013) Electrode feeding path searching for 5-axis EDM of integral shrouded blisks. Procedia Cirp 6:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2013.03.041
Fu Y, Gao H, Wang X, Guo D (2017) Machining the integral impeller and blisk of aero-engines: a review of surface finishing and strengthening technologies. Chin J Mech Eng (English Edition) 30(3):528–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10033-017-0123-3
Selvarajan L, Sathiya Narayanan C, Jeyapaul R, Manohar M (2016) Optimization of EDM process parameters in machining Si3N4-TiN conductive ceramic composites to improve form and orientation tolerances. Measurement 92:114–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.05.018
Sivaraj M, Selvakumar N (2015) Experimental analysis of Al-TiC sintered nano composite on EDM process parameters using ANOVA. Mater Manuf Processes 31(6):802–812. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1048471
Avijeet S, Tripathy S, Pallavi SN, Kumar BM (2017) Optimization of EDM process parameters for AlSiC-20% SiC reinforced metal matrix composite with multi response using TOPSIS. Mater Today: Proc 4(2):3043–3052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.02.187
Mukherjee R, Chakraborty S (2012) Selection of EDM process parameters using biogeography-based optimization algorithm. Mater Manuf Processes 27(9):954–962. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2011.610089
Singh B, Kumar J, Kumar S (2014) Influences of process parameters on MRR improvement in simple and powder mixed EDM of AA6061/10%SiC composite. Mater Manuf Process 30(3):303–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.930888
Kansal HK, Singh S, Kumar P (2007) Effect of silicon powder mixed EDM on machining rate of AISI D2 die steel. J Manuf Process 9(1):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1526-6125(07)70104-4
Hyacinth Suganthi X, Natarajan U et al (2013) Prediction of quality responses in micro-EDM process using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68(1–4):339–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-4731-5
Kuwar M, Singh K, Pradeep S, Kamal GRC (2016) Investigation of process parameter of EDM using genetic algorithm (GA) approach for carbon fiber based two phase epoxy composites. Mater Today: Proc 3(10):4102–4108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.11.081
Zhou M, Mu X, He L, Ye Q (2019) Improving EDM performance by adapting gap servo-voltage to machining state. J Manuf Process 37:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.11.013
Liang W, Tong H, Li Y, Li B, Kong Q (2019) Sliding-mode controller and algorithm for improving servo control of discharge gap in precise fast hole EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:2689–2698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04481-9
Jing Q, Li J, Zhang Y et al (2020) A study of influence of servo-control strategy on machining efficiency in micro-EDM. Nanomanuf Metrol 3:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41871-019-00054-2
Mu X, Zhou M, Zhang J, Lu N, Ye Q (2022) Intelligent electrical discharge machining (EDM) molybdenum-titanium-zirconium alloy by an extended adaptive control system. J Manuf Process 77:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.03.003
Zhou S, Yang Y, Zhou M, Sun H (2020) Electrical discharge machining Inconel 718 with adaptively regulating gap servo-voltage. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109:2575–2585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05835-4
Xi X, Chen M, Zhao W (2017) Improving electrical discharging machining efficiency by using a Kalman filter for estimating gap voltages. Precis Eng 47:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.08.003
Liu H, Xi X, Chen M, Zhao W (2018) A look-ahead transition algorithm and jump motion planning in multi-axis EDM for shrouded blisks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 98(1–4):947–958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2286-1
Xi X, Liu H, Chen H, Ye L, Zhao W (2019) Kinematics for a six-axis EDM machine by screw theory and its application in feedrate planning in EDM for shrouded blisks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:1457–1467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04311-y
Chen H, Xi X, Zhao W, Chen M (2017) Feedrate planning for synchronized movements involving rotary axes in multi-axis EDM for shrouded blisks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90(9–12):2645–2654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9575-3
Xi X, Chen H, Liu H, Chen M, Zhao W (2019) Extended unit arc length increment interpolation for generalized NURBS curves in multi-axis EDM. Precis Eng 59:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2019.05.014
Xi X, Liu H, Chen M, Zhao W (2021) Velocity planning in multi-axis EDM based on a coder-player architecture. J Manuf Syst 59:299–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.01.010
Li Z, Chu H, Xi X, Xia W, Sun Y, Zhao W (2021) Improving reciprocating traveling WEDM performance by a new adaptive servo feedrate control system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114:1409–1425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06961-3
Åström K, Wittenmark B (1989) Adaptive control, reading, MA, USA: Addison-Wesley
Funding
This research is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52075333).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y-XS: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, writing — original draft and editing. X-CX: funding acquisition, supervision, writing — review and editing. W-SZ: supervision, writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, YX., Xi, XC. & Zhao, WS. Adaptive servo sensitivity control algorithm for EDM of shrouded blisks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 130, 837–849 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12763-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12763-6