Abstract
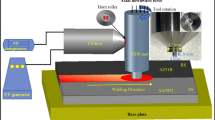
A novel method, friction stir spot welding using a consumable sheet (FSSW-C), is introduced here with the aim of joining dissimilar sheets. In this process, faying surfaces of the base materials are kept at a specific gap, and a consumable sheet is placed on the top of the base materials. When the tool progresses into the consumable sheet, the plasticized consumable material gets extruded into the gap and joining occurs between the base materials. The tool never touches the steel base material overcoming the tool wear problem. In the present work, AA6063-T6 and CRCA/IS-513 are the base sheets, and AA6063-T6 is the consumable sheet. The effect of tool rotational speed on the joint formation, interface characteristics, microhardness, temperature evolution, lap shear strength, bend shear strength, and fracture modes have been analyzed. Microstructural zones are also revealed. The rotational speed of 900 rpm is the best choice for FSSW-C of AA6063-T6 and CRCA/IS-513 sheets, keeping 2-mm/min plunge speed, 2-mm plunge depth, 5-s dwell time, and 1.5-mm gap constant. However, additional case studies reveal a plunge depth of 1.5 mm (at 900 rpm) as a better choice due to further lap shear fracture load improvement.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lan S, Liu X, Ni J (2016) Microstructural evolution during friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloy to advanced high-strength steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(9–12):2183–2193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7531-2
Derazkola HA, Khodabakhshi F (2019) Underwater submerged dissimilar friction-stir welding of AA5083 aluminum alloy and A441 AISI steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102(9–12):4383–4395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03544-1
Ramachandran KK, Murugan N, Shashi Kumar S (2016) Performance analysis of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminium alloy AA5052 and HSLA steel butt joints using response surface method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(9–12):2373–2392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8337-6
Bozzi S, Helbert-Etter AL, Baudin T (2010) Influence of FSSW parameters on fracture mechanisms of 5182 aluminium welds. J Mater Process Technol 210:1429–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.03.022
Luo SY, Liao YS, Tsai YY (1999) Wear characteristics in turning high hardness alloy steel by ceramic and CBN tools. J Mater Process Technol 88:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(98)00376-8
Park SHC, Sato YS, Kokawa H (2009) Boride Formation Induced by pcBN Tool Wear in Friction-Stir-Welded Stainless Steels. Metall Mat Trans A 40(3):625–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9709-9
Rai R, De A, Bhadeshia HKDH, DebRoy T (2011) Review: friction stir welding tools. Sci Technol Weld Joining 16(4):325–342. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171811Y.0000000023
Liu HJ, Feng JC, Fujii H, Nogi K (2005) Wear characteristics of a WC–Co tool in friction stir welding of AC4A+30vol%SiCp composite. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(14):1635–1639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.11.026
Liyanage T, Kilbourne J, Gerlich AP, North TH (2009) Joint formation in dissimilar Al alloy/steel and Mg alloy/steel friction stir spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Joining 14(6):500–508. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217109X456960
da Silva AAM, Aldanondo E, Alvarez P (2010) Friction stir spot welding of AA 1050 Al alloy and hot stamped boron steel (22MnB5). Sci Technol Weld Joining 15(8):682–687. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217110X12785889549462
Ghosh M, Kar A, Kumar K, Kailas SV (2012) Structural characterisation of reaction zone for friction stir welded aluminium–stainless steel joint. Mater Technol 27(2):169–172. https://doi.org/10.1179/175355509X12608916825994
Chen CM, Kovacevic R (2004) Joining of Al 6061 alloy to AISI 1018 steel by combined effects of fusion and solid state welding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(11):1205–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.03.011
Lee C-Y, Choi D-H, Yeon Y-M, Jung S-B (2009) Dissimilar friction stir spot welding of low carbon steel and Al–Mg alloy by formation of IMCs. Sci Technol Weld Joining 14(3):216–220. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217109X400439
Bozzi S, Helbert-Etter AL, Baudin T (2010) Intermetallic compounds in Al 6016/IF-steel friction stir spot welds. Mater Sci Eng: A 527:4505–4509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.03.097
Movahedi M, Kokabi HA, Reihani Seyed MS, Cheng JW, Wang JC (2013) Effect of annealing treatment on joint strength of aluminum/steel friction stir lap weld. Mater Des 44:487–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.08.028
Yu M, Zhao H, Zhang Z, Li Z, Song X (2022) Friction surfacing assisted refilled friction stir spot welding of AA6061 alloy and Q235 steel. J Manuf Process 77:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.03.006
Gandra J, Miranda RM, Vilaça P (2012) Performance analysis of friction surfacing. J Mater Process Technol 212(8):1676–1686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.03.013
Paidar M, Bokov D, Mehrez S, Nasution MKM, Ojo OO, Zain Mohd A (2022) The influence of the backing plate materials on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction spot extrusion brazing of AA2024-T3 aluminum alloy and Brass sheets. J Manuf Process 74:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.12.002
Zhang G, Zhang L, Kang C, Zhang J (2016) Development of friction stir spot brazing (FSSB). Mater Des 94:502–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.01.057
Huang Y, Huang T, Wan L (2019) Material flow and mechanical properties of aluminum-to-steel self-riveting friction stir lap joints. J Mater Process Technol 263:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.08.011
Liu S, Zhang H, Guo Y (2022) Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Copper-Steel Dissimilar Friction Stir Weld Fabricated by Presetting an Integrated Aluminum Barrier Layer. J Mater Eng Perform. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07725-0
Zheng Q, Feng X, Shen Y (2016) Dissimilar friction stir welding of 6061 Al to 316 stainless steel using Zn as a filler metal. J Alloy Compd 686:693–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.092
Das Chowdhury I, Sengupta K, Singh DK (2021) Study of mechanical properties of mild steel joint made by electrically assisted friction stir welding using DC and AC. Mater Today: Proc 44:3959–3966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.011
Bang H, Bang H, Jeon G (2012) Gas tungsten arc welding assisted hybrid friction stir welding of dissimilar materials Al6061-T6 aluminum alloy and STS304 stainless steel. Mater Des 37:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.12.018
Chang WS, Rajesh SR, Chun C-K, Kim HJ (2011) Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Laser-Friction Stir Welding between AA6061-T6 Al Alloy and AZ31 Mg Alloy. J Mater Sci Technol 27(3):199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-0302(11)60049-2
Saha R, Biswas P (2022) Current status and development of external energy-assisted friction stir welding processes: a review. Weld World 66:577–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-021-01228-7
Zhao S, Ni J, Wang G (2018) Effects of tool geometry on friction stir welding of AA6061 to TRIP steel. J Mater Process Technol 261:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.06.003
Derazkola HA, Aval HJ, Elyasi M (2015) Analysis of process parameters effects on dissimilar friction stir welding of AA1100 and A441 AISI steel. Sci Technol Weld Joining 20(7):553–562. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171815Y.0000000038
Venukumar S, Yalagi S, Muthukumaran S (2013) Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of conventional and refilled friction stir spot welds in AA 6061–T6 using filler plate. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 23(10):2833–2842. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62804-6
Sierra G, Peyre P, Deschaux Beaume F (2008) Galvanised steel to aluminium joining by laser and GTAW processes. Mater Charact 59(12):1705–1715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2008.03.016
Forcellese A, Simoncini M (2012) Plastic flow behaviour and formability of friction stir welded joints in AZ31 thin sheets obtained using the “pinless” tool configuration. Mater Des (1980-2015) 36:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.11.017
Al Bosta MMS, Ma K-J, Chien H-H (2013) The effect of MAO processing time on surface properties and low temperature infrared emissivity of ceramic coating on aluminium 6061 alloy. Infrared Phys Technol 60:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2013.06.006
de Deus VS, de Castro JA, Corrêa SRR (2020) Prediction of the Emissivity Curve at High Temperatures of Low Carbon Steel. JMSR 9(2):29–40. https://doi.org/10.5539/jmsr.v9n2p59
Su P, Gerlich A, North TH, Bendzsak GJ (2006) Energy utilisation and generation during friction stir spot welding. Sci Technol Weld Joining 11(2):163–169. https://doi.org/10.1179/174329306X84373
Fereiduni E, Movahedi M, Kokabi AH (2015) Aluminum/steel joints made by an alternative friction stir spot welding process. J Mater Process Technol 224:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.04.028
Klobčar D, Tušek J, Smolej A, Simončič S (2015) Parametric study of FSSW of aluminium alloy 5754 using a pinless tool. Weld World 59:269–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-014-0208-x
Bakavos D, Prangnell PB (2009) Effect of reduced or zero pin length and anvil insulation on friction stir spot welding thin gauge 6111 automotive sheet. Sci Technol Weld Joining 14(5):443–456. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217109X427494
Zimmer S, Langlois L, Laye J, Bigot R (2010) Experimental investigation of the influence of the FSW plunge processing parameters on the maximum generated force and torque. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47:201–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2188-3
Piccini JM, Svoboda HG (2017) Tool geometry optimization in friction stir spot welding of Al-steel joints. J Manuf Process 26:142–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.02.004
Pathak N, Bandyopadhyay K, Sarangi M, Panda SK (2013) Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Friction Stir Spot-Welded Aluminum-5754 Sheets. J Mater Eng Perform 22(1):131–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0244-x
Sun Y, Fujii H, Zhu S, Guan S (2019) Flat friction stir spot welding of three 6061–T6 aluminum sheets. J Mater Process Technol 264:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.09.031
Mubiayi MP, Akinlabi ET, Makhatha ME (2018) Current state of friction stir spot welding between aluminium and copper. Mater Today: Proc 5:18633–18640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.208
Ferreira AC, Campanelli LC, Suhuddin UFH (2020) Investigation of internal defects and premature fracture of dissimilar refill friction stir spot welds of AA5754 and AA6061. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106:3523–3531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04819-3
Balamurugan M, Gopi S, Mohan DG (2021) Influence of tool pin profiles on the filler added friction stir spot welded dissimilar aluminium alloy joints. Mater Res Express 8:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ac2771
Liu X, Lan S, Ni J (2014) Analysis of process parameters effects on friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloy to advanced high strength steel. Mater Des 59:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.003
Hussein SA, Tahir ASM, Hadzley AB (2015) Characteristics of aluminum-to-steel joint made by friction stir welding: A review. Mater Today Commun 5:32–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2015.09.004
Ramachandran KK, Murugan N, Shashi Kumar S (2015) Effect of tool axis offset and geometry of tool pin profile on the characteristics of friction stir welded dissimilar joints of aluminum alloy AA5052 and HSLA steel. Mater Sci Eng: A 639:219–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.04.089
Mahto RP, Bhoje R, Pal SK (2016) A study on mechanical properties in friction stir lap welding of AA 6061–T6 and AISI 304. Mater Sci Eng: A 652:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.11.064
Anton Savio Lewise K, Edwin Raja Dhas J (2022) FSSW process parameter optimization for AA2024 and AA7075 alloy. Mater Manuf Processes 37(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2021.1962532
Gopkalo O, Liu X, Long F (2019) Non-isothermal thermal cycle process model for predicting post-weld hardness in friction stir welding of dissimilar age-hardenable aluminum alloys. Mater Sci Eng: A 754:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.03.025
Yazdipour A, Heidarzadeh A (2016) Dissimilar butt friction stir welding of Al 5083–H321 and 316L stainless steel alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(9–12):3105–3112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8705-2
Elyasi M, Aghajani Derazkola H, Hosseinzadeh M (2016) Investigations of tool tilt angle on properties friction stir welding of A441 AISI to AA1100 aluminium. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B: J Eng Manuf 230(7):1234–1241. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405416645986
Gao K, Zhang S, Mondal M, Basak S, Hong S-T, Shim H (2021) Friction Stir Spot Butt Welding of Dissimilar S45C Steel and 6061–T6 Aluminum Alloy. Metals 11(8):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081252
Li W, Li J, Zhang Z (2014) Improving mechanical properties of pinless friction stir spot welded joints by eliminating hook defect. Mater Des (1980-2015) 62:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.05.028
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Central Workshop, Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Central Instruments Facility of IIT Guwahati (IITG), to carry out the experiments and the analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sukanta Das: Writing, original draft; writing, review and editing; conceptualization; investigation; formal analysis; methodology; validation; data curation.
R. Ganesh Narayanan: Writing, review and editing; conceptualization; investigation; methodology; validation; data curation; supervision
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
We declare that the final version of the manuscript entitled “Friction Stir Spot Welding of Aluminum and Steel Sheets Using a Consumable Sheet” is approved. The manuscript is our original contribution. It is not published or under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Narayanan, R.G. Friction stir spot welding of aluminum and steel sheets using a consumable sheet. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 128, 221–241 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11863-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11863-7