Abstract
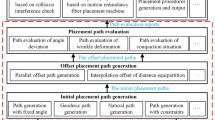
In automated fiber placement (AFP), the abrupt variations of orientations affect layup quality and kinematic performance. This paper proposes a quaternion-based orientation smoothing method constrained by the Domain of Admissible Orientation (DAO) to solve this problem. The DAO is the orientation domain attached to each orientation and defined by the interference avoidance and layup process constraints. All the placement orientations are interpolated into a quaternion curve, and the quaternion curve is smoothed by minimizing its energy function. The energy function is presented in three-dimensional (3D) space, so to facilitate this minimization, the DAO is also transformed into 3D space to constrain the orientation. Then, a spline shortcut generation (SPSG) algorithm is proposed to geometric smooth the curve by generating a spline passing through all DAOs. After that, a Resampling method nonlinearly optimizes the energy function by sampling the curve parameters to redefine the layup orientation within the DAO. Experiments show that the method effectively smooths the orientation trajectory under layup constraints and improves the kinematic performance of APF machines.
Graphical Abstract
































Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
Code availability
The codes used in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cao D, Malakooti S, Kulkarni VN, Ren Y, Liu Y, Nie X, Qian D, Griffith DT, Lu H (2021) Nanoindentation measurement of core-skin interphase viscoelastic properties in a sandwich glass composite. Mech Time-Depend Mater 25:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-020-09448-y
Cao D, Malakooti S, Kulkarni VN, Ren Y, Liu Y, Nie X, Qian D, Griffith DT, Lu H (2021) The effect of resin uptake on the flexural properties of compression molded sandwich composites. Wind Energy 25:71–93
Wang X, Xu T, Andrade MJ, Rampalli I, Cao D, Haque MH, Roy S, Baughman RH, Lu H (2021) The Interfacial Shear Strength of Carbon Nanotube Sheet Modified Carbon Fiber Composites. Challenges Mech Time Dependent Mater 2:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59542-5_4
Chae HG, Newcomb BA, Gulgunje PV, Liu Y, Gupta KK, Kamath MG, Lyons KM, Ghoshal S, Pramanik C, Giannuzzi L, Şahin K, Chasiotis I, Kumar S (2015) High strength and high modulus carbon fibers. Carbon 93:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.05.016
Lukaszewicz DHJA, Ward C, Potter KD (2012) The engineering aspects of automated prepreg layup: History, present and future. Compos B Eng 43:997–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2011.12.003
Brasington A, Sacco C, Halbritter J, Wehbe R, Harik R (2021) Automated fiber placement: A review of history, current technologies, and future paths forward. Compos Part C: Open Access 6:100182. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCOMC.2021.100182
Debout P, Chanal H, Duc E (2011) Tool path smoothing of a redundant machine: Application to Automated Fiber Placement. Comput Aided Des 43:122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2010.09.011
Wu L, Chen M, Xu J, Sun S, Li L (2021) Minimum-acceleration local modification method for planning tool orientations in 5-axis ball-end machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114:2271–2287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06968-w
Castagnetti C, Duc E, Ray P (2008) The Domain of Admissible Orientation concept: A new method for five-axis tool path optimisation. Comput Aided Des 40:938–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2008.07.002
Qu W, Gao J, Ye Y, Yang D, He M, Yang Q, Cheng L, Ke Y (2022) Determination and application of posture adjustable domain under constraints of placement quality. J Reinf Plast Compos. https://doi.org/10.1177/07316844221105657
Kang IG, Park FC (1999) Cubic spline algorithms for orientation interpolation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 46:45–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19990910)46:1%3c45::AID-NME662%3e3.0.CO;2-K
Wisama Khalil ED (2002) Modeling, Identification and Control of Robots, 3rd edn. Taylor & Francis, New York
Ahn J, Chung W, Jung C (2012) Realization of orientation interpolation of 6-axis articulated robot using quaternion. J Cent South Univ 19:3407–3414. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11771-012-1422-6
Murray RM, Li Z, Sastry SS (1994) A Mathematical Introduction to Robotic Manipulation, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Shahbazi M, Kashiri N, Caldwell D, Tsagarakis N (2018) On the orientation planning with constrained angular velocity and acceleration at endpoints. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS). IEEE, pp 7033–7038. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2018.8593657
Yang J, Altintas Y (2013) Generalized kinematics of five-axis serial machines with non-singular tool path generation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 75:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJMACHTOOLS.2013.09.002
Hanotaux G, Peroche B (1993) Interactive control of interpolations for animation and modeling. In: Proceedings of graphics interface '93. CIPS, pp 201–208. https://doi.org/10.20380/GI1993.29
Shoemake K (1985) Animating rotation with quaternion curves. Comput Graph (New York, N.Y.) 19:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1145/325334.325242
Nielson GM (2004) v-quaternion splines for the smooth interpolation of orientations. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 10:224–229. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2004.1260774
Nielson GM (1993) Smooth interpolation of orientations. In Models and techniques in computer animation. Springer, pp 75–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-66911-1_8
Kim MJ, Kim MS, Shin SY (1995) A general construction scheme for unit quaternion curves with simple high order derivatives. In: Proceedings of the 22nd annual conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques. ACM, pp 369–376. https://doi.org/10.1145/218380.218486
Kim MJ, Kim MS, Shin SY (1996) A compact differential formula for the first derivative of a unit quaternion curve. J Visual Comput Animat 7:43–57. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1778(199601)7:1%3C43::AID-VIS136%3E3.0.CO;2-T
Kim MJ, Kim MS, Shin SY (1995) A C2-continuous B-spline quaternion curve interpolating a given sequence of solid orientations. In: Proceedings Computer Animation'95. IEEE, pp 72–81. https://doi.org/10.1109/CA.1995.393545
Xing Y, Xu RZ, Tan JQ, Fan W, Hong L (2015) A class of generalized B-spline quaternion curves. Appl Math Comput 271:288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2015.09.025
Barr AH, Currin B, Gabriel S, Hughes JF (1992) Smooth interpolation of orientations with angular velocity constraints using quaternions. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics 26:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1145/133994.134086
Fangt YC, Hsieh CC, Kim MJ, Chang JJ, Woo TC (1998) Real time motion fairing with unit quaternions. Comput Aided Des 30:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-4485(97)00057-2
Niu X, Wang T (2018) C2-continuous orientation trajectory planning for robot based on spline quaternion curve. Assem Autom 38:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1108/AA-04-2017-050
Xiang Y, Li Q, Jiang X (2021) Dynamic rotational trajectory planning of a cable-driven parallel robot for passing through singular orientations. Mech Mach Theory 158:104223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2020.104223
Jiang X, Barnett E, Gosselin C (2018) Dynamic Point-to-Point Trajectory Planning Beyond the Static Workspace for Six-DOF Cable-Suspended Parallel Robots. IEEE Trans Robot 34:781–793. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2018.2794549
Yuen A, Zhang K, Altintas Y (2013) Smooth trajectory generation for five-axis machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 71:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJMACHTOOLS.2013.04.002
Kallmann M, Aubel A, Abaci T, Thalmann D (2003) Planning Collision-Free Reaching Motions for Interactive Object Manipulation and Grasping. Comput Graph Forum 22:313–322. https://doi.org/10.1145/1401132.1401209
Yang K, Sukkarieh S (2010) An Analytical Continuous-Curvature Path-Smoothing Algorithm. IEEE Trans Robot 26:561–568. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2010.2042990
Douglas DH, Peucker TK (1973) Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature. Cartogr: Int. J Geogr Inf Geovisualization 10:112–122. https://doi.org/10.3138/FM57-6770-U75U-7727
Ho MC, Hwang YR, Hu CH (2003) Five-axis tool orientation smoothing using quaternion interpolation algorithm. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:1259–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00107-X
Chang JW, Wang W, Kim MS (2010) Efficient collision detection using a dual OBB-sphere bounding volume hierarchy. Comput Aided Des 42:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2009.04.010
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No.52105535].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qian Yang: writing original draf, methodology, experiment, writing-review and editing. Weiwei Qu: software, writing-review and editing. Jiaxin Gao: formal analysis, resources. Yanzhe Wang: writing guidance, validation. Xiaowen Song: writing guidance. Yingjie Guo: writing guidance. Yinglin Ke: supervison.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to publication in The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Qu, W., Gao, J. et al. Quaternion-based placement orientation trajectory smoothing method under the Domain of Admissible Orientation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 128, 491–510 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11810-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11810-6