Abstract
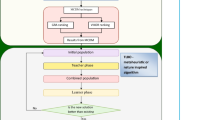
Many present day applications require machining and finishing of complex-shaped and tough to machine materials with precision and accuracy by conventional or non-conventional machining and polishing processes. Ultrasonically aided electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining (UAEMAM) process is a novel non-conventional machining technique which can machine and finish the product for better surface quality. In present research work, the development and performance evaluation of UAEMAM process for machining of SS 316L is reported. The UAEMAM process is optimised using response surface methodology (RSM) based on central composite design (CCD) and grey relational analysis. The main machining variables of UAEMAM such as work piece rotational speed, working gap, concentration of NaNO3, percentage of abrasives by weight and pulse on time were considered to determine percentage improvement in surface finish (PISF) and material removal rate (MRR). The significant machining factors and the best combination levels of machining parameters associated with PISF and MRR were determined. The present work shows complete elimination of oxide layer from work piece surface, subsequently increasing the PISF value to 84.73 which is 2.73% higher than value achieved by previous studies employed. The benefits of ultrasonic aided electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining were also confirmed from the micrograph observations of the surface. Experimental results show that UAEMAM process is effective for machining and polishing components for better surface finish.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Authors wish to declare that all the data and material are available in the manuscript itself.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Choi JP, Jeon BH, Kim BH (2007) Chemical-assisted ultrasonic machining of glass. J Mater Process Technol 191:153–162
Kozak J, Rajurkar KP (2000) Hybrid machining process evaluation and development, Keynote Paper. 2nd International Conference on Machining and Measurements of Sculptured Surfaces, Krakow, Poland 501–536
Kim J, Choi M (1997) Development of the magneto-electrolytic-abrasive polishing system (MEAPS) and finishing characteristics of a Cr-coated roller. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 37(7):997–1006
Venkatesan K, Ramanujam R (2016) Improvement of machinability using laser-aided hybrid machining for Inconel 718 alloy. Mater Manuf Process 31(14):1825–1835. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1117626
Sun X, Fu Y, Hang W (2021) Investigation on the electrochemical assisted magnetic abrasive finishing for a stainless steel of SUS304. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 116:1509–1522
Kant R, Dhami SS (2021) Investigating process parameters of abrasive water jet machine using EN31. Mater Manuf Process 36(14):1597–1603. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2021.1914849
Lin YC, Hung JC, Lee HM, Wang AC (2017) Machining characteristics of a hybrid process of EDM in gas combined with ultrasonic vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:2801–2808
Sihag N, Kala P, Pandey PM (2014) Chemo-ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing: experimental investigations. 5th International & 26th All India Manufacturing Technology, Design and Research Conference (AIMTDR) 823
El-Taweel TA (2008) Modelling and analysis of hybrid electrochemical turning-magnetic abrasive finishing of 6061 Al/Al2O3 composite. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:705–714
Elhami S, Razfar MR, Farahnakian M (2016) Experimental study of surface roughness and tool flank wear during hybrid milling. Mater Manuf Process 31(7):933–940. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1048474
Brar BS, Walia RS, Singh VP (2015) Electrochemical-aided abrasive flow machining (ECA2FM) process: a hybrid machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:329–342
Judal KB, Yadava V (2013) Electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining of AISI304 stainless steel tubes. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 14:37–43
Jain RK, Jain VK, Dixit PM (1999) Modeling of material removal and surface roughness in abrasive flow machining process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 39(12):1903–1923
Mori T, Hirota K, Kawashima Y (2003) Clarification of magnetic abrasive finishing mechanism. J Mater Process Technol 143–144:682–686
Singh DK, Jain VK, Raghuram V (2004) Parametric study of magnetic abrasive finishing process. J Mater Process Technol 149(1–3):22–29
Singh P, Singh L, Singh S (2020) Manufacturing and performance analysis of mechanically alloyed magnetic abrasives for magneto abrasive flow machining. J Manuf Process 50:161–169
Yadav RD, Singh AK, Arora K (2020) Parametric analysis of magnetorheological finishing process for improved performance of gear profile. J Manuf Process 57:254–267
Dabrowski L, Marciniak M, Szewczyk T (2006) Analysis of abrasive flow machining with an electrochemical process aid. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 220(3):397–403
Farwaha HS, Deepak D, Brar GS (2019) Process parameter optimization of ultrasonic assisted electrochemical magnetic abrasive finishing of 316L stainless steel. J Phys Conf Ser 1240:012041
Farwaha HS, Deepak D, Brar GS (2020) Mathematical modeling and process parameters optimization of ultrasonic assisted electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining. J Mech Sci Technol 34:5063–5073
Farwaha HS, Deepak D, Brar GS (2020) Design and performance of ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process set up for machining and finishing of 316L stainless steel. Mater Today Proc 33(3):1626–1631
Kalpakjian S, Schmid SR (2003) Manufacturing engineering and technology, 4th edn. Pearson Education Inc., New Delhi
Sun X, Zou Y (2017) Development of magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process for finishing SUS304 stainless steel plane. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:3373–3384
Tatavarthi UD, Rao VN, Allam AR, Gumpeny RS (2011) Insilico promoter prediction using grey relational analysis. J Theor Appl Inf Technol 24(2):107–112
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge their gratitude to Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering, GNDEC Ludhiana and ME Department, Punjabi University, Patiala, for their valuable assistance in carrying out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Harnam Singh Farwaha and Gurinder Singh Brar. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dharmpal Deepak and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Farwaha, H.S., Deepak, D. & Brar, G.S. Investigation of a novel ultrasonically aided electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining process for SS 316L. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 122, 2343–2359 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10045-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10045-1