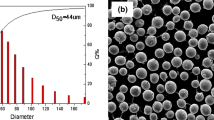
Abstract
Austenitic stainless steel was subjected to multiple laser peening (LP) with high coverages and the gradient structures and corresponding mechanical behaviors were investigated in detail. Body-centered cubic α′ phase and hexagonal-close packed ε phase martensite induced by peening deformation accumulate in multiple LPed 304 austenitic stainless steel surface layer with the increasing coverage. In samples with 240 layers multiple LP, high density martensite in block and twins can be observed. The EBSD results show that the γ → ε → α′ martensitic transformation can be noticed to occur in grain boundaries and twins. Martensitic transformation volume fraction, twin volume fraction and hardness of multiple LPed 304 SS exhibit gradient characteristic from the top surface to substrate. The hardness of the specimens increased with the peening coverage near the top layers, and the influence of laser peening on hardness gradually vanished until 2 mm in depth, the tensile strength increased while the tensile elongation decreased, resulting from a peak power density of 8.19 GW/cm2. Multiple laser peening can be utilized as a solution to modify the mechanical performances by tailoring the gradient structure. Among the investigating range, the optimal multiple LP layers is suggested as 80 where both a relative high strength and ductility can be obtained.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the present paper.
References
Byun TS (2003) On the stress dependence of partial dislocation separation and deformation microstructure in austenitic stainless steels. Acta Mater 51:3063–3071. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(03)00117-4
Chen XH, Lu J, Lu L, Lu K (2005) Tensile properties of a nanocrystalline 316L austenitic stainless steel. Scr Mater 52:1039–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.01.023
Xiong L, You ZS, Lu L (2017) Fracture behavior of an austenitic stainless steel with nanoscale deformation twins. Scr Mater 127:173–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.09.012
Yi HY, Yan FK, Tao NR, Lu K (2016) Work hardening behavior of nanotwinned austenitic grains in a metastable austenitic stainless steel. Scr Mater 114:133–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.12.021
Hedayati A, Najafizadeh A, Kermanpur A, Forouzan F (2010) The effect of cold rolling regime on microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 304L stainless steel. J Mater Process Technol 210:1017–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.02.010
Ueno H, Kakihata K, Kaneko Y, Hashimoto S, Vinogradov A (2011) Enhanced fatigue properties of nanostructured austenitic SUS 316L stainless steel. Acta Mater 59:7060–7069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.07.061
Mine Y, Horita Z, Murakami Y (2009) Effect of hydrogen on martensite formation in austenitic stainless steels in high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 57:2993–3002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.03.006
Ebrahimi M, Amini S, Mahdavi SM (2017) The investigation of laser shock peening effects on corrosion and hardness properties of ANSI 316L stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88:1557–1565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8873-0
Jiao Y, He W, Shen X (2019) Enhanced high cycle fatigue resistance of Ti-17 titanium alloy after multiple laser peening without coating. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104:1333–1343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03993-8
Zhu Y, Fu J, Zheng C, Ji Z (2016) Structural and mechanical modifications induced on Zr-based bulk metallic glass by laser shock peening. Opt Laser Technol 86:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2016.07.003
Hu Y, Yao Z, Hu J (2006) 3-D FEM simulation of laser shock processing. Surf Coat Technol 201:1426–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.02.018
Ye C, Suslov S, Lin D, Cheng GJ (2012) Deformation-induced martensite and nanotwins by cryogenic laser shock peening of AISI 304 stainless steel and the effects on mechanical properties. Philos Mag 92:1369–1389. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786435.2011.645899
Murr LE, Staudhammer KP, Hecker SS (1982) Effects of strain state and strain rate on deformation-induced transformation in 304 stainless steel: Part II Microstructural study. Metall Trans A 13:627–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644428
Hecker SS, Stout MG, Staudhammer KP, Smith JL (1982) Effects of strain state and strain rate on deformation-induced transformation in 304 stainless steel: Part I. Magnetic measurements and mechanical behavior. Metall Trans A 13:619–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644427
Gussev MN, Busby JT, Byun TS, Parish CM (2013) Twinning and martensitic transformations in nickel-enriched 304 austenitic steel during tensile and indentation deformations. Mater Sci Eng A 588:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.08.072
Lu JZ, Luo KY, Zhang YK, Sun GF, Gu YY, Zhou JZ, Ren XD, Zhang XC, Zhang LF, Chen KM, Cui CY, Jiang YF, Feng AX, Zhang L (2010) Grain refinement mechanism of multiple laser shock processing impacts on ANSI 304 stainless steel. Acta Mater 58:5354–5362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.06.010
Zhou L, He W, Luo S, Long C, Wang C, Nie X, He G, Shen X, Li Y (2016) Laser shock peening induced surface nanocrystallization and martensite transformation in austenitic stainless steel. J Alloys Compd 655:66–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.06.268
Mao B, Liao Y, Li B (2018) Gradient twinning microstructure generated by laser shock peening in an AZ31B magnesium alloy. Appl Surf Sci 457:342–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.176
Lu HF, Luo KY, Wu LJ, Cui CY, Lu JZ (2019) Effects of service temperature on tensile properties and microstructural evolution of CP titanium subjected to laser shock peening. J Alloys Compd 770:732–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.161
Lu Y, Sun GF, Wang ZD, Su BY, Zhang YK, Ni ZH (2020) The effects of laser peening on laser additive manufactured 316L steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107:2239–2249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05167-3
Wang H, Huang Y, Zhang W, Ostendorf A (2018) Investigation of multiple laser shock peening on the mechanical property and corrosion resistance of shipbuilding 5083Al alloy under a simulated seawater environment. Appl Opt 57:6300–6308. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.006300
Rai AK, Biswal R, Gupta RK, Singh R, Rai SK, Ranganathan K, Ganesh P, Kaul R, Bindra KS (2019) Study on the effect of multiple laser shock peening on residual stress and microstructural changes in modified 9Cr-1Mo (P91) steel. Surf Coat Technol 358:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.11.027
Zhu Y, Ameyama K, Anderson PM, Beyerlein IJ, Gao H, Kim HS, Lavernia E, Mathaudhu S, Mughrabi H, Ritchie RO, Tsuji N, Zhang X, Wu X (2021) Heterostructured materials: superior properties from hetero-zone interaction. Mater Res Lett 9:1–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2020.1796836
Wu XL, Jiang P, Chen L, Zhang JF, Yuan FP, Zhu YT (2014) Synergetic strengthening by gradient structure. Mater Res Lett 2:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2014.935821
Wang YF, Huang CX, Wang MS, Li YS, Zhu YT (2018) Quantifying the synergetic strengthening in gradient material. Scr Mater 150:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.02.039
Ding J, Li Q, Li J, Xue S, Fan Z, Wang H, Zhang X (2018) Mechanical behavior of structurally gradient nickel alloy. Acta Mater 149:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.02.021
Zhu L, Ruan H, Chen A, Guo X, Lu J (2017) Microstructures-based constitutive analysis for mechanical properties of gradient-nanostructured 304 stainless steels. Acta Mater 128:375–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.02.035
Montross CS, Wei T, Ye L, Clark G, Mai Y-W (2002) Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: a review. Int J Fatigue 24:1021–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-1123(02)00022-1
Kisko A, Misra RDK, Talonen J, Karjalainen LP (2013) The influence of grain size on the strain-induced martensite formation in tensile straining of an austenitic 15Cr–9Mn–Ni–Cu stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 578:408–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.04.107
Sohrabi MJ, Naghizadeh M, Mirzadeh H (2020) Deformation-induced martensite in austenitic stainless steels: a review. Arch Civ Mech Eng 20:124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00130-1
Peyre P, Fabbro R, Merrien P, Lieurade HP (1996) Laser shock processing of aluminium alloys. Application to high cycle fatigue behaviour. Mater Sci Eng A 210:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(95)10084-9
Wu XL, Yang MX, Yuan FP, Chen L, Zhu YT (2016) Combining gradient structure and TRIP effect to produce austenite stainless steel with high strength and ductility. Acta Mater 112:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.04.045
Heinrich H, Karnthaler HP, Waitz T, Kostorz G (1999) Transformation dislocations in Co–Fe. Mater Sci Eng A 272:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00474-8
Guo N, Sun C, Fu M, Han M (2017) Misorientation-dependent twinning induced hardening and texture evolution of TWIP steel sheet in plastic deformation process. Metals 7:348. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7090348
Yang X-S, Sun S, Ruan H-H, Shi S-Q, Zhang T-Y (2017) Shear and shuffling accomplishing polymorphic fcc γ → hcp ε → bct α martensitic phase transformation. Acta Mater 136:347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.07.016
Wang J, Li N, Anderoglu O, Zhang X, Misra A, Huang JY, Hirth JP (2010) Detwinning mechanisms for growth twins in face-centered cubic metals. Acta Mater 58:2262–2270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.12.013
Naghizadeh M, Mirzadeh H (2018) Microstructural evolutions during reversion annealing of cold-rolled AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans A 49:2248–2256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4583-6
Soleimani M, Kalhor A, Mirzadeh H (2020) Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) in advanced steels: A review. Mater Sci Eng A 795:140023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140023
Funding
The authors acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grant Nos. U20A20284 and 52075323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yaofei Sun: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft. Zhibao Hou: Visualization, Analysis, Writing—review & editing. Zhenqiang Yao: Analysis, Writing—review & editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision. Yongxiang Hu: Conceptualization, Methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Hou, Z., Yao, Z. et al. Gradient structure and mechanical behavior induced by multiple laser peening in 304 austenitic stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 120, 3383–3392 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08984-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08984-w