Abstract
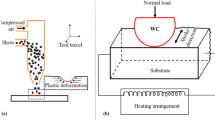
In this paper, the laser shot peening (LSP) technology of H13 steel is studied to improve the friction and wear performance of shield machine hob. And to utilize the LSP experiment and simulation analysis, the influence of LSP parameters on the friction and wear performance of H13 steel after strengthening is studied. The numerical simulation study reveals the variation law of laser parameters on residual stress and stress layer depth. Study on friction and wear characteristics of H13 steel after LSP. The results show that the maximum residual stress of H13 steel is 911 MPa, and the hardness is 650.7 HV, when there are three times of black paint absorption and LSP. Compared with the raw material, the residual stress is increased by 125%, and the hardness is increased by 18%. And its friction coefficients and wear volume were relatively lower than other schemes. The average friction coefficient and wear volume were reduced by 10.8% and 57.2% respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Telasang G, Majumdar JD, Padmanabham G, Manna I (2015) Wear and corrosion behavior of laser surface engineered AISI H13 hot working tool steel. Surf Coat Technol 261:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.11.058
Ren DJ, Shen JS, Chai JC, Zhou A (2018) Analysis of disc cutter failure in shield tunneling using 3D circular cutting theory. Eng Fail Anal 90:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.02.015
Wu Z, Bao H, Xing YQ, Liu L (2021) Tribological characteristics and advanced processing methods of textured surfaces: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 114:1241–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06954-2
Jia ZX, Liu YW, Li JQ, Liu LJ, Li HL (2015) Crack growth behavior at thermal fatigue of H13 tool steel processed by laser surface melting. Int J Fatigue 78:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2015.04.005
Dadoo A, Boutorabi SMA (2020) Correlation between pulsed laser parameters and MC carbide morphology in H13 tool steel/TiC composite coating. Opt Laser Technol 127:106120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106120
Yang HP, Wu XC, Cao GH, Yang Z (2016) Enhanced boronizing kinetics and high temperature wear resistance of H13 steel with boriding treatment assisted by air blast shot peening. Surf Coat Technol 307:506–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.09.029
Liu B, Wang B, Yang XD, Zhao XF, Qin M, Gu JF (2019) Thermal fatigue evaluation of AISI H13 steels surface modified by gas nitriding with pre- and post-shot peening. Appl Surf Sci 483:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.291
Hu YX, Yang RY, Wang DY, Yao ZQ (2018) Geometry distortion and residual stress of alternate double-sided laser peening of thin section component. J Mater Process Technol 251:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.08.033
Wang H, Ning CY, Huang YH, Cao ZY, Chen XX, Zhang WW (2017) Improvement of abrasion resistance in artificial seawater and corrosion resistance in NaCl solution of 7075 aluminum alloy processed by laser shock peening. Opt Lasers Eng 90:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.10.016
Ren NF, Yang HM, Yuan SQ, Wang Y, Tang SX, Zheng LM, Ren XD, Dai FZ (2014) High temperature mechanical properties and surface fatigue behavior improving of steel alloy via laser shock peening. Mater Des 53:452–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.009
Angulo I, Cordovilla F, García-Beltrán A, Smyth NS, Langer K, Fitzpatrick ME, Ocaña JL (2019) The effect of material cyclic deformation properties on residual stress generation by laser shock processing. Int J Mech Sci 156:370–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.03.029
Cho KT, Song K, Oh SH, Lee YK, Lee WB (2013) Surface hardening of shot peened H13 steel by enhanced nitrogen diffusion. Surf Coat Technol 232:912–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.06.123
Lu JZ, Lu HF, Xu X, Yao JH, Cai J, Luo KY (2020) High-performance integrated additive manufacturing with laser shock peening -induced microstructural evolution and improvement in mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V alloy components. Int J Mach Tool Manufact 148:103475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.103475
Prabhakaran S, Kalainathan S, Shukla P, Vasudevan VK (2019) Residual stress, phase, microstructure and mechanical property studies of ultrafine bainitic steel through laser shock peening. Opt Laser Technol 115:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.02.041
Shukla P, Nath S, Wang GJ, Shen XJ, Lawrence J (2017) Surface property modifications of silicon carbide ceramic following laser shock peening. J Eur Ceram Soc 37:3027–3038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.03.005
Fabbro R, Fournier J, Ballard P, Devaux D, Virmont J (1990) Physical study of laser-produced plasma in confined geometry. J Appl Phys 68:775–784. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.346783
Funding
This work is supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (51575234, 51872122), The Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2017M620286), The Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province, China (2018CXGC0809), Major basic research projects of Shandong Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020ZD06), Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Youth Innovation Science and Technology Program (2019KJB021), and Taishan Scholars and Youth Innovation in Science & Technology Support Plan of Shandong Province University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Yifeng Zhang; methodology, Yifeng Zhang and Xuefeng Yang; validation, Yifeng Zhang, Xuefeng Yang and Shouren Wang; formal analysis, Yifeng Zhang; investigation, Yifeng Zhang; data curation, Yifeng Zhang; writing — original draft, Yifeng Zhang; writing — review and editing, Xuefeng Yang and Wanyang Li; visualization, Yifeng Zhang and Wanyang Li; supervision, Qiang Wu, Wangliang Zhao and Yang Gao; project administration, Xuefeng Yang and Kai Wang. All the authors were participants in this study and agreed to the publication of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article meets the ethical standards: (1) there is no potential conflict of interest; (2) studies that do not involve human participants or animals; (3) the submissions have obtained the informed consent of all authors.
Consent to participate
The authors declare their approval to participate in the submitted manuscript.
Consent for publication
All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Wang, S. et al. Research on tribological properties of H13 steel of shield machine hob by laser shot peening. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119, 7121–7131 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08578-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08578-y