Abstract
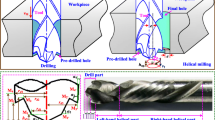
High aspect ratio (HAR) structures are widely utilized in diverse applications, including the defense industries, medical treatment, and aerospace. Studies show that the micro-milling has superiorities such as high efficiency and high flexibility over other methods. Currently, the biggest problem of micro-milling is the influence of burrs on the milling performance, which is an enormous challenge to remove. In the present study, numerical simulations through the finite element method (FEM) and experiments are carried out to optimize cutting parameters of the specimen made of Cr12MoV alloy. Moreover, an improved constitutive model is proposed by considering the size effect of the micro-milling. The proposed model is based on the J-C constitutive model, and it is concluded that the cutting force error is 4.6% through the comparison of experiment and FEM, which further proves the convergence of the improved constitutive model. It is also found that the side burr of HAR slots and the top burr of shallow slots are the biggest factors affecting the surface quality. The depth of cut (DoC) affects the maximum bending angle of the tool, the feed per tooth (FpT) affects the size of the unremoved area, and the spindle speed (SpS) affects the dynamic balance of the micro-mill, through the exploration of the above cutting parameters which can effectively improve the cutting state of the tool and finally achieve the purpose of curbing burr.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun F, Zhang DQ, Cheng L, Zheng P, Liao DM, Zhu B (2019) Microstructure evolution modeling and simulation for dynamic recrystallization of Cr12MoV die steel during hot compression based on real metallographic image. Met Mater Int 25:966–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00249-8
Ren S, Zhang YF, Zhao YL, An ZG, Xue F, Yao JT, Sun ZY, Chang JB (2019) Enhanced surface properties and microstructure evolution of Cr12MoV using ultrasonic surface rolling process combined with deep cryogenic treatment. J Mater Eng Perform 28:1132–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3843-3
Chen N, Li L, Wu JM, Qian J, He N, Reynaerts D (2019) Research on the ploughing force in micro milling of soft-brittle crystals. Int J Mech Sci 155:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.03.004
Zhu LD, Liu CF (2020) Recent progress of chatter prediction, detection and suppression in milling. Mech Syst Signal Process 143:106840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106840
Yang ZC, Zhu L, Zhang GX, Ni CB, Lin B (2020) Review of ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining in advanced materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 156:103594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2020.103594
Wu Y, Chen N, Bian R, He N, Li ZJ, Li L (2020) Investigations on burr formation mechanisms in micro milling of high-aspect-ratio titanium alloy ti-6al-4 v structures. Int J Mech Sci 185:105884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105884
Li ZJ, Chen N, Li L, Wu Y, He N (2020) Influence of the grain size of CVD diamond on the thermal conductivity, material removal depth and surface roughness in nanosecond laser machining. Ceram Int 46:20510–20520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.157
Chen N, Yuan Y, Guo C, Zhang XL, Hao XQ, He N (2020) Design, optimization and manufacturing of polycrystalline diamond micro-end-mill for micro-milling of GH4169. Diam Relat Mater 108:107915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.107915
Shen XH, Shi YL, Zhang JH, Zhang QJ, Tao GC, Bai LJ (2020) Effect of process parameters on micro-textured surface generation in feed direction vibration assisted milling. Int J Mech Sci 167:105267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105267
Medeossi F, Sorgato M, Bruschi S, Savio E (2018) Novel method for burrs quantitative evaluation in micro-milling. Precis Eng 54:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2018.07.007
Niu ZC, Jiao FF, Cheng K (2018) An innovative investigation on chip formation mechanisms in micro-milling using natural diamond and tungsten carbide tools. J Manuf Process 31:382–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.11.023
Brousseau EB, Dimov SS, Pham DT (2010) Some recent advances in multi-material micro- and nano-manufacturing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47:161–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2214-5
Knowles MRH, Rutterford G, Karnakis D, Ferguson A (2007) Micro-machining of metals, ceramics and polymers using nanosecond lasers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-0967-2
Huo DH, Cheng K, Wardle F (2010) Design of a five-axis ultra-precision micro-milling machine—UltraMill. Part 1: holistic design approach, design considerations and specifications. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47:867–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2128-2
Fleischer J, Kotschenreuther J (2007) The manufacturing of micro molds by conventional and energy-assisted processes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0596-1
Vázquez E, Rodríguez CA, Elías-Zúñiga A, Ciurana J (2010) An experimental analysis of process parameters to manufacture metallic micro-channels by micro-milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:945–955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2685-4
Aurich JC, Bohley M, Reichenbach IG, Kirsch B (2017) Surface quality in micro milling: influences of spindle and cutting parameters. CIRP Ann 66:101–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2017.04.029
Venkatarao K (2019) A study on performance characteristics and multi response optimization of process parameters to maximize performance of micro milling for Ti-6Al-4V. J Alloys Compd 781:773–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.105
Zhang XW, Yu TB, Dai YX, Qu S, Zhao J (2020) Energy consumption considering tool wear and optimization of cutting parameters in micro milling process. Int J Mech Sci 178:105628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105628
Hajiahmadi S (2019) Burr size investigation in micro milling of stainless steel 316L. Int J Light Mater Manuf 2:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlmm.2019.07.004
Lu XH, Jia ZY, Wang H, Feng YX, Liang SY (2019) The effect of cutting parameters on micro-hardness and the prediction of Vickers hardness based on a response surface methodology for micro-milling Inconel 718. Measurement 140:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.03.037
Shinge AR, Dabade UA (2018) The effect of process parameters on material removal rate and dimensional variation of channel width in micro-milling of aluminium alloy 6063 T6. Procedia Manuf 20:168–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.02.024
Aslantas K, Ekici E, Çiçek A (2018) Optimization of process parameters for micro milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy using Taguchi-based gray relational analysis. Measurement 128:419–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.06.066
Han JJ, Hao XQ, Li L, Liu LH, Chen N, Zhao GL, He N (2020) Investigation on surface quality and burr generation of high aspect ratio (HAR) micro-milled grooves. J Manuf Process 52:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.041
Kara F, Aslantaş K, Çiçek A (2016) Prediction of cutting temperature in orthogonal machining of AISI 316L using artificial neural network. Appl Soft Comput 38:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.09.034
Kara F, Aslantas K, Çiçek A (2015) ANN and multiple regression method-based modelling of cutting forces in orthogonal machining of AISI 316L stainless steel. Neural Comput Appl 26:237–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1721-y
Özbek O, Saruhan H (2020) The effect of vibration and cutting zone temperature on surface roughness and tool wear in eco-friendly MQL turning of AISI D2. J Mater Res Technol 9:2762–2772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.010
Gong SQ, Meng FT, Sun Y, Su ZP, Jin LY (2020) Experimental study on fabricating ball micro end mill with spiral blades by low speed wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 108:2541–2558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05446-z
Du YC, Song QH, Liu ZQ, Wang B, Wan Y (2019) Size-dependent responses of micro-end mill based on strain gradient elasticity theory. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100:1839–1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2821-0
Li SS, Zou B, Xu KT, Yi SW (2019) Machined channel quality and tool life using cermet micro-mill in micro-milling aluminum alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 101:2205–2216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3120-5
Han JJ, Hao XQ, Li L, He N, Zhao GL, Chen N (2019) Fabrication of large aspect ratio (LAR) PCD micro-end mill with a hybrid method and performance verification. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104:1473–1483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04047-9
Yuan H, Zhao WX, Liang ZQ, Li SD, Wang XB, Zhou TF, Sun XF, Jiang LK (2020) Structural design and fabrication of polycrystalline diamond micro ball-end mill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 108:1899–1911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05436-1
Li SH, Xie YZ, Wu XC (2010) Hardness and toughness investigations of deep cryogenic treated cold work die steel. Cryogenics (Guildf) 50:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cryogenics.2009.12.005
Jia YQ (2007) Handbook of common metal materials. China Standards Press
Johnson GR, Cook WH (1985) Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures. Eng Fract Mech 21:31–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7944(85)90052-9
Yue CX, Huang C, Liu XL, Hao SY, Liu J (2017) 3D FEM simulation of milling force in corner machining process. Chinese J Mech Eng 30:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10033-017-0088-2
Lai XM, Li HT, Li CF, Lin ZQ, Ni J (2008) Modelling and analysis of micro scale milling considering size effect, micro cutter edge radius and minimum chip thickness. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2007.08.011
Xu HB, Tang L, Wu JS, Zhang JG (2000) Effect of spray forming and aging treatment on Cr 12MoV steel. J Shang Hai Jiao Tong Univ 34:1601–1605. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1006-2467.2000.12.001
Wang J, Zhou J, Zhu SS, Zhang JS (2017) Friction properties of groove texture on Cr12MoV surface. J Cent South Univ 24:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3431-y
Gao SL, An LB (2016) Finite element simulation of cutting force using cubic boron nitride cutting tools in dry hard turning conditions. Mach Des Res 32:131-134, 138. 10.13952/j.cnki.jofmdr.2016.0073
Ding X, He N, Li L, Hao XQ (2016) Development of CNC system software for micro-milling machine based on PMAC. Manuf Technol Mach Tool 176–180. 10.19287/j.cnki.1005-2402.2016.08.035
NS TOOL CO., LTD (2020) https://www.ns-tool.com/ja/products/detail/68. Accessed 10 Jun 2020
Ma J, Liu XL, Yue CX, Song SG, Feng HZ (2014) Research on mold steel minimum cutting thickness based on ABAQUS. Mater Sci Forum 800–801:311–315. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.800-801.311
Hashimura M, Hassamontr J, Dornfeld DA (1999) Effect of in-plane exit angle and rake angles on burr height and thickness in face milling operation. J Manuf Sci Eng 121:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2830566
Lekkala R, Bajpai V, Singh RK, Joshi SS (2011) Characterization and modeling of burr formation in micro-end milling. Precis Eng 35:625–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2011.04.007
Schueler GM, Engmann J,Marx T, Haberland R, Aurich JC (2010) Burr formation and surface characteristics in micro-end milling of titanium alloys. In: Aurich J., Dornfeld D. (eds) Burrs - analysis, control and removal. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 129–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00568-8_14
Chen MJ, Ni HB, Wang ZJ, Jiang Y (2012) Research on the modeling of burr formation process in micro-ball end milling operation on Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62:901–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3865-6
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Nos. 51905270 and U1601204), the NSF of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20180435), Defense Industrial Technology Development Program (JCKY2018605C018), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019TQ0149 and 2019M660116). Part of this work was also funded by the Foundation of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Precision and Micro-Manufacturing Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, N., Zhang, X., Wu, J. et al. Suppressing the burr of high aspect ratio structure by optimizing the cutting parameters in the micro-milling process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 111, 985–997 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06088-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06088-x