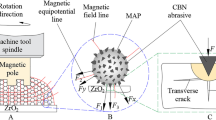
Abstract
Magnetic abrasive powders (MAPs) form a flexible abrasive brush as a polishing tool and deliver a fine finish on the workpiece surface during the magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF) process. However, hard abrasives are easily thrown away from the magnetic field at high rotational speeds. The small holding force affects the finishing performance and efficiency. Therefore, a bonded type of spherical MAPs was developed via an atomization technology to overcome this disadvantage. Cubic boron nitride (CBN) abrasives were densely and uniformly embedded into the surface of MAPs. The low coercivity (Hc) and small remnant magnetization (Mr) for the prepared CBN/Fe-based MAPs suggest that the samples have excellent soft magnetic properties. The atomized MAPs were used to polish Ti-6Al-4 V in the MAF process. The effect of working gap, rotational speed of the magnetic pole, and size of MAPs on the surface roughness and material removal efficiency were investigated. Experimental results demonstrated that a fine 42-nm roughness was produced after 15 min of polishing and an optimum 17.2 mg material removal was obtained in the MAF process. Therefore, spherical CBN/Fe-based MAPs can produce a smooth surface on Ti-6Al-4 V.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Givi M, Fadaei Tehrani A, Mohammadi A (2012) Polishing of the aluminum sheets with magnetic abrasive finishing method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61(9–12):989–998
Jiao AY, Quan HJ, Li ZZ, Zou YH (2015) Study on improving the trajectory to elevate the surface quality of plane magnetic abrasive finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80(9–12):1613–1623
Jain VK (2009) Magnetic field assisted abrasive based micro-nano-finishing. J Mater Process Technol 209:6022–6038
Chang GW, Yan BH, Hsu RT (2002) Study on cylindrical magnetic abrasive finishing using unbonded magnetic abrasives. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:575–583
Wang AC, Lee SJ (2009) Study the characteristics of magnetic finishing with gel abrasive. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49:1063–1069
Kala P, Pandey PM (2015) Comparison of finishing characteristics of two paramagnetic materials using double disc magnetic abrasive finishing. J Manuf Process 17:63–77
Choopani Y, Razfar MR, Saraeian P, Farahnakian M (2015) Experimental investigation of external surface finishing of AISI 440Cstainless steel cylinders using the magnetic abrasive finishing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:1811–1821
Verma GC, Kala P, Pandey PM (2017) Experimental investigations into internal magnetic abrasive finishing of pipes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88:1657–1668
Zhou K, Chen Y, Du ZW, Niu FL (2015) Surface integrity of titanium part by ultrasonic magnetic abrasive finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80:997–1005
Lee YH, Wu KL, Jhou JH, Tsai YH, Yan BH (2013) Two-dimensional vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing of stainless steel SUS304. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(9–12):2723–2733
Lee YH, Wu KL, Bai CT, Liao CY, Yan BH (2015) Planetary motion combined with two-dimensional vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76(9–12):1865–1877
Saito T, Koike K, Yamato H, Kuwana A, Suzuki A, Yamaguchi H, Shinmura T (2005) Development of gas-atomized magnetic tools. Key Eng Mater 291-292:287–290
Zhang GX, Zhao YG, Zhao DB, Yin FS, Zhao ZD (2011) Preparation of white alumina spherical composite magnetic abrasive by gas atomization and rapid solidification. Scr Mater 65:416–419
Gao YW, Zhao YG, Zhang GG (2018) Preparation of Al2O3 magnetic abrasives by gas-solid two-phase double-stage atomization and rapid solidification. Mater Lett 215:300–304
Gao YW, Zhao YG, Zhang GX, Zhang GG, Yin FS (2018) Polishing of paramagnetic materials using atomized magnetic abrasive powder. Mater Manuf Process 34:604–611. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1532087
Shokrollahi H, Janghorban K (2007) Soft magnetic composite materials (SMCs). J Mater Processing Tech 189:1–12
Tavakolia M, Shokrollahi H, Karimi L, Janghorban K (2013) Investigation of structural, microstructural and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed nanostructured (Fe50Co50)100- x Mox(x = 25,35) powders. Powder Technol 234:13–18
Gopalan R, Kündig AA, Ohnuma M, Kishimoto S, Hono K (2005) Coercivity enhancement in melt-spun SmCo5 by Sn addition. Scr Mater 52:761–765
Chandrasekhar SB, Prabhu D, Gopinath M, Chandrasekaran V, Ramakrishna M, Uma V, Gopalan R (2013) High saturation magnetization in Fe–0.4 wt% P alloy processed by a two-step heat treatment. J Magn Magn Mater 345:239–242
Shinmura T, Takazawa K, Hatano E, Matsunaga M, Matsuo T (1990) Study on magnetic abrasive finishing. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 39:325–328
Gao YW, Zhao YG, Zhang GX, Yin FS, Zhang HY (2020) Modeling of material removal in magnetic abrasive finishing process with spherical magnetic abrasive powder. Int J Mech Sci 177:105601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105601
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge all the support received from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51875328).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhang, G. et al. Characteristics of a novel atomized spherical magnetic abrasive powder. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 110, 283–290 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05810-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05810-z