Abstract
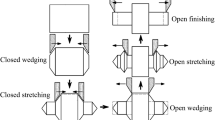
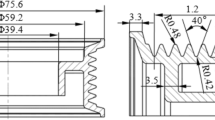
Prefabricating blank ends into special shape is the most effective and commonly used method to eliminate end-face cavities for realizing cross-wedge rolling (CWR) without stub bar. A hot rotary shearing forming method based on metal-plastic forming together with its implementing mechanism for the manufacturing of special-shaped ends blank was proposed in this paper. The hot rotary shearing forming method was firstly investigated by finite element simulation, and the forming process of the special-shaped end with the movement of the shear blade is analyzed. Then the implementing mechanism characterized by the combination of a differential elliptical gear train with conjugate cam was designed. To obtain the structural parameters that can make the shear blade move as designed, kinematics model of the mechanism was deduced by analyzing its working principle. Based on the model, a computer-aided analysis program for the hot rotary shearing mechanism, using MATLAB, is developed. Finally, one application example was conducted. The experimental results revealed that the dimension of the special-shaped end blank obtained by this method was close to the designed dimension. The research result verifies the correctness of the kinematic model and the feasibility of the forming method.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu ZH, Zhang KS, Wang BY, Shu XD (2004) Formed technology and simulation of parts about the cross-wedge rolling. Publ House Metall 1ad, Beijing (in chinese)
Shu XD, Shchukin VY, Kozhevnikova G, Sun BS, Peng WF (2014) The theory and forming technology of cross-wedge rolling. Publ House Science, Beijing (in chinese)
Pater Z (2000) Theoretical and experimental analysis of cross wedge rolling process. Int J Mach Tool Manu 40(1):49–63
Pater Z (2014) Cross-wedge rolling. Comprehensive Mater Process 3(4):211–279
Pater Z, Tomczak J, Bulzak T (2018) New forming possibilities in cross wedge rolling processes. Arch Civil Mech Eng 18(1):149–161
Ma ZH, Yang CP, Hu ZH (2002) Study on the influence factors of the end concave of cross wedge rolling. Forging Stamping Technol 27:29–30 (in chinese)
Wei XH, Shu XD, Peng WF (2012) Analysis of stress and strain based on cross wedge rolling process of block wedge. Hot Work Technol 41(17):81–87 (in chinese)
Pater Z, Tomczak J, Bulzak T (2019) Cavity formation in cross-wedge rolling processes. J Iron Steel Res Int 26(1):1–10
Zeng J, Xu CG, Ren WW, Li P (2017) Study on the deformation mechanism for forming shafts without concavity during the near-net forming cross wedge rolling process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(1–4):127–136
Yang CP, Zheng ZH, Hu ZH (2018) Simulation and experimental study on the concavity of workpiece formed by cross wedge rolling without stub bar. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(1–4):707–717
Han ST, Shu XD, Shu C (2018) Study on near-net forming technology for stepped shaft by cross-wedge rolling based on variable cone angle billets. Materials 11(8):1278–1295
Wei J, Shu XD, Tian DY (2017) Study in shaft end forming quality of closed-open cross wedge rolling shaft using a wedge block. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(1–4):1095–1105
Wei YL, Shu XD, Han ST (2018) Analysis of microstructure evolution during different stages of closed-open cross wedge rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(5–8):1975–1988
Liao W, Zhao Y, Fang MH (2009) Application and parameter optimization of bass cochlia gear in splicing-and-inserting mechanism. Journal of Zhejiang University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition) 26(4):547–551 (in Chinese)
He JL, Wu XT, Li JG (2004) Kinematic characteristics and gear pair design of modified elliptic gear linkage mechanism. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering 40(1):62–65 (in Chinese)
Mundo D, Gatti G, Dooner DB (2009) Optimized five-bar linkages with non-circular gears for exact path generation. Mechanism & Machine Theory 44(4):751–760
Ottaviano E, Mundo D, Danieli GA, Ceccarelli M (2008) Numerical and experimental analysis of non-circular gears and cam-follower systems as function generators. Mech Mach Theory 43(8):996–1008
Dooner DB (2001) Function generation utilizing an eight-link mechanism and optimized non-circular gear elements with application to automotive steering. ARCHIVE Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part C Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science 215(7):847–857
Mundo D (2006) Geometric design of a planetary gear train with non-circular gears[J]. Mechanism & Machine Theory 41(4):456–472
Guo LS, Zhang WJ (2001) Kinematic analysis of a rice transplanting mechanism with eccentric planetary gear trains. Mechanism & Machine Theory 36(11):1175–1188
Bae KY, Yang YS (2007) Design of a non-circular planetary-gear-train system to generate an optimal trajectory in a rice transplanter. J Eng Des 18(4):361–372
Zhang R, Wu XT, Nie G, Li JG (2005) The research and design of high order denatrox ellitogear. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ 07:726–730 (in Chinese)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.51505239), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.LY19E050001), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Provincial Universities of Zhejiang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, R., Zhang, X. et al. Study on manufacturing of special-shaped ends blank for cross wedge rolling without stub bar. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109, 2465–2480 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05795-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05795-9