Abstract
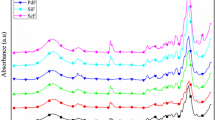
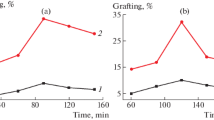
Momordica angustisepala fiber (MAf) is like other natural fibers that usually have weak interfacial bonding when used in the production of polymer composites. Natural fibers are usually treated to improve their properties. This present work investigates surface modification of Momordica angustisepala fiber using temperature-activated amino-functionalized alkali-silane treatment. The fibers were soaked in an 80 ml sodium hydroxide (OH) solution before silane functionalization in 2 ml of aminopropyltriethoxysilane in 100 ml ethanol (OH-APS). The temperature of the APS solution was 75 and 150 °C with soaking time of 3 and 6 h. Optimized properties were obtained at a treatment temperature of 150 °C and a time of 3 h. It was established that the combined effect of activated temperature and OH-APS chemical treatment of MAf is promising and can be used to improve the interfacial bonding during polymer composite production.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atuanya CU, Ebunoha EO, Isaac GO, Aigbodion VS (2012) Characterization of the thermo-mechanical behavior of Momordica angustisepala fiber intended for the manufacturing of polymer composites. Pac J Sci Technol 14:40–47
Ede AN, Olofinnade OM, Ugwu EI, Salau AO (2018) Potentials of Momordica angustisepala fiber in enhancing strengths of normal portland cement concrete. Cogent Eng 5:1431353
Achigan-Dako EG (2012) Momordica angustisepala harms. In M. Brink & E. G. Achigan-Dako (eds.), PROTA 16: Fibres/ Plantes à fibers. [CD-rom] (pp. 334). Wageningen: PROTA
Ezechukwu VC (2020) Development of eco-friendly polymer composites for bolted flange joint in oil and gas applications using sustainable materials, Ph.D. ongoing, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu University, Anambra State Nigeria
Oushabi A, Hassani FO, Abboud Y, Sair S, Tanane O, El Bouari A (2018) Improvement of the interface bonding between date palm fibers and polymeric matrices using alkali-silane treatments. Int J Ind Chem 9:335–343
Pai AR, Jagtap RN (2015) Surface morphology & mechanical properties of some unique natural fiber reinforced polymer composites- a review. J Mater Environ Sci 6(4):902–917
Fathi B, Foruzanmehr M, Elkoun S, Robert M (2019) Novel approach for silane treatment of flax fiber to improve the interfacial adhesion in flax/bio epoxy composites. J Compos Mater 0(0):1–10 The Author(s)
Asim M, Jawaid M, Abdan K, Ishak MR (2016) Effect of alkali and silane treatments on mechanical and fibre-matrix bond strength of kenaf and pineapple leaf fibres. J Bionic Eng 13:426–435
Jia C, Zhang R, Yuan C, Ma Z, Yunzhe D, Liu L, Huang Y (2020) Surface modification of aramid fibers by amino-functionalized silane grafting to improve the interfacial property of aramid fibers reinforced composite. Polym Compos:1–8
Abdelmouleh M, Boufi S, Salah A b, Belgacem MN, Gandini A (2002) Interaction of silane coupling agents with cellulose. Langmuir 18:3203–3208
Aigbodion VS, Edokpia RO, Asuke F, Eke MN (2018) Development of egg shell powder solution as ecofriendly reagent: for chemical treatment of natural fibers for polymer composites production. J Mater Environ Sci 9(2):559–564
Odera RS, Onukwuli OD, Aigbodion VS (2019) Effect of alkali-silane chemical treatment on the tensile properties of raffia palm fiber. Australian J Multi Discip Eng 15(1):91–99
Xie Y, Hill CAS, Xiao Z, Militz H, Mai C (2010) Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: a review. Compos Part A 41:806–819
Zhu J, Brington J, Zhu H, Abhyankar H (2015) Effect of alkali, esterification and silane surface treatments on properties of flax fibres. J Sci Res Rep 4(1):1–11
Hossain SI, Hasan M, Hasan NM, Hassan V Effect of chemical treatment on physical, mechanical and thermal properties of ladies finger natural fiber. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2013, Article ID 824274:6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declared that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezechukwu, V.C., Nwobi-Okoye, C.C. & Atanmo, P.N. Surface modification of Momordica angustisepala fiber using temperature-activated amino-functionalized alkali-silane treatment. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109, 1397–1407 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05697-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05697-w