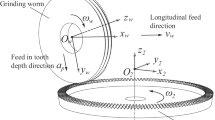
Abstract
For the worm gear grinding machine using flood cooling technology, the coolant absorbs the grinding heat in the machining process and flows on the machine bed, which directly affects the relative position between tool and workpiece. The existing thermal structure analysis and the temperature control research lack in-depth research on thermal problems related with the coolant flowing along the machine bed. In order to reduce the thermal deformation of the machine bed, this paper proposes a novel structure with double-layer coolant channel to improve the thermal characteristics of the machine bed, and the cooling fluid is controlled to maintain an even temperature distribution of machine bed through this structure. In addition, based on a comprehensive analysis of the machine bed heat sources and boundary conditions, a more accurate coolant convection heat transfer coefficient distribution was obtained by using CFX software, and a flow-thermal-structural multi-field sequential coupling finite element thermal characteristic analysis model was established to study the thermal characteristics of the machine bed. The results show that the maximum prediction error of the model is less than 6.77% compared with the experimental data under the same working conditions. The temperature distribution of the proposed machine bed structure is more uniform than that of the original one. The maximum temperature difference is reduced by 1.7 °C, which shows that this method can effectively reduce the relative deflection between the workpiece column and the column. The proposed machine bed structure decreases the thermal deformation’s sensitivity to the temperature of the coolant and has a high adaptability to external temperature fluctuations.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mayr J, Jedrzejewski J, Uhlmann E et al (2012) Thermal issues in machine tools. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61:771–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2012.05.008
Bryan JB (1990) International status of thermal error research. Annals CIRP[J]. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 39(2):645–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63001-7
Ramesh R, Mannan MA, Poo AN (2000) Error compensation in machine tools—a review : Part II: thermal errors[J]. Int J Mach Tool Manu 40(9):1257–1284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(00)00010-9
Maier T, Zaeh MF (2012) Modeling of the Thermomechanical Process Effects on Machine Tool Structures[J]. Proc CIRP 4:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2012.10.014
Zhang J et al (2013) A method of thermal performance modeling and simulation of machine tools[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68:1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-4939-4
Mayr J, Gebhardt M, Massow BB, Weikert S, Wegener K Cutting fluid influence on thermal behavior of 5-axis machine tools[C]. The 6th CIRP International Conference on High Performance Cutting, HPC2014:395-400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.03.085
Shi XJ, Zhu K, Wang WK (2018) A thermal characteristic analytic model considering cutting fluid thermal effect for gear grinding machine under load[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 99(5-8):1755–1976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2562-0
Fan LJ, Shi XJ, Zhu K (2018) Experimental study on the effect of coolant on the thermal characteristics of gear grinding machine under load[J]. Int J Mechatron Manuf Syst 11(1):53–66. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMMS.2018.10012329
Povilionis A, Bargelis A (2010) Structural optimization in product design process. Mechanika 1(81):66–70 URL: http://web.b.ebscohost.com/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=1&sid=99bcc1f1-2ce3-4cce-b326-08d653b6f195%40pdc-v-sessmgr05
Zhang J (2013) Thermal structure design and analysis of a machine tool headstock[J]. Mechanika 19(4):478–485. https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.mech.19.4.5044
Mayr J, Weikert S, Wegener K (2007) Comparing the thermo-mechanical behavior of machine tool frame designs using a FDM-FEM simulation approach[C]. Proceedings of ASPE, 17-20 (URL: http://aspe.pointinspace.com/publications/Annual_2007/PAPERS/1DESIGNA/2208.PDF)
Jedrzjewski J, Kaczmarek J et al (1990) Numerical optimization of thermal behavior of machine tools. [J]. Ann CIRP 39(1):379–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61077-4
Jiang S, Min X (2011) Thermal design of the vertical machining centre headstock by the forced cooling method[C]. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci 226(3):738–751. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406211414642
Yoshioka H, Matsumura S, Hashizume H et al (2006) Minimizing thermal deformation of aerostatic spindle system by temperature control of supply air[J]. JSME Int J Ser C 49(2):606–611 URL: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jsmec/49/2/49_2_606/_pdf
Zhu K, Shi X, Gao J, Li F (2018) Thermal characteristics analysis for a motorized spindle with shaft core cooling based on numerical simulation and experimental research [J]. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ, 04 (URL: http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XAJT201804006.htm)
Fajing L, Gao JM, XiaoJun S et al (2018) Experimental investigation of single loop thermosyphons utilized in motorized spindle shaft cooling[J]. Appl Therm Eng 134:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.141
Fajing L, Jianmin G, Xiaojun S et al (2018) Evaluation of R404a single loop thermosyphon for shaft cooling in motorized spindle[J]. Appl Therm Eng 134C:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.06.072
Fajing L, Jianmin G, Xiaojun S et al (2018) Experimental investigation of an R600a two-phase loop thermosiphon to cool a motorized spindle shaft[J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 97:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.141
Jinqiang N, Vinh N, Yong H, Hartwig KT, Liang SY (2018) Inverse determination of Johnson-cook model constants of ultra-fine-grained titanium based on chip formation model and iterative gradient search[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2508-6
Zuo KT, Chen LP, Zhang YQ, Yang J (2006) Manufacturing- and machining-based topology optimization[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27(5-6):531–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2210-8
Wang JQ, Niu WT, Ma Y, Xue LJ, Cun H, Nie Y, Zhang D (2017) A CAD/CAE-integrated structural design framework for machine tools[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(1-4):545–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9721-y
Shi XJ, Wang WK, Mu YJ et al Thermal characteristics testing and thermal error modeling on a worm gear grinding machine considering cutting fluid thermal effect [J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03650-0
Funding
The financial support of the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (51875446) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Yang, X., Chen, G. et al. Thermal structure design optimization and temperature control for worm gear grinding machine using flood cooling technology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 108, 2419–2431 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05600-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05600-7