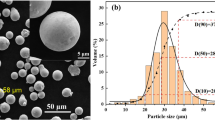
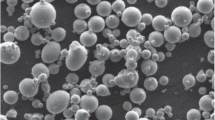
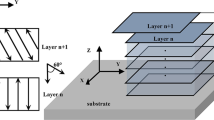
Abstract
In the present study, the properties of selective laser melted IN718 superalloy specimens, prepared by using different processing parameters, were investigated. The scanning strategy (island strategy with and without 30° interlayer rotation and continuous bi-directional scanning with and without 90° interlayer rotation) and scanning speeds of 500, 700, and 1000 mm/s were selected as variables to prepare the superalloy samples. Then, the microstructure and mechanical properties (hardness and compressive strength) were characterized. The results showed, in a given scanning strategy, the density decreases as the scanning speed increases. Also, the island strategy with interlayer rotation during fabrication process leads to a higher level of density (near full density, about 8.20 g/cm3). Interlayer rotation resulted in a more uniform structure by re-melting of deposit layers in different directions during deposition of next layers in both scanning strategies. The higher values of hardness and compressive yield strength were obtained from the samples produced using continuous scanning strategy. Among the investigated samples, the sample produced with continuous scanning strategy with 90° interlayer rotation, 500 mm/s scanning speed has the highest value of hardness, 330 Vickers, and compressive yield strength, 686 MPa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trosch T, Strößner J, Völkl R, Glatzel U (2016) Microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Inconel 718 compared to forging and casting. Mater Lett 164:428–431
Jia Q, Gu D (2014) Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 superalloy parts: densification, microstructure and properties. J Alloys Compd 585:713–721
Valdez M, Kozuch C, Faierson EJ, Jasiuk I (2017) Induced porosity in superalloy 718 through the laser additive manufacturing process: microstructure and mechanical properties. J Alloys Compd 725:757–764
Xia M, Gu D, Yu G, Dai D, Chen H, Shi Q (2017) Porosity evolution and its thermodynamic mechanism of randomly packed powder-bed during selective laser melting of Inconel 718 alloy. Int J Mach Tool Manu 116:96–106
Tucho WM, Cuvillier P, Sjolyst-Kverneland A, Hansen V (2017) Microstructure and hardness studies of Inconel 718 manufactured by selective laser melting before and after solution heat treatment. Mater Sci Eng A 689:220–232
Deng D, Peng RL, Brodin H, Moverare J (2018) Microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 produced by selective laser melting: sample orientation dependence and effects of post heat treatments. Mater Sci Eng A 713:294–306
Caiazzo F, Alfieri V, Corrado G, Argenio P (2017) Laser powder-bed fusion of Inconel 718 to manufacture turbine blades. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93:4023–4031
Cheng B, Shrestha S, Chou K (2016) Stress and deformation evaluations of scanning strategy effect in selective laser melting. Addit Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2016.05.007
Wang Z, Guan K, Gao M, Li X, Chen X, Zeng X (2012) The microstructure and mechanical properties of deposited-IN718 by selective laser melting. J Alloys Compd 513:518–523
Choi JP, Shin GH, Yang S, Yang DY, Lee JS, Brochu M, Yu JH (2017) Densification and microstructural investigation of Inconel 718 parts fabricated by selective laser melting. Powder Technol 30 C:60–66
ASTM B962-15 (2015) Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM E9-09 (2009) Standard Test Methods of Compression Testing of Metallic Materials at Room Temperature, West Conshohocken
Sames WJ, List FA, Pannala S, Dehoff RR, Babu SS (2016) The metallurgy and processing science of metal additive manufacturing. Int Mater Rev 61(5):315–360
Greene GA, Finfrock CC (2001) Oxidation of Inconel 718 in air at high temperatures. Oxid Met 55(5):505–521
Takamichi I, Roderick ILG (1993) The physical properties of liquid metals. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Guan K, Wang Z, Gao M, Li X, Zeng X (2013) Effects of processing parameters on tensile properties of selective laser melted 304 stainless steel. Mater Des 50:581–586
Li R, Shi Y, Liu J, Yao H, Zhang W (2009) Effects of processing parameters on the temperature field of selective laser melting metal powder. Powder Metall Met Ceram 48(3–4):186–195
King WE, Barth HD, Castillo VM, Gallegos GF, Gibbs JW, Hahn DE, Kamath C, Rubenchik AM (2014) Observation of keyhole-mode laser melting in laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing. J Mater Process Technol 214(12):2915–2925
Raghavan S, Zhang B, Wang P, Sun C-N, Nai MLS, Li T, Wei J (2017) Effect of different heat treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties in selective laser melted Inconel 718 alloy. Mater Manuf Process 32(14):1588–1595
Chlebus E, Gruber K, Kuźnicka B, Kurzac J, Kurzynowski T (2015) Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 processed by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A 639(Supplement C):647–655
Strößner J, Terock M, Glatzel U (2015) Mechanical and microstructural investigation of nickel-based superalloy IN718 manufactured by selective laser melting (SLM). Adv Eng Mater 17(8):1099–1105
Mostafa APR, Brailovski V, Jahazi M, Medraj M (2017) Structure, texture and phases in 3D printed IN718 alloy subjected to homogenization and HIP treatments. Metals 7(6):23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirjan, M., Sakiani, H. Effect of scanning strategy and speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted IN718 nickel-based superalloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103, 1769–1780 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03545-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03545-0