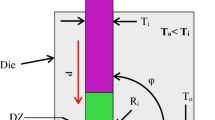
Abstract
The influence of inner fillet radius, as part of the shear deformation zone, on effective strain homogeneity in equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) of AZ91 magnesium alloy was analyzed in this paper. The uniaxial compression and ring upsetting were carried out to obtain the true stress-strain curve of AZ91 billet and friction factor between billet and die, respectively. The flow net experiment and hardness testing experiment were used to verify the simulation results. The results show the inner fillet radius, as the secondary factor (as we all known, the outer corner angle was the most important factor), had an influence on both the quantity and distribution of effective strain. With the increment of inner fillet radius, the effective strain value decreased in both the inner and outer regions. This mainly attributed to the alleviating effect of compression stress of extruded billet in ECAP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demirtas M, Purcek G, Yanar H, Zhang ZJ, Zhang ZF (2016) Effect of different processes on lamellar-free ultrafine grain formation, room temperature superplasticity and fracture mode of Zn–22Al alloy. J Alloys Compd 663:775–783. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.142
Naseri R, Koohkan K, Ebrahimi M, Djavanroodi F, Ahmadian H (2016) Horn design for ultrasonic vibration-aided equal channel angular pressing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-016-9517-0
Minárik P, Král R, Čížek J, Chmelík F (2016) Effect of different c/a ratio on the microstructure and mechanical properties in magnesium alloys processed by ECAP. Acta Mater 107:83–95. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2015.12.050
Mostaed E, Fabrizi A, Dellasega D, Bonollo F, Vedani M (2015) Microstructure, mechanical behavior and low temperature superplasticity of ECAP processed ZM21 Mg alloy. J Alloys Compd 638:267–276. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.03.029
Naseri R, Kadkhodayan M, Shariati M (2016) An experimental investigation of casing effect on mechanical properties of billet in ECAP process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-016-9658-1
Majzoobi G-H, Nemati J, Pipelzadeh MK, Sulaiman S (2015) Characterization of mechanical properties of Al-6063 deformed by ECAE. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 84:663–672. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7709-7
Kim WJ, Namkung JC (2005) Computational analysis of effect of route on strain uniformity in equal channel angular extrusion. Mater Sci Eng A 412:287–297. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2005.08.222
Chalay-Amoly A, Zarei-Hanzaki A, Changizian P, Fatemi-Varzaneh SM, Maghsoudi MH (2013) An investigation into the microstructure/strain pattern relationship in backward extruded AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater Des 47:820–827. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2013.01.006
Chen T, Wang L, Yang J, Lu S (2016) Thixoforming of AM50 magnesium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-016-9495-2
Chung S (2004) The non-uniform behavior during ECAE process by 3-D FVM simulation. Scripta Mater 50:1079–1083. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2003.11.062
Kim WJ, Namgung JC, Kim JK (2005) Analysis of strain uniformity during multi-pressing in equal channel angular extrusion. Scripta Mater 53:293–298. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.04.014
Djavanroodi F, Omranpour B, Ebrahimi M, Sedighi M (2012) Designing of ECAP parameters based on strain distribution uniformity. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International 22:452–460. doi:10.1016/j.pnsc.2012.08.001
Zhang X-H, Luo S-J, Du Z-M (2008) Uniformity and continuity of effective strain in AZ91D processed by multi-pass equal channel angular extrusion. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 18:92–98. doi:10.1016/s1003-6326(08)60017-5
Mahallawy NE, Shehata FA, Hameed MAE, Aal MIAE, Kim HS (2010) 3D FEM simulations for the homogeneity of plastic deformation in Al–Cu alloys during ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A 527:1404–1410. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2009.10.032
Wongsa-Ngam J, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2012) The development of hardness homogeneity in a Cu–Zr alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A 556:526–532. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2012.07.022
Kim WJ, Hong SI, Kim YS, Min SH, Jeong HT, Lee JD (2003) Texture development and its effect on mechanical properties of an AZ61 Mg alloy fabricated by equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater 51:3293–3307. doi:10.1016/s1359-6454(03)00161-7
Kim HK, Kim WJ (2004) Microstructural instability and strength of an AZ31 Mg alloy after severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A 385:300–308. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2004.06.055
Jahadi R, Sedighi M, Jahed H (2014) ECAP effect on the micro-structure and mechanical properties of AM30 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 593:178–184. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2013.11.042
Nagasekhar AV, Tick-Hon Y, Seow HP (2007) Deformation behavior and strain homogeneity in equal channel angular extrusion/pressing. J Mater Process Technol 192-193:449–452. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.04.093
Djavanroodi F, Ebrahimi M (2010) Effect of die channel angle, friction and back pressure in the equal channel angular pressing using 3D finite element simulation. Mater Sci Eng A 527:1230–1235. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2009.09.052
Zhilyaev AP, Oh-ishi K, Raab GI, McNelley TR (2006) Influence of ECAP processing parameters on texture and microstructure of commercially pure aluminum. Mater Sci Eng A 441:245–252. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.08.029
Yoon SC, Quang P, Hong SI, Kim HS (2007) Die design for homogeneous plastic deformation during equal channel angular pressing. J Mater Process Technol 187-188:46–50. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.11.117
Balasundar I, Sudhakara RM, Raghu T (2009) Equal channel angular pressing die to extrude a variety of materials. Mater Des 30:1050–1059. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2008.06.057
Duan ZC, Langdon TG (2011) An experimental evaluation of a special ECAP die containing two equal arcs of curvature. Mater Sci Eng A 528:4173–4179. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.003
Luis Pérez CJ (2004) On the correct selection of the channel die in ECAP processes. Scripta Mater 50:387–393. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2003.10.007
Hu H-J, Zhang D-F, Pan F-S (2010) Die structure optimization of equal channel angular extrusion for AZ31 magnesium alloy based on finite element method. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 20:259–266. doi:10.1016/s1003-6326(09)60132-1
Nagasekhar AV, Tick-Hon Y (2004) Optimal tool angles for equal channel angular extrusion of strain hardening materials by finite element analysis. Comput Mater Sci 30:489–495. doi:10.1016/j.commatsci.2004.02.041
Nagasekhar AV, Tick-Hon Y, Li S, Seow HP (2005) Effect of acute tool-angles on equal channel angular extrusion/pressing. Mater Sci Eng A 410-411:269–272. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2005.08.043
Patil BV, Chakkingal U, Prasanna Kumar TS (2009) Study of channel angle influence on material flow and strain inhomogeneity in equal channel angular pressing using 3D finite element simulation. J Mater Process Technol 209:89–95. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.01.031
Sordi VL, Filho AM, Valio GT, Springer P, Rubert JB, Ferrante M (2015) Equal-channel angular pressing: influence of die design on pressure forces, strain homogeneity, and corner gap formation. J Mater Sci 51:2380–2393. doi:10.1007/s10853-015-9547-2
Dogan E, Vaughan MW, Wang SJ, Karaman I, Proust G (2015) Role of starting texture and deformation modes on low-temperature shear formability and shear localization of Mg–3Al–1Zn alloy. Acta Mater 89:408–422. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2014.12.006
Xu C, Furukawa M, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2005) The evolution of homogeneity and grain refinement during equal-channel angular pressing: a model for grain refinement in ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A 398:66–76. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2005.03.083
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Cheng, Y. Influence of inner fillet radius on effective strain homogeneity in equal channel angular pressing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 4001–4008 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0468-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0468-x