Abstract
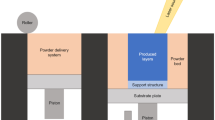
The spot nanofinishing of surface plays an important role for improving the surface quality of miniature mechanical, electronics, and optics components. The nano-level finishing of these miniature components is highly demanded in today’s industry to fulfill the operational and functional requirement. The principal innovation of the present work is generating uniform magnetic field at the end of a magnetizable rotating core tool for providing a uniform surface roughness on a spot finishing of precision components. To fulfill this requirement, a ball nose magnetorheological nanofinishing process based on solid rotating core tool is developed. The existing ball end magnetorheological finishing (BEMRF) process uses a rotating core with central hole for flow of polishing fluid at the tool end surface. Due to central hole inside the rotating core, a non-uniform magnetic flux density has been experienced at the tool end surface which may result in non-uniform surface roughness in spot finishing, i.e., on a fixed location without any X-Y-axis linear feed rates. The magnetostatic finite element analysis clearly revealed the uniform magnetic flux density at the end surface of the solid rotating core tool than existing BEMRF tool core having central hole. The experimentation has been carried out for spot finishing on ferromagnetic workpiece surface in order to study the variation in surface roughness values. The present ball nose magnetorheological finishing process with solid rotating core tool produced uniform average surface roughness values as 20 nm from 290 nm after 90 min of spot finishing on the ferromagnetic workpiece surface. The experimental results confirmed the effectiveness of generating uniform magnetic field at the end of a magnetizable rotating core tool for a spot uniform nanofinishing of precision components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jain VK, Ranjan P, Suri VK, Komanduri R (2010) Chemo-mechanical magneto-rheological finishing (CMMRF) of silicon for microelectronics applications. CIRP Ann–Manuf Technol 59(1):323–328
Bedi TS, Singh AK (2016) Magnetorheological methods for nanofinishing—a review. Particul Sci Technol 34(4):412–422
Kordonski WI, Jacobs SD (1996) Magnetorheological finishing. Int J Mod Phys B 10:2857–2865
Jha S, Jain VK (2004) Design and development of the magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (MRAFF) process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44:1019–1029
Kordonski W, Shorey A (2007) Magnetorheological (MR) jet finishing technology. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 18:1127–1130
Sadiq A, Shunmugam MS (2009) Investigation into magnetorheological abrasive honing (MRAH). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49(7-8):554–560
Singh AK, Jha S, Pandey PM (2011) Design and development of nanofinishing process for 3D surfaces using ball end MR finishing tool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51:142–151
Das M, Jain VK, Ghoshdastidar PS (2012) Nanofinishing of flat workpiece using rotational-magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (R-MRAFF) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(1):405–420
Chen M, Liu H, Su Y, Yu B, Fang Z (2016) Design and fabrication of a novel magnetorheological finishing process for small concave surfaces using a ball-end permanent-magnet polishing head. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83(5):823–834
Shorey AB, Jacobs SD, Kordonski WI, Gans RF (2001) Experiments and observations regarding mechanisms of glass removal in magnetorheological finishing. Appl Opt 40(1):20–33
Lopez-Lopez MT, Kuzhir P, Lacis S, Bossis G, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Duran JDG (2006) Magnetorheology for suspensions of solid particles dispersed in ferro fluids. J Phys Condens Matter 18:s2803–s2813
Carlson JD, Jolly MR (2000) MR fluid, foam and elastomers devices. Mechatron 10(4-5):555–569
Cheng H, Feng Z, Wang Y, Lei S (2005) Magnetorheological finishing of SiC aspheric mirrors. Mater Manuf Process 20(6):917–931
Wang J, Chen W, Han F (2015) Study on the magnetorheological finishing method for the WEDMed pierced die cavity. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76(9):1969–1975
Sidpara A, Jain VK (2012) Experimental investigations into surface roughness and yield stress in magnetorheological fluid based nano-finishing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 13(6):855–860
Singh AK, Jha S, Pandey PM (2012) Nanofinishing of a typical 3D ferromagnetic workpiece using ball end magnetorheological finishing process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 63:21–31
Niranjan MS, Jha S (2015) Experimental investigation into tool aging effect in ball end magnetorheological finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80(9):1895–1902
Saraswathamma K, Jha S, Rao PV (2015) Experimentation investigation into ball end magnetorheological finishing of silicon. Precis Eng 42:218–223
Singh AK, Jha S, Pandey PM (2013) Mechanism of material removal in ball end magnetorheological finishing process. Wear 302:1180–1191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khurana, A., Singh, A.K. & Bedi, T.S. Spot nanofinishing using ball nose magnetorheological solid rotating core tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 1173–1183 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0166-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0166-8