Abstract
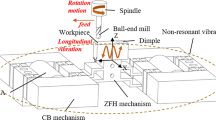
Micro-milling of glass is a technique to fabricate micro-optics with complex geometry using a defined cutting edge. This paper presents the experimental study on the surface generation in vibration-assisted micro-milling of a BK-7 optical glass. A piezoelectric-actuated 2D vibration stage with flexure design is developed to apply vibration assistance on the workpiece in the micro-milling process. The effects of vibration direction, vibration amplitude and frequency on the surface roughness and profile are determined from a series of vibration-assisted micro-milling experiments. It is concluded that the vibration applied in normal direction has a major effect on the improvement of surface quality. The vibration assistance enhances the brittle-ductile transition of glass material and therefore reduces the damage on the machined surface. Higher vibration frequencies improve the surface quality by reducing the waviness on the surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang FZ, Zhang XD, Weckenmann A, Zhang GX, Evans C (2013) Manufacturing and measurement of freeform optics. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 62(2):823–846
Komanduri R, Lucca DA, Tani Y (1997) Technological advances in fine abrasive processes. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 46(2):545–596
Arif M, Rahman M, San WY (2011) Ultraprecision ductile mode machining of glass by micromilling process. J Manuf Process 13(1):50–59
Arif M, Rahman M, San WY, Doshi N (2011) An experimental approach to study the capability of end-milling for microcutting of glass. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:1063–1073
Arif M, Rahman M, San WY (2012) A model to determine the effect of tool diameter on the critical feed rate for ductile-brittle transition in milling process of brittle material. ASME J Manuf Sci Eng 134(5):051012
Arif M, Rahman M, San WY (2011) Analytical model to determine the critical feed per edge for ductile-brittle transition in milling process of brittle materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51(3):170–181
Blackley W, Scattergood R (1991) Ductile-regime machining model for diamond turning of brittle materials. Precis Eng 13(2):95–103
Muhammad A, Mustafizur R, Wong YS (2012) An experimental study on the machining characteristics in ductile-mode milling of BK-7 glass. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60:487–495
Fang FZ, Zhang GX (2004) An experimental study of optical glass machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 23:155–160
Moriwaki T, Shamoto E (1995) Ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 44(1):31–34
Liu D, Cong W, Pei ZJ, Tang Y (2012) A cutting force model for rotary ultrasonic machining of brittle materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 52(1):77–84
Brehl D, Dow T, Garrard K, Sohn A (1999) Micro-structure fabrication using elliptical vibration-assisted machining (EVAM). ASPE Proc 39:511–515
Moriwaki T, Shamoto E, Inoue K (1992) Ultraprecision ductile cutting of glass by applying ultrasonic vibration. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 41(1):141–144
Chen G, Chang Y (2005) Using two-dimensional vibration cutting for micro-milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46:659–666
Ding H, Chen SH, Cheng K (2011) Dynamic surface generation modeling of two-dimensional vibration-assisted micro-end-milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:1075–1079
Ding H, Chen S-J, Cheng K (2010) Two-dimensional vibration-assisted micro end milling: cutting force modelling and machining process dynamics. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 224(12):1775–1783
Hsu C, Huang C, Wu C (2007) Milling of MAR-M247 nickel-based superalloy with high temperature and ultrasonic aiding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(9-10):857–866
Ding H, Ibrahim R, Cheng K, Chen S-J (2010) Experimental study on machinability improvement of hardened tool steel using two dimensional vibration-assisted micro-end-milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(12):1115–1118
Zarchi MMA, Razfar MR, Abdullah A (2012) Investigation of the effect of cutting speed and vibration amplitude on cutting forces in ultrasonic-assisted milling. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 226(7):1185–1191
Zarchi MA, Razfar M, Abdullah A (2013) Influence of ultrasonic vibrations on side milling of AISI 420 stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 66(1-4):83–89
Janghorbanian J, Razfar MR, Zarchi MMA (2013) Effect of cutting speed on tool life in ultrasonic-assisted milling process. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 227(8):1157–1164
Xing D, Zhang J, Shen X, Zhao Y, Wang T (2013) Tribological properties of ultrasonic vibration assisted milling aluminium alloy surfaces. Procedia CIRP 6:540–545
Shen X-H, Zhang J-H, Li H, Wang J-J, Wang X-C (2012) Ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of aluminum alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 63(1-4):41–49
Li K-M, Wang S-L (2013) Effect of tool wear in ultrasonic vibration-assisted micro-milling. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 0954405413510514
Ding H, Chen S, Ibrahim R, Cheng K (2011) Investigation of the size effect on burr formation in two-dimensional vibration-assisted micro end milling. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 225(11):2032–2039
Razfar M, Sarvi P, Zarchi MA (2011) Experimental investigation of the surface roughness in ultrasonic-assisted milling. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 225(9):1615–1620
Shen X-H, Zhang J, Xing DX, Zhao Y (2012) A study of surface roughness variation in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58(5-8):553–561
Yoshino M, Aoki T, Shirakashi T (2001) Scratching test of hard-brittle materials under high hydrostatic pressure. J Manuf Sci Eng 123(2):231–239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, X., Xie, B. Experimental study on surface generation in vibration-assisted micro-milling of glass. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81, 507–512 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7211-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7211-2