Abstract
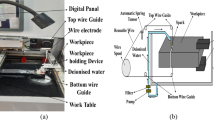
Al-Mg2Si composite is a new group of metal matrix composites (MMCs). Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a nonconventional machining process for machining electrically conductive materials regardless of hardness, strength and temperature resistance, complex shapes, fine surface finish/textures and accurate dimensions. A copper electrode and oil-based dielectric fluid mixed with aluminum powder were used. The polarity of electrode was positive. Response surface methodology (RSM) was used to analyze EDM of this composite material. This research illustrates the effect of input variables (voltage, current, pulse ON time, and duty factor) on material removal rate (MRR), electrode wear ratio (EWR), and microstructure changes. The results show that voltage, current, two-level interaction of voltage and current, two-level interaction of current and pulse ON time, and the second-order effect of voltage are the most significant factors on MRR. Pulses ON time and second-order effect of pulse ON time are the most significant factors affecting EWR. Microstructure analysis of EDM on Al-Mg2Si samples revealed that voltage, current, and pulse ON time have a significant effect on the profile and microstructure of machined surfaced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kung K-Y, Horng J-T, Chiang K-T (2009) Material removal rate and electrode wear ratio study on the powder mixed electrical discharge machining of cobalt-bonded tungsten carbide. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40(1–2):95–104
Liu H, Tarng Y (1997) Monitoring of the electrical discharge machining process by abductive networks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 13(4):264–270
Tang L, Guo Y (2014) Electrical discharge precision machining parameters optimization investigation on S-03 special stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(5–8):1369–1376
Teimouri R, Baseri H (2013) Experimental study of rotary magnetic field-assisted dry EDM with ultrasonic vibration of workpiece. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(5–8):1371–1384
Keskin Y, Halkacı HS, Kizil M (2006) An experimental study for determination of the effects of machining parameters on surface roughness in electrical discharge machining (EDM). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28(11–12):1118–1121
Sidhu SS, Batish A, Kumar S (2013) EDM of metal matrix composite for parameter design using lexicographic goal programming. Mater Manuf Processes 28(4):495–500
Yan BH, Wang CC, Liu W, Huang FY (2000) Machining characteristics of Al2O3/6061Al composite using rotary EDM with a disklike electrode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 16(5):322–333
Assarzadeh S, Ghoreishi M (2013) A dual response surface-desirability approach to process modeling and optimization of Al2O3 powder-mixed electrical discharge machining (PMEDM) parameters. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(9–12):1459–1477
Garg R, Singh K, Sachdeva A, Sharma VS, Ojha K, Singh S (2010) Review of research work in sinking EDM and WEDM on metal matrix composite materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50(5–8):611–624
Jahangiri A, Idris MH, Farahany S (2013) Investigation on tungsten inert gas welding of in situ Al-15 and 20 Mg2Si composites with an Al-Si filler. J Compos Mater 47(10):1283–1291
Zhao Y, Qin Q, Zhao Y, Liang Y, Jiang Q (2004) In situ Mg2Si/Al–Si composite modified by K2TiF6. Mater Lett 58(16):2192–2194
Tjong SC, Ma Z (2000) Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng R: Reports 29(3):49–113
Qin Q, Zhao Y, Xiu K, Zhou W, Liang Y (2005) Microstructure evolution of in situ Mg2Si/Al-Si-Cu composite in semisolid remelting processing. Mater Sci Eng A 407(1):196–200
Seo Y, Kim D, Ramulu M (2006) Electrical discharge machining of functionally graded 15–35 vol.% SiCp/Al composites. Mater Manuf processes 21(5):479–487
Sidhu SS, Batish A, Kumar S (2014) Study of surface properties in particulate reinforced MMC using powder-mixed EDM. Mater Manuf processes 29(1):46–52
Gopalakannan S, Senthilvelan T (2013) EDM of cast Al/SiC metal matrix nanocomposites by applying response surface method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(1–4):485–493
Gopalakannan S, Senthilvelan T (2013) A parametric study of electrical discharge machining process parameters on machining of cast Al/B4C metal matrix nanocomposites. J Eng Manuf 227(7):993–1004
Kumar R, Singh I, Kumar D (2013) Electro discharge drilling of hybrid MMC. Procedia Eng 64:1337–1343
Singh S, Yeh M-F (2012) Optimization of abrasive powder mixed EDM of aluminum matrix composites with multiple responses using gray relational analysis. J Mater Eng Perform 21(4):481–491
Velmurugan C, Subramanian R, Thirugnanam S, Ananadavel B (2011) Experimental investigations on machining characteristics of Al 6061 hybrid metal matrix composites processed by electrical discharge machining. Int J Eng Sci Technol 3(8):87–101
Ahamed AR, Asokan P, Aravindan S (2009) EDM of hybrid Al–SiCp–B4Cp and Al–SiCp–Glassp MMCs. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(5–6):520–528
Aggarwal A, Singh H, Kumar P, Singh M (2008) Optimizing power consumption for CNC turned parts using response surface methodology and Taguchi’s technique—a comparative analysis. J Mater Process Technol 200(1–3):373–384
Egashira K, Matsugasako A, Tsuchiya H, Miyazaki M (2006) Electrical discharge machining with ultralow discharge energy. Precision Eng 30(4):414–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hourmand, M., Farahany, S., Sarhan, A.A.D. et al. Investigating the electrical discharge machining (EDM) parameter effects on Al-Mg2Si metal matrix composite (MMC) for high material removal rate (MRR) and less EWR–RSM approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77, 831–838 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6491-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6491-2