Abstract
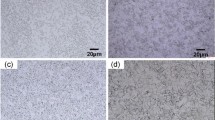
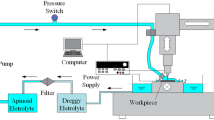
Selecting an appropriate electrolyte is very important for high-efficiency electrochemical machining novel S-03 special stainless steel aerospace component. A series of experiments were conducted with NaCl, NaNO3, and their admixture solutions. This research focused on the relationship between current efficiency and current density. The current density effects on surface roughness, machining velocity, and grain boundary corrosion were analyzed. The results showed that: the current efficiency in NaCl electrolyte was 100 % with different concentrations. Under the conditions of 24 V voltage, 30 °C electrolyte, and 0.8 MPa electrolyte pressure, the 10 % NaCl electrolyte can obtain 3.6 mm/min cathode feed speed; the surface roughness is Ra 0.08 μm; and the material removal rate is 411.4 mm3/min. Comparing forward flow to forward flow with added backpressure, we found that: the surface roughness value decreased sharply at 3.6 mm/min in NaCl electrolyte.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajurkar KP, Zhu D, McGeough JA, Kokaz J, De Silva A (1999) New development in electrochemical machining. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 48(2):567–579
Fan ZJ, Zhao GG, Zhang LJ (2012) Design of anasys-based cathode with complex groove. J China ordnance 8(1):31–34
Klocke F, Zeis M, Klink A (2012) Technological and economical capabilities of manufacturing titaniumand nickel-based alloys via electrochemical machining (ECM). Key Eng Mater 504:1237–1242
Shokrani A, Dhokia V, Newman ST (2012) Environmentally conscious machining of difficult-to-machine materials with regard to cutting fluids. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 57:83–101
Labib AW, Keasberry VJ, Atkinson J, Frost HW (2011) Towards next generation electrochemical machining controllers: a fuzzy logic control approach to ECM. Expert Syst Appl 38(6):7486–7493
Walther B, Schilm J, Michaelis A, Lohrengel M (2007) Electrochemical dissolution of hard metal alloys. Electrochim Acta 52(27):7732–7737
Xu ZY, Xu Q, Zhu D, Gong T (2013) A high efficiency electrochemical machining method of blisk channels. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 62:187–190
Liu CW, Chen YL, Wu WC (2012) Integrated development of a modularized ECM manufacturing system based on the reconfigurable manufacturing system concept. Key Eng Mater 516(18):102–107
Hewidy MS, Ebeid SJ, El-Taweel TA, Youssef AH (2007) Modelling the performance of ECM assisted by low frequency vibrations. J Mater Process Technol 189(1):466–472
Jian LJ (2012) Study on superposed magnetic field ECM of square hole. Adv Mater Res 443:899–904
Fan ZJ, Wang GG, Tang L (2010) Design of device and experiment on magnetic field assisted electrochemical machining. Chinese J Mech Eng 46(1):194–198 (in Chinese)
Coteata M, Schulze HP, Slatineanu L (2011) Drilling of difficult-to-cut steel by electrochemical discharge machining. Mater Manuf Process 26(12):1466–1472
Lee SJ, Chen YH, Liu CP, Fan TJ (2013) Electrochemical mechanical polishing of flexible stainless steel substrate for thin-film solar cells. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:6878–6888
Tsui HP, Hung JC, You JC, Yan BH (2008) Improvement of electrochemical microdrilling accuracy using helical tool. Mater Manuf Process 23(5):499–505
Wang W, Zhu D, Qu NS, Huang SF, Fang XL (2010) Electrochemical drilling with vacuum extraction of electrolyte. J Mater Process Technol 210(2):238–244
Sun Q, Zhang QL, Sun Y (2012) Influence of frequency agility to radar detection performance under ECM. Adv Mater Res 403:549–552
Swain AK, Sundaram MM, Rajurkar KP (2012) Use of coated microtools in advanced manufacturing: an exploratory study in electrochemical machining (ECM) context. J Manuf Process 14(2):150–159
Malapati M, Bhattacharyya B (2011) Investigation into electrochemical micromachining process during micro-channel generation. Mater Manuf Process 26(8):1019–1027
Thanigaivelan R, Arunachalam RM (2010) Experimental study on the influence of tool electrode tip shape on electrochemical micromachining of 304 stainless steel. Mater Manuf Process 25(10):1181–1185
Wu JM (2010) Numerical simulation of three-dimensional cathode flow field of ECM for inner-wall rectangle weight-reduction blind groove. Adv Mater Res 102:321–325
Yang Y, Kang M, Fu XQ (2011) Research on the process of NC-ECM with ball-end cathode based on FEM. Key Eng Mater 458:93–98
Hewidy MS (2005) Controlling of metal removal thickness in ECM process. J Mater Process Technol 160:348–353
Zanjani MY, Kashani HG, Mirahmadi A (2013) Improvement of electrochemical turning for machining complex shapes using a simple gap size sensor and a tubular shape tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 1–7
Lu YH, Liu K, Zhao DB (2011) Experimental investigation on monitoring interelectrode gap of ECM with six-axis force sensor. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 55(5–8):565–572
Dhobe SD, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2011) Analysis of surface characteristics of titanium during ECM. Int J Mach Mach Mater 10(4):293–309
Klocke F, Zeis M, Klink A (2012) Technological and economical capabilities of manufacturing titaniumand nickel-based alloys via electrochemical machining (ECM). Key Eng Mater 504:1237–1242
Burger M, Koll L, Werner EA, Platz A (2012) Electrochemical machining characteristics and resulting surface quality of the nickel-base single-crystalline material LEK94. J Manuf Process 14(1):62–70
Shibuya N, Ito Y, Natsu W (2012) Electrochemical machining of tungsten carbide alloy micro-pin with NaNO3 solution. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13(11):2075–2078
Holstein N, Krauss W, Konys J (2011) Development of novel tungsten processing technologies for electrochemical machining (ECM) of plasma facing components. Fusion Eng Des 86(9–11):1611–1615
Wang MH, Peng W, Yao CY, Zhang QF (2010) Electrochemical machining of the spiral internal turbulator. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49:969–973
Schneider M, Schroth S, Schubert N, Michaelis A (2012) In-situ investigation of the surface-topography during anodic dissolution of copper under near-ECM conditions. Mater Corros 63(2):96–104
Zhu D, Zhu D, Xu ZY (2012) Optimal design of the sheet cathode using W-shaped electrolyte flow mode in ECM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(1–4):147–156
De Silva AKM, Altena HSJ, McGeough JA (2003) Influence of electrolyte concentration on copying accuracy of precision—ECM. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 52(1):165–168
Demyantseva NG, Kuzmin SM, Balmasov AV (2012) Evaluation of shaping accuracy upon electrochemical machining of metals. Surf Eng Appl Electrochem 48(3):230–233
Lohrengel MM, Rosenkranz C (2005) Microelectrochemical surface and product investigations during electrochemical machining (ECM) in NaNO3. Corros Sci 47(3):785–794
Lohrengel MM (2005) Pulsed electrochemical machining of iron in NaNO3: fundamentals and new aspects. Mater Manuf Process 20(1):1–8
Neto JCS, Silva EM, Silva MB (2006) Intervening variables in electrochemical machining. J Mater Process Technol 179:92–96
Brusilovski Z (2008) Adjustment and readjustment of electrochemical machines and control of the process parameters in machining shaped surfaces. J Mater Process Technol 196(1–3):311–320
Gopal AV, Chakradhar D (2012) Parametric optimization in electrochemical machining of EN-31 steel based on Grey relation approach. Appl Mech Mater 110:1649–1656
Qu NS, Xu ZY (2013) Improving machining accuracy of electrochemical machining blade by optimization of cathode feeding directions. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 1–8
Datta M, Landolt D (1980) On the role of mass transport in high rate dissolution of iron and nickel in ECM electrolytes—I. Chloride solutions. Electrochim Acta 25(10):1255–1262
Datta M, Landolt D (1980) On the role of mass transport in high rate dissolution of iron and nickel in ECM electrolytes—II. Chlorate and nitrate solutions. Electrochim Acta 25(10):1263–1271
Bannard J (1977) Effect of flow on the dissolution efficiency of mild steel during ECM. J Appl Electrochem 7(3):267–270
Mao KW, Chin DT (1974) Anodic behavior of mild steel in NaClO3 at high current densities. Int J Electrochem Sci 121(2):191–194
Bejar MA, Gutierrez F (1993) On the determination of current efficiency in electrochemical machining with a variable gap. J Mater Process Technol 37(1):691–699
Datta M, Landolt D (1981) Electrochemical machining under pulsed current conditions. Electrochim Acta 26(7):899–907
Datta M, Landolt D (1977) On the influence of electrolyte concentration, pH and temperature on surface brightening of nickel under ECM conditions. J Appl Electrochem 7(3):247–252
Mileham AR, Harvey SJ, Stout KJ (1986) The characterization of electrochemically machined surfaces. Wear 109(1):207–214
Sautebin R, Froidevaux H, Landolt D (1980) Theoretical and experimental modeling of surface leveling in ECM under primary current distribution conditions. Int J Electrochem Sci 127(5):1096–1100
Hoare JP, LaBoda MA, McMillan ML, Wallace AJ (1969) An Investigation of the differences between NaCl and NaClO3 as electrolytes in electrochemical machining. Int J Electrochem Sci 116(2):199–203
Datta M, Landolt D (1975) Surface brightening during high rate nickel dissolution in nitrate electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 122(11):1466–1472
Hoare JP (1970) Oxide film studies on iron in electrochemical machining electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 117(1):142–145
Ghoshal B, Bhattacharyya B (2013) Generation of microfeatures on stainless steel by electrochemical micromachining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 1–12
Chin DT, Wallace AJ (1973) Anodic current efficiency and dimensional control in electrochemical machining. Int J Electrochem Sci 120(11):1487–1493
Hoare JP, Wiese CR (1975) Current efficiency during the electrochemical machining of iron and nickel. Corros Sci 15(6):435–440
Chin DT, Mao KW (1974) Transpassive dissolution of mild steel in NaNO3 electrolytes. J Appl Electrochem 4(2):155–161
Landolt D (1972) Throwing power measurements during high rate nickel dissolution under active and transpassive conditions. Int J Electrochem Sci 119(6):708–712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Li, B., Yang, S. et al. The effect of electrolyte current density on the electrochemical machining S-03 material. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71, 1825–1833 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5617-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5617-x