Abstract
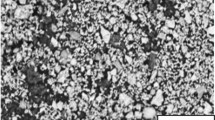
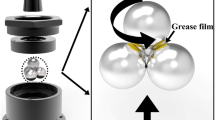
The new technology that uses nanoparticles as additive of lubricant has become an attractive study recently. The performance of nano-SiO2 which acts as the nanoparticle in the lubrication system is investigated. Tests were conducted at nanolubrication mixing ratio of 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 0.55, 0.6, and 0.8 wt.% of SiO2 with plain bearings using a 2,750 rpm high-speed rotating motor. For each mixing ration, the frictional temperature and weight loss of plain bearings were recorded and compared. During the surface morphology, the worn bearing surfaces are investigated by scanning electron microscopy. The surface element analysis was also employed to get more morphology investigation by using energy dispersive x-ray spectrometer as well as element mapping. The results showed that tribology performance of nanolubricant is at optimum by using 0.5 wt.% mixing ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarhan AAD, Sayuti M, Hamdi M (2012) Reduction of power and lubricant oil consumption in milling process using a new SiO2 nanolubrication system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-3940-7
Lee K, Hwang Y, Cheng S, Choi Y, Kwon L, Lee J, Kim SH (2009) Understanding the role of nanoparticles in nano-oil lubrication. Tribol Lett 35:127–131
Wu YY, Tsui WC, Liu TC (2006) Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 262:819–825
Xu T, Zhao JZ, Xu K (1996) The ball-bearing effect of diamond nanoparticles as an oil additive. J Phys D Appl Phys 29:2932–2937
Li W, Zheng SH, Cao BQ, Ma SY (2011) Friction and wear properties of ZrO2/SiO2 composite nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13:2129–2137
Liu G, Li N, Lu N, Fan R, (2005), Enhancing AW/EP property of lubricant oil by adding nano Al/Sn particles. Tribology Letters 18(1). doi:10.1007/s11249-004-1760-0.
Zhang M, Wang XB, Fu XS, Xia YQ (2009) Performance and anti-wear mechanism of Caco3 nanoparticles as a green additive in poly-alpha-olefin. Tribol Int 42:1029–1039
Zhao YB, Zhang ZJ, Dang HX (2004) Fabrication and tribological properties of Pb nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 6:47–51
Cho Y, Park J, Ku B, Lee J, Park WG, Lee J, Kim SH (2012) Synergistic effect of a coating and nano-oil lubricant on the tribological properties of friction surfaces. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13(1):97–102
Sayuti M, Sarhan AAD, Hamdi M (2012) Investigation on the Morphology of the machines surface in end milling of aerospace AL6061-T6 using SiO2 nanolubrication system. University Malaya, Malaysia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sia, S.Y., Sarhan, A.A.D. Morphology investigation of worn bearing surfaces using SiO2 nanolubrication system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70, 1063–1071 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5340-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5340-z