Abstract
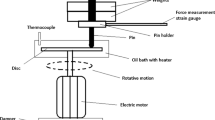
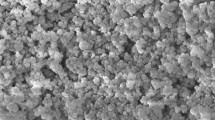
A disc-on-disc type tester was used to examine the role of fullerene nanoparticles dispersed in a mineral oil-based lubricant. In the friction test, the friction coefficient of the disc specimen immersed in the nano-oil was significantly lower than that of the disc specimen immersed in the mineral oil. This suggests that the nanoparticles dispersed in mineral oil played the important role in the lubrication enhancement of nano-oil. A series of experiments in this study were carried out to delineate the two effects [i.e., direct effect (e.g., rolling/sliding/filming) and surface enhancement effect (e.g., mending/polishing)] of nanoparticles for nano-oil-based lubrication enhancement. The disc specimens immersed in the nano-oils during the friction test was removed, and then they were re-immersed in new mineral oil for an additional friction test. The direct and surface enhancement effect of nanoparticles was then visualised by the evolution of the friction coefficient of the disc specimen immersed in the mineral- and nano-oil. The results showed that the direct effect of nanoparticles was much more dependent on the magnitude of the applied normal load than the surface enhancement effect.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rapoport, L., Leshchinsky, V., Lvovsky, M., Nepomnyashchy, O., Volovik, Y., Tenne, R.: Mechanism of friction of fullerenes. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 54, 171–176 (2002)
Wu, Y.Y., Tsui, W.C., Liu, T.C.: Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 262, 819–825 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2006.08.021
Chin˜as-Castillo, F., Spikes, H.A.: Mechanism of action of colloidal solid dispersions. J. Tribol. 125, 552–557 (2003)
Hu, Z.S., Lai, R., Lou, F., Wang, L.G., Chen, Z.L., Chen, G.X., Dong, J.X.: Preparation and tribological properties of nanometer magnesium borate as lubricating oil additive. Wear 252, 370–374 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00862-6
Xiaodong, Z., Xun, F., Huaqiang, S., Zhengshui, H.: Lubricating properties of Cyanex 302-modified MoS2 microspheres in base oil 500SN. Lubr. Sci. 19, 71–79 (2007)
Ginzburg, B.M., Shibaev, L.A., Kireenko, O.F., Shepelevskii, A.A., Baidakova, M.V., Sitnikova, A.A.: Antiwear effect of fullerene C60 additives to lubricating oils. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 75(8), 1330–1335 (2002)
Zhou, J., Yang, J., Zhang, Z., Liu, W., Xue, Q.: Study on the structure and tribological properties of surface-modified Cu nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 34(9), 1361–1367 (1999)
Rastogi, R.B., Yadav, M., Bhattacharya, A.: Application of molybdenum complexes of 1-aryl-2,5-dithiohydrazodicarbonamides as extreme pressure lubricant additives. Wear 252, 686–692 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00878-X
Liu, G., Li, X., Qin, B., Xing, D., Guo, Y., Fan, R.: Investigation of the mending effect and mechanism of copper nano-particles on a tribologically stressed surface. Tribol. Lett. 17, 4 (2004). doi:10.1007/s11249-004-8109-6
Tao, X., Jiazheng, Z., Kang, X.: The ball-bearing effect of diamond nanoparticles as an oil additive. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 29, 2932–2937 (1996). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/29/11/029
Liu, G., Li, X., Lu, N., Fan, R.: Enhancing AW/EP property of lubricant oil by adding nano Al/Sn particles. Tribol. Lett. 18(1), 85–90 (2004)
Greenberg, R., Halperin, G., Etsion, I., Tenne, R.: The effect of WS2 nanoparticles on friction reduction in various lubrication regimes. Tribol. Lett. 17(2), 179–186 (2004)
Qiu, S., Zhou, Z., Dong, J., Chen, G.: Preparation of Ni nanoparticles and evaluation of their tribological performance as potential additives in oils. J. Tribol. 123, 441–443 (2001). doi:10.1115/1.1286152
Hu, Z.S., Dong, J.X.: Study on antiwear and reducing friction additive of nanometer titanium borate. Wear 216, 87–91 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(97)00249-4
Hu, Z.S., Dong, J.X.: Study on antiwear and reducing friction additive of nanometer titanium borate. Wear 216, 92–96 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(97)00252-4
Xue, Q., Liu, W., Zhang, Z.: Friction and wear properties of a surface-modified TiO2 nanoparticle as an additive in liquid paraffin. Wear 213, 29–32 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(97)00200-7
Rapoport, L., Leshchinsky, V., Lapsker, I., Volovik, Y., Nepomnyashchy, O., Lvovsky, M., Popovitz-Biro, R., Feldman, Y., Tenne, R.: Tribological properties of WS2 nanoparticles under mixed lubrication. Wear 255, 785–793 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00044-9
Liu, W., Chen, S.: An investigation of the tribological behaviour of surface-modified ZnS nanoparticles in liquid paraffin. Wear 238, 120–124 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(99)00344-0
Zhou, J., Wu, Z., Zhang, Z., Liu, W., Dang, H.: Study on an antiwear and extreme pressure additive of surface coated LaF3 nanoparticles in liquid paraffin. Wear 249, 333–337 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(00)00547-0
Hu, Z.S., Dong, J.X., Chen, G.X.: Study on antiwear and reducing friction additive of nanometer ferric oxide. Tribol. Int. 31(7), 355–360 (1998)
Chen, S., Liu, W., Yu, L.: Preparation of DDP-coated PbS nanoparticles and investigation of the antiwear ability of the prepared nanoparticles as additive in liquid paraffin. Wear 218, 153–158 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00220-8
Lee, J.K., Cho, S.W., Hwang, Y.J., Cho, H.J., Lee, C.G., Choi, Y.M., Ku, B.C., Lee, H.K., Lee, B.C., Kim, D.H., Kim, S.H.: Application of fullerene-added nano-oil for lubrication enhancement in friction surfaces. Tribol. Int. 42, 440–447 (2009)
Kline, S.J., McClintock, F.A.: Describing uncertainties in single-sample experiments. Mech. Eng. 75, 3–8 (1953)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K., Hwang, Y., Cheong, S. et al. Understanding the Role of Nanoparticles in Nano-oil Lubrication. Tribol Lett 35, 127–131 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9441-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9441-7