Abstract
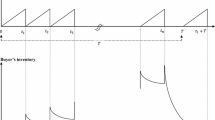
In this study, an integrated vendor–buyer inventory model is proposed. The vendor produces a product in a batch environment and delivers it to a buyer facing normally distributed demand. In the current study, several assumptions are used that the combination of these assumptions has not been studied in previous papers. Here is the list of these assumptions: service-level constraint instead of shortage cost is used; ordering cost reduction is allowed, and decreasing lead time by a cost dependent on two factors including shortened lead time and ordering quantity is considered. An algorithm is developed to obtain the optimal solution of the proposed model. A numerical example is included to illustrate the results of the model. Also, the effects of assumptions used in this paper are evaluated and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goyal SK (1976) An integrated inventory model for a single supplier–single customer problem. Int J Prod Res 15(1):107–111
Banerjee A (1986) A joint economic-lot-size model for purchaser and vendor. Decis Sci 17(3):292–311
Goyal SK (1988) A joint economic-lot-size model for purchaser and vendor: a comment. Decis Sci 19(1):236–241
Lu L (1995) A one-vendor multi-buyer integrated inventory model. Eur J Oper Res 81:312–23
Lee WC, Wu JW, Lei CL (2007) Computational algorithmic procedure for optimal inventory policy involving ordering cost reduction and back-order discounts when lead time demand is controllable. Appl Math Comput 189(1):186–200
Liao CJ, Shyu CH (1991) An analytical determination of lead time with normal demand. Int J Oper Prod Manag 11(9):72–78
Ben-Daya M, Raouf A (1994) Inventory models involving lead time as a decision variable. J Oper Res Soc 45(5):579–582
Ouyang LY, Yeh NC, Wu KS (1996) Mixture inventory model with backorders and lost sales for variable lead time. J Oper Res Soc 47:829–832
Ouyang LY, Wu KS (1997) Mixture inventory model involving variable lead time with a service level constraint. Comput Oper Res 24(9):875–882
Pan JCH, Yang JS (2002) A study of an integrated inventory with controllable lead time. Int J Prod Res 40(5):1263–1273
Ouyang LY, Chang HC (2002) Lot size reorder point inventory model with controllable lead time and set-up cost. Int J Syst Sci 33(8):635–642
Sharma S (2008) Theory of exchange. Eur J Oper Res 186:128–136
Sharma S (2009) A composite model in the context of a production-inventory system. Optim Lett 3(2):239–251
Sharma S (2009) Single/multiple parameter swapping in the context of Sanjay Sharma's Theory of Exchange. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 40:629–635
Ouyang LY, Wu KS, Ho CH (2004) Integrated vendor–buyer cooperative models with stochastic demand in controllable lead time. Int J Prod Econ 92(3):255–266
Chang HC, Ouyang LY, Wu KS, Ho CH (2006) Integrated vendor–buyer cooperative inventory models with controllable lead time and ordering cost reduction. Eur J Oper Res 170(2):481–495
Jha JK, Shanker K (2009) Two-echelon supply chain inventory model with controllable lead time and service level constraint. Comput Ind Eng 57:1096–1104
Annadurai A, Uthayakumar R (2010) Ordering cost reduction in probabilistic inventory model with controllable lead time and a service level. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag 5(6):403–410
Hall RW (1983) Zero inventories. Dow Jones-Irwin, Homewood
Porteus EL (1985) Investing in reduced setups in the EOQ model. Manag Sci 31:998–1010
Nasri F, Affisco JF, Paknejad MJ (1990) Setup cost reduction in an inventory model with finite-range stochastic lead times. Int J Prod Res 28:199–212
Kim KL, Hayya JC, Hong JD (1992) Set-up reduction in economic production quantity model. Decis Sci 23:500–508
Paknejad MJ, Nasri F, Affisco JF (1995) Defective units in a continuous review (s, Q) system. Int J Prod Res 33(10):2767–2777
Hadley G, Whitin T (1963) Analysis of inventory systems. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Ravindran A, Phillips DT, Solberg JJ (1987) Operations research: principles and practice. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahpouri, S., Fattahi, P., Arkan, A. et al. Integrated vendor–buyer cooperative inventory model with controllable lead time, ordering cost reduction, and service-level constraint. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65, 657–666 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4205-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4205-1