Abstract
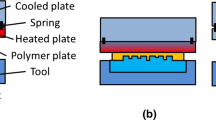
A homemade apparatus was used to apply ultrasonic-vibration to assist the glass hot embossing processes. To operate at high temperatures for glass hot embossing, the ultrasonic vibration system was appropriately designed with an embedded cooling system, and an ultrasonic horn was specifically modified for high-temperature use. Molds with both V-groove and Fresnel structures were manufactured for hot embossing experiments on PSK-100 glass. The heights of the molded structures were increased significantly with the assistance of ultrasonic vibration. This technology demonstrates the capability to upgrade the performance of the glass hot embossing process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meden-Pielinger GAA, Van de Heuvel JHP (1983) Precision pressed optical componentsmade of glass and glass suitable modeling. US Patent 4391915
Taniguchi Y (1999) Mold for molding optical element. US Patent 5855641
Firestone GC, Jain A, Yi AY (2005) Precision laboratory apparatus for high temperature compression molding of glass lenses. Rev Sci Instrum 76:063101. doi:10.1063/1.1921367
Yi AY, Huang C, Klocke F, Brecher C, Pongs G, Winterschladen M, Demmer A, Lange S, Bergs T, Merz M, Niehaus F (2006) Development of a compression molding process for three-dimensional tailored free-form glass optics. Appl Optics 45:6511–6518. doi:10.1364/AO.45.006511
Wang X, Zhou J, Gan GK, Ngoi B (2002) Theoretical and experimental studies of ultraprecision machining of brittle materials with ultrasonic vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 20:99–102
Gan J, Wang X, Zhou M, Ngoi B, Zhong Z (2003) Ultraprecision diamond turning of glass with ultrasonic vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 21:952–955
Shen XH, Zhang J, Xing DX, Zhao Y (2010) A study of surface roughness variation in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3399-y
Azarhoushang B, Tawakoli T (2011) Development of a novel ultrasonic unit for grinding of ceramic matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3347-x
Lin CH, Chen R (2006) Ultrasonic nanoimprint lithography: a new approach to nanopatterning. J Microlith Microfab Microsyst 5:011003. doi:10.1117/1.2172992
Mekaru M, Noguchi T, Goto H, Takahashi M (2007) Nanoimprint lithography combined with ultrasonic vibration on polycarbonate. Jpn J Appl Phys 46:6355–6362
Mekaru M, Noguchi T, Goto H, Takahashi M (2008) Effect of applying ultrasonic vibration in thermal nanoimprint lithography. Microsyst Technol 14:1325–1333. doi:10.1143/JJAP.46.6355
Mekaru M, Noguchi T (2009) Frequency and amplitude dependences of molding accuracy in ultrasonic nanoimprint technology. J Micromech Microeng 19:125026. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/19/12/125026
Lee CH, Jung PG, Lee SM, Park SH, Shin BS, Kim JH, Hwang KY, Kim KM, Ko JS (2010) Replication of polyethylene nano-micro hierarchical structures using ultrasonic forming. J Micromech Microeng 20:035018. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/20/3/035018
Elevated temperature physical properties of stainless steels, British Stainless Steel Association. http://www.bssa.org.uk/topics.php?article=139
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Metal Industries Research & Development Centre and Instrument Technology Research Center, for their assistances with the mold fabrications and profile measurements of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, YP., Hung, JC., Yin, LC. et al. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted optical glass hot embossing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60, 1207–1213 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3669-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3669-8