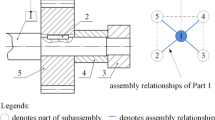
Abstract
This paper presents a new formalized reasoning method for assembly sequences generation which reduces the solution space dramatically. Firstly, a polychromatic sets (PS) matrix is introduced to describe the relations between the part-match and freedom; Secondly, the polychromatic sets matrix of entirety and element are used to describe the relations between the parts and assembly constraints; assembly constraint models and connector assembly models are constructed in this phase; then, the solution method for constraint equations is given; and the reasoning algorithm of feasible sequence is presented. Finally, an application case is studied to demonstrate the effectiveness of the method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai YW, Chen ZN, Bin HZ, Hun J (2005) An effective integration approach toward assembly sequence planning and evaluation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27(1–2):96–105 doi:10.1007/s00170-004-2155-y
Wang JF, Liu JH, Zhong YF (2005) A novel ant colony algorithm for assembly sequence planning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(11–12):1137–1143 doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1952-z
Bourjault A (1984) Contribution a une approche methodologique de l’assemblage automatise: Elaboration automatique des sequences operatoires. Universite de Franche-Comte, Besancon These d’Etat
De Fazio TL, Whitney DE (1987) Simplified generation of all mechanical assembly sequences. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 3(6):640–658
Baldwin DF, Abell TE, Lui MCM, De Fazio TL, Whitney DE (1991) An integrated computer aid for generating and evaluating assembly sequences for mechanical products. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 7(1):78–94 doi:10.1109/70.68072
Wilson RH (1995) Minimizing user queries in interactive assembly planning. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 11(2):308–312 doi:10.1109/70.370514
Minzu V, Bratcu A, Henrioud JM (1999) Construction of the precedence graphs equivalent to a given set of assembly sequences. Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Assembly and Planning Porto, Portugal, July
Homen de Mello LS, Sanderson AC (1991) A correct and complete algorithm for the generation of mechanical assembly sequence. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 7(2):228–24 doi:10.1109/70.75905
Dini G, Santochi M (1992) Automated sequencing and subassembly detection in assembly planning. Ann CIRP 41(1):1–4
Gottipolu RB, Ghosh K (1995) An integrated approach to the generation of assembly sequences. Int J Comput Appl Technol 8(33):125–138
Laperrière L, El Maraghy HA (1994) Assembly sequences planning for simultaneous engineering applications. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 9(4):231–244 doi:10.1007/BF01751121
Yin ZP, Ding H, Li HX, Xiong YL (2003) A connector-based hierarchical approach to assembly sequence planning for mechanical assemblies. Computer-Aided Des 35(1):37–56 doi:10.1016/S0010-4485(01)00174-9
Lai HY, Huang CT (2004) A systematic approach for automatic assembly sequence plan generation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 24(9–10):752–763 doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1760-5
Bonneville F, Perrard C, Henrioud JM (1995) A genetic algorithm to generate and evaluate assembly plans. Proc IEEE Symp Emerging Technol Factory Automation 3:231–239
Sebaaly MF, Fujimoto H (1996) A genetic planner for assembly automation. Proc IEEE Conf Evol Comput May:401–406
Chen SF, Liu Y (2001) An adaptive genetic assembly sequence planner. Int J Comput Integrated Manuf 14(5):489–500 doi:10.1080/09511920110034987
Hong DS, Cho HS (1999) A genetic-algorithm-based approach to the generation of robotic assembly sequences. Control Eng Pract 7(2):151–159 doi:10.1016/S0967-0661(98)00177-4
Senin N, Groppetti R, Wallace DR (2000) Concurrent assembly planning with genetic algorithm. Robot Compute Integr Manuf 16(4):65–72 doi:10.1016/S0736-5845(99)00058-7
Lazzerini B, Marcelloni F (2000) A genetic algorithm for generating optimal assembly plans. Artif Intell Eng 14(4):319–329 doi:10.1016/S0954-1810(00)00011-X
Smith GC, Smith SS-F (2002) An enhanced genetic algorithm for automated assembly planning. Robot Comput Integrate Manuf 18(5–6):355–364 doi:10.1016/S0736-5845(02)00029-7
Marian RM, Luong LHS, Abhary K (2006) A genetic algorithm for the optimization of assembly sequences. Comput Ind Eng 50(4):503–527 doi:10.1016/j.cie.2005.07.007
Chakrabarty S, Wolter J (1994) A hierarchical approach to assembly planning. IEEE Inter Conf Robot Autom May:258–263
Swaminathan A, Barber KS (1996) An experience-based assembly sequence planner for mechanical assemblies. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 12(2):252–67 doi:10.1109/70.488945
Zha XF (2000) An object-oriented knowledge based Petri net approach to intelligent integration of design and assembly planning. Artif Intell Eng 14(1):83–112 doi:10.1016/S0954-1810(99)00029-1
Dong TY, Tong RF, Zhang L (2007) A knowledge-based approach to assembly sequence planning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(11–12):1232–1244 doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0438-1
Eastman CM (1981) The design of assemblies. Society of Automotive Engineering, Warrendale technical paper series 0148-7191/81/0223-0197
Wolter JD (1988) On the automatic generation of plans for mechanical assembly, PhD Thesis. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Gottipolua RB, Ghosh K (2003) A simplified and efficient representation for evaluation and selection of assembly sequence. Comput Ind 50(3):251–264 doi:10.1016/S0166-3615(03)00015-0
Wang H, Xiang D, Duan GH, Zhang LX (2007) Assembly planning based on semantic modeling approach. Comput Ind 58(3):227–239 doi:10.1016/j.compind.2006.05.002
Van Holland W, Brosvoort WF (2000) Assembly features in modeling and planning. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 16(4):277–294 doi:10.1016/S0736-5845(00)00014-4
Kim JS, Kim KS, Lee JY, Jeong JH (2005) Generation of assembly models from kinematic constraints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26(1–2):131–137 doi:10.1007/s00170-004-2231-3
Li Z, Xu L (2003) Polychromatic Sets and its application in simulating complex objects and systems. Comput Oper Res 30(6):851–860 doi:10.1016/S0305-0548(02)00038-2
Zhang LX, Tong BS (1999) Study on an assembly simulation system in CE and its key technologies. J Comput Aided Des Comput Graph 11(2):164–167 in Chinese
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Li, Z. Formalized reasoning method for assembly sequences based on Polychromatic Sets theory. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42, 993–1004 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1655-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1655-6