Abstract
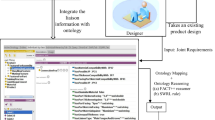
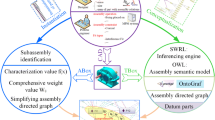
This paper presents a case-based reasoning (CBR) method in combination with ontology theory to carry out decision making for assembly sequence planning (ASP). Due to the ontology unifying various kinds of assembly sequence-related knowledge from different sources, the CBR approach enables a unified structured representation of previous cases and target cases to achieve integration and sharing of knowledge. Based on the similarity measure of classes and properties in ontology theory, the similarity calculation between target ASP case and previous ASP cases is carried out by considering the connection type, motion-transmission type, and location-support type, and a similarity-based previous cases retrieval algorithm is proposed. The combination of ontology and CBR enables flexible and high-quality assembly sequence decisions under various conditions; the ontology-based rule-based reasoning (RBR) method is also adopted as a supplement to CBR in the assembly sequence construction process. Additionally, a reducer case is used to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ou LM, Xu X (2013) Relationship matrix based automatic assembly sequence generation from a CAD model. Comput Aided Des 45(7):1053–1067
Xu LD, Wang CG, Bi ZM, Yu JP (2012) AutoAssem: an automated assembly planning system for complex products. IEEE T Ind Inform 8(3):669–678
Wu WB, Huang ZD, Zeng JN, Fan K (2021) A decision-making method for assembly sequence planning with dynamic resources. Int J Prod Res 60(15):4797–4816
Mei B, Liang ZS, Zhu WD, Ke YL (2021) Positioning variation synthesis for an automated drilling system in wing assembly. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 67:102044
Deepak B, Murali GB, Bahubalendruni M, Biswal BB (2019) Assembly sequence planning using soft computing methods: a review. P I Mech Eng E-J Pro 233(3):653–683
Chen J, Jia X (2019) A multimedia case-based reasoning framework for assembly sequence planning. Assem Autom 39(4):673–684
Gruber TR (1993) A translation approach to portable ontology specifications. Knowl Acquis 5(2):199–220
Lu WL, Qin YC, Qi QF, Zeng WH, Zhong YR, Liu XJ, Jiang XQ (2016) Selecting a semantic similarity measure for concepts in two different CAD model data ontologies. Adv Eng Inform 30(3):449–466
Zeid I, Gupta SM, Bardasz T (1997) A case-based reasoning approach to planning for disassembly. J Intell Manuf 8(2):97–106
Veerakamolmal P, Gupta SM (2002) A case-based reasoning approach for automating disassembly process planning. J Intell Manuf 13(1):47–60
Su Q (2007) Applying case-based reasoning in assembly sequence planning. Int J Prod Res 45(1):29–47
Seo Y, Sheen D, Kim T (2007) Block assembly planning in shipbuilding using case-based reasoning. Expert Syst Appl 32(1):245–253
Qu SP, Jiang ZH, Tao NR (2013) An integrated method for block assembly sequence planning in shipbuilding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(5-8):1123–1135
Brown D, Aldea A, Harrison R, Martin C, Bayley I (2018) Temporal case-based reasoning for type 1 diabetes mellitus bolus insulin decision support. Artif Intell Med 85:28–42
Mohammed MA, Ghani MKA, Arunkumar N, Obaid OI, Mostafa SA, Jaber MM, Burhanuddin MA, Matar BM, Abdullatif SK, Ibrahim DA (2018) Genetic case-based reasoning for improved mobile phone faults diagnosis. Comput Electr Eng 71:212–222
Khosravani MR, Nasiri S, Weinberg K (2019) Application of case-based reasoning in a fault detection system on production of drippers. Appl Soft Comput 75:227–232
Faia R, Pinto T, Abrishambaf O, Fernandes F, Vale Z, Corchado JM (2017) Case based reasoning with expert system and swarm intelligence to determine energy reduction in buildings energy management. Energ Buildings 155:269–281
Guo Y, Hu J, Peng YH (2012) A CBR system for injection mould design based on ontology: a case study. Comput Aided Des 44(6):496–508
Guo Y, Peng YH, Hu J (2013) Research on high creative application of case-based reasoning system on engineering design. Comput Ind 64(1):90–103
Sanfilippo EM, Belkadi F, Bernard A (2019) Ontology-based knowledge representation for additive manufacturing. Comput Ind 109:182–194
Xing XJ, Zhong BT, Luo HB, Li H, Wu HT (2019) Ontology for safety risk identification in metro construction. Comput Ind 109:14–30
He W, Wang FK, Akula V (2017) Managing extracted knowledge from big social media data for business decision making. J Knowl Manag 21(2):275–294
Gao J, Bernard A (2018) An overview of knowledge sharing in new product development. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(5-8):1545–1550
Xie XL, Lin L, Zhong SS (2013) Handling missing values and unmatched features in a CBR system for hydro-generator design. Comput Aided Des 45(6):963–976
Ruiz PAP, Kamsu-Foguem B, Noyes D (2013) Knowledge reuse integrating the collaboration from experts in industrial maintenance management. Knowl-Based Syst 50:171–186
Qin YC, Lu WL, Qi QF, Liu XJ, Huang MF, Scott PJ, Jiang XQ (2018) Towards an ontology-supported case-based reasoning approach for computer-aided tolerance specification. Knowl-Based Syst 141:129–147
Gong HQ, Shi LL, Zhai X, Du YM, Zhang ZJ (2022) Assembly process case matching based on a multilevel assembly ontology method. Assem Autom 42(1):80–98
Chen YN, Zhu XH, Fang K, Wu YB, Deng YC, He X, Zou ZY, Guo T (2021) An optimization model for process traceability in case-based reasoning based on ontology and the genetic algorithm. IEEE Sens J 21(22):25123–25132
Ke C, Jiang ZG, Zhang H, Wang Y, Zhu S (2020) An intelligent design for remanufacturing method based on vector space model and case-based reasoning. J Clean Prod 277:123269
Shi X, Tian X, Wang G, Zhao D, Zhang M (2020) Semantic-based subassembly identification considering non-geometric structure attributes and assembly process factors. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 110(1-2):439–455
Acknowledgements
The authors would also like to thank the editors and anonymous referees for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaolin Shi: conceptualization, methodology, analysis, investigation, methodology validation, writing original draft; Xitian Tian: conceptualization, methodology; Jianguo Gu: investigation, methodology validation; Gangfeng Wang: analysis, methodology; Dongping Zhao: methodology validation, editing; Liping Ma: methodology validation, editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Tian, X., Gu, J. et al. A hybrid approach of case- and rule-based reasoning to assembly sequence planning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 127, 221–236 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11525-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11525-8