Abstract
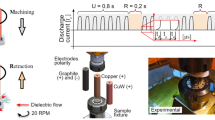
This study investigates how machining characteristics and surface modifications affect low-carbon steel (S15C) during electrical discharge machining (EDM) processes with semi-sintered electrodes. Among the machining characteristics determined, the material removal rate (MRR), surface deposit rate (SDR), and electrode wear rate (EWR) are included. Additionally, exactly how semi-sintered electrodes affect the surface modifications is also evaluated by electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA), micro hardness, and corrosion resistance tests. The experimental results confirmed that the composition of the semi-sintered electrodes is transferred onto the machined surface efficiently and effectively during the EDM process, and that the process is feasible and can easily form a modified layer on the machined surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EDM:
-
Electrical discharge machining
- MRR:
-
Material removal rate (g/min)
- SDR:
-
Surface deposit rate (g/min)
- EWR:
-
Electrode wear rate (g/min)
- EPMA:
-
Electron probe microanalyzer
- EDA:
-
Electrical discharge alloying
- P/M:
-
Powder metallurgy
- WDS:
-
Wavelength dispersive spectrometry
- I p :
-
Peak current (A)
- τ p :
-
Pulse duration (μs)
- V 0 :
-
No-load voltage (V)
- DF:
-
Duty factor
- WT:
-
Working time (s)
References
Ando T, Rawles RE, Yamamoto K, Kamo M, Sato Y, Nishitani-Gamo M (1996) Chemical modification of diamond surfaces using a chlorinated surface as an intermediate state. Diamond Relat Mater 5(1):1136–1142
Katoh M, Ohte T, Takahashi A, Miyashita K, Ohtani S, Kojima A (1997) Differences between effects of ions in plasma on the edge surface of carbon material and those on the basal surface. Surf Coat Technol 92(3):230–234
De Damborenea J (1998) Surface modification of metals by high power lasers. Surf Coat Technol 100–101(1–3):377–382
Dong H, Bell T (1999) State-of-the-art overview: ion beam surface modification of polymers towards improving tribological properties. Surf Coat Technol 111(1):29–40
Takahashi K, Iwaki M (2000) Electrochemical characterization for ion-implanted materials surface. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 19(3):281–290
Khan TI, Rizvi SA, Matsuura K (2000) The effect on wear behaviour of H13 tool steel surfaces modified using a tungsten arc heat source. Wear 244(1):154–164
Yan BH, Tsai HC, Huang FY (2005) The effect in EDM of a dielectric of a urea solution in water on modifying the surface of titanium. Int J Mach Tools Manufact 45(2):194–200
Tsunekawa Y, Okumiya M, Mohri N, Takahashi I (1994) Surface modification of aluminum by electrical discharge alloying. Mater Sci Eng A 174(2):193–198
Kruth J-P, Stevens L, Froyen L, Lauwers B (1995) Study of the white layer of a surface machined by die sinking electro discharge machining. Ann CIRP 44(1):169–172
Lin YC, Yan BH, Huang FY (2001) Surface modification of Al-Zn-Mg aluminum alloy using the combined process of EDM with USM. J Mater Process Technol 115(3):359–366
Ogata I, Mukoyama Y (1993) Carburizing and decarburizing phenomena in EDM’d surface. Int J Jap Soc Precis Eng 27(3):197–202
Ming QY, He LY (1995) Powder-suspension dielectric fluid for EDM. J Mater Process Technol 52(1):44–54
Wong YS, Lim LC, Rahuman I, Tee WM (1998) Near-mirror-finish phenomenon in EDM using powder-mixed dielectric. J Mater Process Technol 79(1):30–40
Yan BH, Lin YC, Huang FY, Wang CH (2001) Surface modification of SKD 61 during EDM with metal powder in the dielectric. Mater Trans JIM 42(12):2597–2604
Mohri N, Saito N, Tsunekawa Y (1993) Metal surface modification by electrical discharge machining with composite electrode. Ann CIRP 42(1):219–222
Tsunekawa Y, Okumiya M, Mohri N, Kuribe E (1997) Formation of composite layer containing TiC precipitates by electrical discharge alloying. Mater Trans JIM 38(7):630–635
Shunmugam MS, Philip PK (1994) Improvement of wear resistance by EDM with tungsten carbide P/M electrode. Wear 171(1–2):1–5
Samuel MP, Philip PK (1997) Power metallurgy tool electrodes for electrical discharge machining. Int J Mach Tools Manufact 37(11):1625–1633
Tsai HC, Yan BH, Huang FY (2003) EDM performance of Cr/Cu-based composite electrodes. Int J Mach Tools Manufact 43(3):245–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YF., Chow, HM., Lin, YC. et al. Surface modification using semi-sintered electrodes on electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36, 490–500 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0859-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0859-x