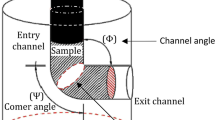
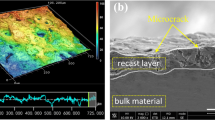
Abstract
This study investigates the impact of different tool electrode materials on the thickness of the resolidified layer produced by sinking electrical discharge machining (SED-machining) on Inconel 718 alloy. The experiments were conducted with various discharge durations and duty factor levels, using an open voltage of 120 V and a discharge current of 2.4 A. Three grades of tool electrode materials were used: graphite (both polarities), copper, and copper-tungsten. The study found that ED-machining performance improved significantly at a duty factor of 0.33, a discharge duration of 24 μs, and a discharge energy of 6.91 mJ. The material removal rate increased to 1.05 mm3/min with the Graphite (−) tool electrode, while the volumetric relative wear improved to 1.66% with the copper-tungsten tool electrode. X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy analyses revealed phase changes, complex carbide formation, and primary dendritic growth in the recast layer due to abrupt thermal gradient changes and material-electrode interactions. The maximum recast layer thickness was 16.52 μm with the graphite (−) tool electrode, while the copper-tungsten tool electrode produced the smoothest surface with the lowest roughness of 1.3 μm. The copper tool electrode yielded the thinnest recast layer at 9.08 μm.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FLTt :
-
Flatness using least squares reference plane (μm)
- î e :
-
Discharge current (A)
- Pin :
-
Dielectric inlet pressure (mPa)
- Ra :
-
Average roughness - two-dimensional (μm)
- Sa :
-
Average height of the selected area—three-dimensional (μm)
- Sdq :
-
Root mean square gradient (−)
- Sdr :
-
Developed interfacial area ratio (%)
- Sku :
-
Kurtosis (−)
- Smr 2 :
-
Peak material component, the fraction of the surface which will carry the load (%)
- Sp :
-
Maximum peak height of selected area (μm)
- Ssk :
-
Skewness (−)
- Sv :
-
Maximum valley depth of selected area (μm)
- t d :
-
Ignition delay time, (μs))
- t e :
-
Discharge duration (μs)
- t i :
-
Pulse duration (μs)
- t o :
-
Pulse interval time (μs)
- t p :
-
Pulse cycle time (μs)
- û e :
-
Discharge voltage (V)
- V e :
-
Electrode wear rate (mm3/min)
- V w :
-
Material removal rate (mm3/min)
- W e :
-
Discharge energy (We = ûe.îe.te) (mJ)
- ϑ :
-
Volumetric relative wear (Ve/Vw) (%)
- τ :
-
Duty factor (ti/tp) (−)
References
Mahesh K, Philip JT, Joshi SN, Kuriachen B (2021) Machinability of Inconel 718: a critical review on the impact of cutting temperatures. Mater Manuf Process 36:753–791. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1843671
Suárez A, Veiga F, Polvorosa R et al (2019) Surface integrity and fatigue of non-conventional machined alloy 718. J Manuf Process 48:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.09.041
Ezugwu EO, Wang ZM, Machado AR (1998) The machinability of nickel-based alloys: a review. J Mater Process Technol 86:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(98)00314-8
De Bartolomeis A, Newman ST, Jawahir IS et al (2021) Future research directions in the machining of Inconel 718. J Mater Process Technol 297:117260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117260
Jafarian F (2020) Electro discharge machining of Inconel 718 alloy and process optimization. Mater Manuf Process 35:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1711919
Czelusniak T, Higa CF, Torres RD et al (2019) Materials used for sinking EDM electrodes: a review. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 41:14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1520-y
Jadam T, Datta S, Mahapatra S, Sankar S (2018) Electro-discharge machining of Inconel 718 using square cross sectioned copper tool electrode: studies on topography and metallurgical features of the EDMed work surface. Mater Today Proc 5:4847–4854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.12.060
Carlini GC, Amorim FL (2022) Variação do Período de Descargas Elétricas e Retração com Diferentes Materiais de Eletrodo Durante a EDM do Inconel 718. XXIV Colóquio Usinagem 1:5. https://doi.org/10.29327/usinagem.478328
DiBitonto DD, Eubank PT, Patel MR, Barrufet MA (1989) Theoretical models of the electrical discharge machining process. I. A simple cathode erosion model. J Appl Phys 66:4095–4103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.343994
Eubank PT, Patel MR, Barrufet MA, Bozkurt B (1993) Theoretical models of the electrical discharge machining process. III. The variable mass, cylindrical plasma model. J Appl Phys 73:7900–7909. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.353942
Schumacher BM (2004) After 60 years of EDM the discharge process remains still disputed. J Mater Process Technol 149:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matprotec.2003.11.060
Kunieda M, Lauwers B, Rajurkar KP, Schumacher BM (2005) Advancing EDM through fundamental insight into the Process. CIRP Ann 54:64–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-8506(07)60020-1
Rahul DS, Biswal BB, Mahapatra SS (2019) Machinability analysis of Inconel 601, 625, 718 and 825 during electro-discharge machining: on evaluation of optimal parameters setting. Meas J Int Meas Confed 137:382–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.01.065
Klocke F, König W (2007) Fertigungsverfahren 3. In: Abtragen, Generieren und Lasermaterialbearbeitung. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin
Amorim FL, Weingaertner WL, Bassani IA (2010) Aspects on the optimization of die-sinking EDM of tungsten carbide-cobalt. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 32:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1678-58782010000500009
Schulze HP (2021) Determining the importance of polarity change in the electrical discharge machining. New Visions Sci Technol 3:76–85. https://doi.org/10.9734/bpi/nvst/v3/12384d
Jadam T, Sahu SK, Datta S, Masanta M (2020) Powder-mixed electro-discharge machining performance of Inconel 718: effect of concentration of multi-walled carbon nanotube added to the dielectric media. Sadhana - Acad Proc Eng Sci 45:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-01378-2
Wang J, Liu D, Ding X et al (2020) Microstructure heredity of Inconel 718 nickel-based superalloy during preheating and following deformation. Crystals 10:303. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040303
Li Z, Bai J (2017) Impulse discharge method to investigate the influence of gap width on discharge characteristics in micro-EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90:1769–1777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9508-1
Davim JP (2010) In: Davim JP (ed) Surface integrity in machining. Springer London, London
Kliuev M, Boccadoro M, Perez R et al (2016) EDM drilling and shaping of cooling holes in Inconel 718 turbine blades. Procedia CIRP 42:322–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.293
Sahu SK, Datta S (2019) Experimental studies on graphite powder-mixed electro-discharge machining of Inconel 718 super alloys: comparison with conventional electro-discharge machining. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part E J Process Mech Eng 233:384–402. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408918787104
Phipon R, Shivakoti I, Sharma A (2020) Sustainable processing of Inconel 718 super alloy in electrical discharge machining process. World J Eng 17:687–695. https://doi.org/10.1108/WJE-03-2020-0077
Shekar C, Kishore K, Laxminarayana P (2020) Material removal rate and surface roughness on machining of Inconel 718 by electrical discharge machine using Taguchi technique. Mater Today Proc 27:1024–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.372
Tanjilul M, Ahmed A, Kumar AS, Rahman M (2018) A study on EDM debris particle size and flushing mechanism for efficient debris removal in EDM-drilling of Inconel 718. J Mater Process Technol 255:263–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.12.016
Dong H, Liu Y, Li M et al (2019) High-speed compound sinking machining of Inconel 718 using water in oil nanoemulsion. J Mater Process Technol 274:116271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116271
Akca E, Gürsel A (2015) A review on superalloys and IN718 nickel-based INCONEL superalloy. Period Eng Nat Sci 3. https://doi.org/10.21533/pen.v3i1.43
Thellaputta GR, Chandra PS, Rao CSP (2017) Machinability of nickel based superalloys: a review. Mater Today Proc 4:3712–3721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.02.266
ASM (1990) ASM Handbook. In: Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials. ASM International
Li XZ, Zhou JP, Zhang Y et al (2020) Discharge characteristics of W-Cu electrode in short electrical arc discharge machining of Inconel 718. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 110:2427–2437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06041-y
Zink ES, Bourdon D, Neias Junior V et al (2020) Study of manufacturing processes for liquid rocket turbopump impellers: test and analysis. J Aerosp Technol Manag 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.5028/jatm.v12.1099
Dong H, Liu Y, Shen Y, Wang X (2016) Optimizing machining parameters of compound machining of Inconel718. Procedia CIRP 42:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.185
Donachie MJ, Donachie SJ (2002) Superalloys: a technical guide, 2nd edn. ASM International, Ohio, USA, pp 44073–40002
Zhao Y, Guo Q, Ma Z, Yu L (2020) Comparative study on the microstructure evolution of selective laser melted and wrought IN718 superalloy during subsequent heat treatment process and its effect on mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng A 791:139735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139735
Touazine H, Jahazi M, Bocher P (2017) Accurate determination of damaged subsurface layers in machined Inconel 718. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88:3419–3427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9039-9
Klocke F, Zeis M, Klink A, Veselovac D (2013) Technological and economical comparison of roughing strategies via milling, sinking-EDM, wire-EDM and ECM for titanium- and nickel-based blisks. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 6:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2013.02.008
Mendes LA, Amorim FL, Weingaertner WL (2014) Automated system for the measurement of spark current and electric voltage in wire EDM performance. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 37:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-014-0171-x
Carlini GC, Amorim FL, Weingaertner WL (2019) Influence of different grades of CuW electrodes when die sinking ED-machining of cemented carbide. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03982-x
Ahmed A, Tanjilul M, Rahman M, Kumar AS (2019) Ultrafast drilling of Inconel 718 using hybrid EDM with different electrode materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04769-w
Leone C, Di Siena M, Genna S, Martone A (2022) Effect of graphite nanoplatelets percentage on the in plane thermal diffusivity of ultra-thin graphene based (nanostructured) composite. Opt Laser Technol 146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107552
Amorim FL, Weingaertner WL (2007) The behavior of graphite and copper electrodes on the finish die-sinking electrical discharge machining (EDM) of AISI P20 tool steel. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 29:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1678-58782007000400004
ISO (2015) ISO 16610-1. Geometrical product specifications (GPS) — filtration — part 1: overview and basic concepts
ISO (2021) ISO 25178-2. Geometrical product specifications (GPS) — surface texture: areal — part 2: terms, definitions and surface texture parameters
Pagani L, Qi Q, Jiang X, Scott PJ (2017) Towards a new definition of areal surface texture parameters on freeform surface. Meas J Int Meas Confed 109:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.05.028
Czifra Á, Barányi I (2020) Sdq-Sdr topological map of surface topographies. Front Mech Eng 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmech.2020.00050
Abhilash PM, Chakradhar D (2022) Multi-response optimization of wire EDM of Inconel 718 using a hybrid entropy weighted GRA-TOPSIS method. Process Integr Optim Sustain 6:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-021-00202-6
Kossman S, Coorevits T, Iost A, Di C (2017) A new approach of the Oliver and Pharr model to fit the unloading curve from instrumented indentation testing. J Mater Res 32:2230–2240. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.120
Holmberg J, Berglund J, Wretland A, Beno T (2019) Evaluation of surface integrity after high energy machining with EDM, laser beam machining and abrasive water jet machining of alloy 718. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100:1575–1591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2697-z
Amorim FL, Weingaertner WL (2005) The influence of generator actuation mode and process parameters on the performance of finish EDM of a tool steel. J Mater Process Technol 166:411–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.08.026
Amorim FL, Stedile LJ, Torres RD et al (2014) Performance and surface integrity of Ti6Al4V after sinking EDM with special graphite electrodes. J Mater Eng Perform 23:1480–1488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0852-0
Mahdieh MS (2020) Recast layer and heat-affected zone structure of ultra-fined grained low-carbon steel machined by electrical discharge machining. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 234:933–944. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405419889202
Lamba A, Vipin (2022) Experimental investigation of machining of EN31 Steel in abrasive mixed rotary EDM with graphite and copper electrode. Sadhana - Acad Proc Eng Sci 47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-022-01906-2
Molnar V (2022) Asymmetric height distribution of surfaces machined by hard turning and grinding. Symmetry (Basel) 14:1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14081591
Imran M, Mativenga PT, Gholinia A, Withers PJ (2015) Assessment of surface integrity of Ni superalloy after electrical-discharge, laser and mechanical micro-drilling processes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:1303–1311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6909-5
Wei J, Zhang Y, Dong G et al (2022) Surface integrity of Inconel 718 in electrical discharge grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10400-2
Shen Y, Liu Y, Dong H et al (2017) Surface integrity of Inconel 718 in high-speed electrical discharge machining milling using air dielectric. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90:691–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9332-7
Liu P, Hu J, Sun S et al (2019) Microstructural evolution and phase transformation of Inconel 718 alloys fabricated by selective laser melting under different heat treatment. J Manuf Process 39:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.02.029
Ergin N, Ozdemir O, Demirkiran S et al (2015) Synthesis of inconel 718 superalloy by electric current activated sintering. Acta Phys Pol A 127:1100–1102. https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.127.1100
Wang W, Zhai H, Chen L et al (2016) Preparation and mechanical properties of TiCx–(NiCu)3Al–CuNi2Ti–Ni hybrid composites by reactive pressureless sintering pre-alloyed Cu/Ti3AlC2 and Ni as precursor. Mater Sci Eng A 670:351–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.06.021
Beri N, Maheshwari S, Sharma C, Kumar A (2014) Surface quality modification using powder metallurgy processed CuW electrode during electric discharge machining of Inconel 718. Procedia Mater Sci 5:2629–2634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.524
Lai A, Bhanumurthy K, Kale GB, Kashyap BP (2012) Diffusion characteristics in the Cu–Ti system. Int J Mater Res 103:661–672. https://doi.org/10.3139/146.110685
Copher G, Harimkar S, Rouser K et al (2022) Microstructure effects of the electrical discharge machining drill on aerospace super alloys. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3604722
Kirka MM, Unocic KA, Raghavan N et al (2016) Microstructure development in electron beam-melted Inconel 718 and associated tensile properties. Jom 68:1012–1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1812-6
Mostafa A, Picazo Rubio I, Brailovski V et al (2017) Erratum: structure, texture and phases in 3D printed IN718 alloy subjected to homogenization and HIP treatments. Metals (Basel) 7:315. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7080315
Jadam T, Rahul DS, Mahapatra SS (2021) Electro-discharge machining (EDM) of superalloy Inconel 718 using triangular cross-sectioned copper tool electrode: emphasis on topography and metallurgical characteristics of the EDMed work surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect A - Phys Sci 91:123–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-019-00642-3
Seow CE, Coules HE, Wu G et al (2019) Wire + arc additively manufactured Inconel 718: effect of post-deposition heat treatments on microstructure and tensile properties. Mater Des 183:108157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108157
Erden A, Kaftanoǧlu B (1981) Thermo-mathematical modelling and optimization of energy pulse forms in electric discharge machining (EDM). Int J Mach Tool Des Res 21:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7357(81)90010-X
Holsten M, Koshy P, Klink A, Schwedt A (2018) Anomalous influence of polarity in sink EDM of titanium alloys. CIRP Ann 67:221–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2018.04.069
Jahan MP, Wong YS, Rahman M (2009) A study on the fine-finish die-sinking micro-EDM of tungsten carbide using different electrode materials. J Mater Process Technol 209:3956–3967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.09.015
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Carlini, G.C., Blödorn, R., Davis, R. et al. Unraveling the technological performance of low-energy ED-machining for processing Inconel 718 alloy: a comparative study of electrode materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 131, 4755–4772 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13334-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13334-z