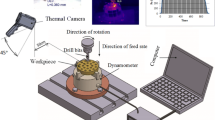
Abstract
Among material secondary machining, drilling is the most frequently applied factor to composites needing structure joining. Drill geometry is considered the most important factor that affects drill performance. A major concern in drilling of composite materials is the delamination that occurs in the exit as well as in the entrance planes. The delamination damage caused by the tool thrust is known as one of the major concerns during the drilling process. The thrust force of step drill with drilling parameters (step angle, stage ratio, feedrate and spindle speed) in drilling carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) laminates were experimentally investigated in this study. The experimental results indicate that the step angle, stage ratio, and feedrate are the most significant factors affecting the overall performance. The optimal combinations, such as A2B2C1D3 (i.e., step angle = 100 ° stage ratio = 0.4 mm/mm, feedrate = 0.01 mm/rev and spindle speed = 1,200 rpm), were used under the adopted drilling condition. An experimental approach to the prediction of thrust force produced by step drill using linear regression analysis of experiments and radial basis function network (RBFN) were proposed in this study. In the confirmation tests, RBFN (errors within 0.3%) has been shown to be a better predictive model than multi-variable linear regression analysis (errors within 28%) for quantitative prediction of drilling-induced thrust force in drilling of composite material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ravishankar SR, Murthy CRL (1996) Ultrasonic imaging for evaluation of drill-induced delaminations in composite laminates. In: Proc 14th World Conference Nondestructive test, 8–13 December. New Delhi, India, pp 489–494
Galloway DF (1957) Some experiments on the influence of various factors on drill performance. ASME 79:191–237
Russell WR (1962) Drill design and drilling conditions for improved efficiency. ASTME Paper No. 397:62
Sakuma K, Yokoo Y, Seto M (1984) Study on drilling of reinforced plastics: relation between tool material and wear behavior. Bull JSME 27(228):1237–1244
Jain S, Yang DCH (1993) Effects of feedrate and chisel edge on delamination in composite drilling. ASME J Eng Ind 115:398–405
Mathew J, Ramakrishnan N, Naik NK (1999) Investigations into the effect of geometry of a trepanning tool on thrust and torque during drilling of GFRP composites. J Mater Process Technol 91:1–11
Piquet R, Ferret B, Lachaud F, Swider P (2000) Experimental analysis of drilling damage in thin carbon/epoxy plate using special drills. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 31(10):1107–1115
Hocheng H, Tsao CC (2003) Comprehensive analysis of delamination in drilling of composite materials with various drill bits. J Mater Process Technol 140:335–339
Tagliaferri V, Caprino G, Diterlizzi A (1990) Effect of drilling parameters on the finish and mechanical properties of GFRP composites. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 30(1):77–84
Mohan NS, Ramachandra A, Kulkarni SM (2005) Influence of process parameters on cutting force and torque during drilling of glass-fiber polyester reinforced composites. Compos Struct 71(3–4):407–413
Kim GW, Lee KY (2005) Critical thrust force at propagation of delamination zone due to drilling of FRP/metallic strips. Compos Struct 69(2):137–141
König W, Wulf C, Grass P, Willerscheid H (1985) Machining of fiber reinforced plastics. Ann CIRP 34(2):536–548
Komanduri R, Zhang B, Vissa CM (1991) Machining of fiber reinforced composites. Proc Manuf Compos Mater 49(27):1–36
Won MS, Dharan CKH (2002) Chisel edge and pilot hole effects in drilling composite laminates. ASME J Manuf Sci Eng 124:242–247
Tsao CC, Hocheng H (2003) The effect of chisel length and associated pilot hole on delamination when drilling composite materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(11):1087–1092
Tsao CC (2006) The effect of pilot hole on delamination when core drill drilling composite materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46(12–13):1653–1661
Ko SL, Chang JE, Yang GE (2003) Burr minimizing scheme in drilling. J Mater Process Technol 140:237–242
Xia RS, Mahdavian SM (2005) Experimental studies of step drills and establishment of empirical equations for the drilling process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(2):235–240
Rangwala S, Dornfeld D (1990) Sensor integration using neural networks for intelligent tool condition monitoring. ASME J Eng Ind 112:219–228
Rahman M, Zhou Q, Hong GS (1995) On-line cutting state recognition in turning using a neural network. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 10(2):87–92
Tsao CC (2002) Prediction of flank wear of different coated drills for JIS SUS 304 stainless steel using neural network. J Mater Process Technol 123(3):354–360
Sanjay C, Neema ML, Chin CW (2005) Modeling of tool wear in drilling by statistical analysis and artificial neural networks. J Mater Process Technol 170(3):494–500
Panda SS, Singh AK, Chakraborty D, Pal SK (2006) Drill wear monitoring using back propagation neural network. J Mater Process Technol 172(2):283–290
Manish TV, Chandrashekhara K (2000) A thick composite-beam model for delamination prediction by the use of neural networks. Compos Sci Technol 60:1773–1779
Stone R, Krishnamurthy K (1996) A neural network thrust force controller to minimize delamination during drilling of graphite-epoxy laminates. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 36(9):985–1003
Karri V (1999) RBF neural network for thrust and torque predictions in drilling operations. In: Proc 3rd International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Applications (ICCIMA’99), 23–26 September. New Delhi, India, pp 55–59
Kawaji S, Arao M, Chen Y (2001) Thrust force control of drilling system using neural network. IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, 8–12 July. IEEE Conference Publications, no. 1, Como, Italy, pp 476–481
Bendell A, Disney J, Pridmore WA (1989) Taguchi methods - application in world application: industries, productivity, improvement and case study, IFS Publication
Davim JP, Reis P (2003) Drilling carbon fiber reinforced plastics manufactured by autoclave-experimental and statistical study. Mater Des 24(5):315–324
Tsao CC, Hocheng H (2004) Taguchi analysis of delamination associated with various drill bits in drilling of composite material. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(10):1085–1090
Enemuoh EU, El-Gizawy AS, Okafor AC (2001) An approach for development of damage-free drilling of carbon fiber reinforced thermosets. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41(12):1795–1814
Davim JP, Reis P (2003) Study of delamination in drilling carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) using design experiments. Compos Struct 59(4):481–487
Park SH (1996) Robust design and analysis for quality engineering. Chapman & Hall, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsao, C.C. Prediction of thrust force of step drill in drilling composite material by Taguchi method and radial basis function network. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36, 11–18 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0808-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0808-8