Abstract
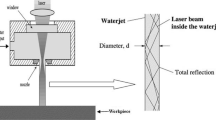
This research deals with the cutting of thin sheet metals at various distances, feed speeds and angles of incidence using a water jet guided laser. In the water jet guided laser process a laser beam is focused into a jet of water, which transmits the beam to the workpiece. This eliminates the need for any focus control. Nevertheless, most of its applications are in planar cutting where this advantage is not utilized. For the laser parameters, jet pressure and diameter in question, the value of 50 mm was found to be a fairly reliable upper limit to the cutting distance for both normal and inclined surfaces. In addition to the laser beam being absorbed partially by the water jet, the jet was found to be susceptible to disturbances. Specimen vibration caused by the water jet also impeded cutting a continuous kerf.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Synova (2002) The water jet guided laser. Synova S.A., Switzerland. http://www.synova.ch/pdf/microjet.pdf. Cited 28 March 2006
Richerzhagen B, Housh R, Wagner F, Manley J (2004) Water jet guided laser cutting: a powerful hybrid technology for fine cutting and grooving. ALAC 2004, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA. http://www.synova.ch/pdf/ALAC04.pdf. Cited 28 March 2006
Nilsson T, Boillat C, Mabillard G, Housh R, Wagner F, Richerzhagen B (2004) A technological leap in stencil cutting. On Board Technology, June 2004. http://www.OnBoard-Technology.com. Cited 28 March 2006
Chaplin M (2005) Water structure and behavior, molecular vibration and absorption. http://www.lsbu.ac.uk/water/vibrat.html. Cited 28 March 2006
Sogandares F, Fry E (1997) Absorption spectrum (340–640 nm) of pure water. l. Photothermal measurements. Appl Opt 36:8699–8709
Nikogosyan D (1997) Properties of optical and laser-related materials. Wiley, Chichester, England
Spiegel Á, Vágó N, Wagner F (2004) High efficiency Raman scattering in micrometer-sized water jets. Opt Eng 43:450–454
Couty P, Spiegel Á, Vágó N, Ugurtas B, Hoffmann P (2004) Laser-induced break-up of water jet waveguide. Exp Fluids 36:919–927
Richerzhagen B (2002) Industrial applications of the water jet guided laser. Ind Laser User 28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porter, J.A., Louhisalmi, Y.A., Karjalainen, J.A. et al. Cutting thin sheet metal with a water jet guided laser using various cutting distances, feed speeds and angles of incidence. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33, 961–967 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0521-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0521-7