Abstract
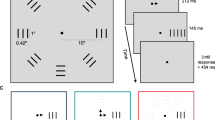
This experiment examined the effect of nonlinear magnification and foveal loading on the detection of peripheral visual targets. Peripheral objects were scaled using cortical magnification factors, and the foveal task was to determine mirror symmetry for pairs of figures. The results showed that nonlinear magnification had the effect of equating target detection performance at the centre and the periphery. The improved detection performance was present in both with and without foveal loading conditions, with the greatest performance improvement occurring for the farthest peripheral targets. These results suggest the potential usefulness of variable resolution projection displays designed to match the psychophysical properties of the human visual system and reduce the tunnel vision effect found in visual inspection and vigilance tasks in manufacturing industries. However, because of a lateral masking effect, it seems necessary to concurrently magnify the inter-object spacings as well as the object sizes to achieve better overall effectiveness with such variable resolution displays.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drury CG (1992) Inspection performance. In: Salvendy G (ed) Handbook of industrial engineering, vol 88. Wiley, New York, pp 2282–2314
Chi CF, Drury CG (1998) Do people choose an optimal response criterion in an inspection task?. IIE Trans 30(3):257–266
Stark L, Yamashita I, Tharp G, Ngo HX (1993) Search patterns and search paths in human visual search. In: Brogan D, Gale A, Carr K (eds) Visual Search in Visual Search 2. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 37–58
Ainsworth I, Ristic M, Brujic D (2000) CAD-based measurement path planning for free-form shapes using contact probes. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 16:23
Gramopadhye AK, Drury CG, Jiang X, Screenivasan R (2002) Visual search and visual lobe size: Can training on one affect the other?. Int J Ind Ergonom 30(3):181
Chow SWH, Chan AHS (1996) Effects of defect occurrence percentage and search time limit on inspection performance. Proc 4th Pan Pacific Conference on Occupational Ergonomics, Taiwan, ROC, pp 268–271
Tsai DM, Lin CP (2002) Fast defect detection in textured surfaces using 1D Gabor filters. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 20:664
Lin YJ, Murugappan P (2000) A new algorithm for CAD-Directed CMM dimensional inspection. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 16:107
Prieto F, Redarce T, Lepage R, Boulanger P (2002) An automated inspection system. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 19:917
Chen WF, Chen WY, Tang YY (2002) Evaluation of contour quality in sampling inspection of two drill types. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 19:66
Wiltschi K, Pinz A, Tony L (2000) An automatic assessment scheme for steel quality inspection. Mach Vision Appl 12:113
Drury CG, Prabhu PV (1994) Human factors in test and inspection. In: Salvendy G, Karwowski W (eds) Design of work and development of personnel in advanced manufacturing. Wiley-Interscience, Wiley Canada, pp 355–401
Drury CG, Addision JL (1973) An industrial study of the effects of feedback and fault density on inspection performance. Ergonomics 16:159
Schoonard JW, Gould JD (1973) Field of view and target uncertainty in visual search and inspection. Hum Factor 15:33
Schoonard JW, Gould JD, Miller LA (1973) Studies of visual inspection. Ergonomics 16:365
Faulkner TW, Murphy TJ (1975) Lighting for difficult visual tasks. In: Drury CG, Fox JG (eds) Human reliability in quality control. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 133–148
Boyce PR (1997) Illumination. In: Salvendy G (ed) Handbook of human factors and ergonomics. Wiley, New York, pp 882
Chan AHS, Ma RCW (2004) Effect of linear magnification on target detection performance in visual inspection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 23:375–382
Courtney AJ, ChanHS (1976) Visual lobe dimensions and search performance for targets on a competing homogeneous background. Percept Psychophys 40(1):39
Kee D, Jung ES, Chung MK (1992) Isoresponse time regions for the evaluation of visual search performance in ergonomic interface models. Ergonomics 35(3):243
Rantenen EM, Goldberg JH (1999) The effect of mental workload on the visual field size and shape. Ergonomics 42(6):816
Barbur JL, Forsyth PM (1988) The effective contrast of coloured targets and its relation to visual search. In: Brogan D (ed) Visual search. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 319–328
Sanders AF, Bruck R (1991) The effect of presentation time on the size of the visual lobe. Bull Psychon Soc 29(3):206
Chan HS, CourtneyAJ (1993) Effects of cognitive foveal load on a peripheral single-target detection task. Percept Motor Skills 77:515
Chan HS, Courtney AJ (1995) Visual performance on detection tasks with two targets. Int J Human Factor Manuf 5(4):417
Chan HS, Courtney AJ (1997) Visual performance on synchronous and asynchronous target detection tasks. Int J Human Factor Ergonom Manuf 7(3):197
Rovamo J, Virsu V (1979) An estimation and application of the human cortical magnification factor. Exp Brain Res 37:495
Virsu V, Nasanen R, Osmoviita K (1987) Cortical magnification and peripheral vision. J Opt Soc Am 4(8):1568
Virsu V, Rovamo J, Laurinen P, Nasanen R (1982) Temporal contrast sensitivity and cortical magnification. Vision Res 22:1211
Rentschler I, Treutwein B (1985) Loss of spatial phase relationships in extrafoveal vision. Nature 313:308
Levi DM, Klein SA, Aitsebaomo AP (1985) Vernier acuity, crowding and cortical magnification. Vision Res 25:963
Saarinen J (1987) Perception of positional relationships between line segments in eccentric vision. Perception 16:583
Gattass R, Sousa APB, Covey E (1985) Cortical visual areas of the macaque: Possible substrates for pattern recognition mechanisms. In: Chagas C, Gattass R, Gross C (eds) Pattern recognition mechanisms. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–20
Deyoe EA, Van Essen DC (1988) Concurrent processing streams in monkey visual cortex. Trends Neurosci 11:219
Van Essen DC, Newsome WT, Maunsell JHR (1984) The visual field representation in the striate cortex of the macaque monkey: asymmetrics, anisotropies and individual variability. Vision Res 24:429
Perry VH, Cowey A (1985) The gang lion cell and cone distributions in the monkey’s retina: Implications for central magnification factors. Vision Res 25:1795
Chan HS, Courtney AJ (1994) Effects of priority assignment of attentional resources, order of testing, and response sequence on tunnel vision. Percept Motor Skills 78:899
Kubala K, Hatch A, Hooker RB, Lewis L (1998) Investigation into variable addressibility image sensors and display systems. In: SID International Symposium Digest of Technical Papers 0098–966X, vol 29, pp 45–420
Wolford G, Chambers L (1983) Lateral masking as a function of spacing. Percept Psychophys 33(2):129
Eriksen CW, Schultz DW (1978) Temporal factors in visual information processing. In: Requin J (ed) Attention and performance VII. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ
Butler BE, Currie A (1986) On the nature of perceptual limits in vision: A new look at lateral masking. Vis Sel Attention, Psychol Res 48(4):201
Norman DA, Bobrow DG (1975) On data-limited and resource-limited processes. Cognit Psychol 7:44
Tullis T (1983) The formatting of alphanumeric displays: A review and analysis. Human Factor 25:657
Panerai FM, Juday RD (1996) Probabilistic anti-aliasing methods for dynamic variable resolution images. Proc Int Soc Opt Eng 2847:130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, A., Ma, R. Improving target detection with nonlinear magnification in visual inspection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28, 362–369 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2358-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2358-2