Abstract
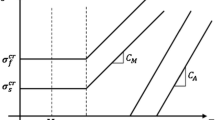
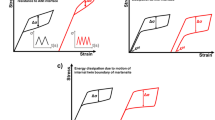
This paper documents an energy-based analysis of temperature oscillation during cyclic stress-induced phase transformation in shape memory alloys (SMAs). The conversion of total hysteresis work into dissipated heat and stored energy in SMAs is discussed, and the temperature oscillation at the shakedown state in cyclically loaded SMAs is modeled. To validate the theoretical model, both strain and stress-controlled tensile tests on pseudoelastic NiTi wires are performed under cyclic loading and an infrared camera is used to record the surface temperature of the wire. The results show that depending of the loading type, strain or stress-controlled loading, the amplitude of temperature oscillation during cyclic stress-induced phase transformation evolves differently with the frequency: The amplitude of the temperature oscillation under strain-controlled loading gradually reaches a saturated value independent of the frequency; however, for stress-controlled loading, the saturated temperature amplitude is frequency-dependent since it reduces significantly if the frequency is increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jani, J.M., Leary, M., Subic, A., Gibson, M.A.: A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 56(Supplement C), 1078–1113 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.084
Tokuda, M., Ye, M., Takakura, M., Sittner, P.: Thermomechanical behavior of shape memory alloy under complex loading conditions. Int. J. Plast. 15(2), 223–239 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(98)00066-7
Shaw, J.A.: Simulations of localized thermo-mechanical behavior in a NiTi shape memory alloy. Int. J. Plast. 16(5), 541–562 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(99)00075-3
Sedlák, P., Frost, M., Benešová, B., Zineb, T.B., Šttner, P.: Thermomechanical model for NiTi-based shape memory alloys including r-phase and material anisotropy under multi-axial loadings. Int. J. Plast. 39, 132–151 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2012.06.008
Benafan, O., Noebe, R., Padula, S., Garg, A., Clausen, B., Vogel, S., Vaidyanathan, R.: Temperature dependent deformation of the B2 austenite phase of a NiTi shape memory alloy. Int. J. Plast. 51, 103–121 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2013.06.003
Soul, H., Isalgue, A., Yawny, A., Torra, V., Lovey, F.C.: Pseudoelastic fatigue of NiTi wires: frequency and size effects on damping capacity. Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 085006 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/19/8/085006
Shaw, J.A., Kyriakides, S.: Thermomechanical aspects of NiTi. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 43(8), 1243–1281 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5096(95)00024-D
Entemeyer, D., Patoor, E., Eberhardt, A., Berveiller, M.: Strain rate sensitivity in superelasticity. Int. J. Plast. 16, 1269–1288 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(00)00010-3
Grabe, C., Bruhns, O.: On the viscous and strain rate dependent behavior of polycrystalline NiTi. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45(7–8), 1876–1895 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2007.10.029
Morin, C., Moumni, Z., Zaki, W.: A constitutive model for shape memory alloys accounting for thermomechanical coupling. Int. J. Plast. 27(5), 748–767 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2010.09.005
Morin, C., Moumni, Z., Zaki, W.: Thermomechanical coupling in shape memory alloys under cyclic loadings: experimental analysis and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plast. 27(12), 1959–1980 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2011.05.005
He, Y.J., Sun, Q.P.: Frequency-dependent temperature evolution in NiTi shape memory alloy under cyclic loading. Smart Mater. Struct. 19(11), 115014 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/19/11/115014
He, Y.J., Sun, Q.P.: On non-monotonic rate dependence of stress hysteresis of superelastic shape memory alloy bars. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48, 1688–1695 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2011.02.017
Pieczyska, E.A., Tobushi, H., Kulasinski, K., Takeda, K.: Impact of strain rate on thermomechanical coupling effects in TiNi SMA subjected to compression. Mater. Trans. 53(11), 1905–1909 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2012212
Yin, H., Yan, Y., Huo, Y., Sun, Q.: Rate dependent damping of single crystal CuAlNi shape memory alloy. Mater. Lett. 109, 287–290 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.07.062
Yu, C., Kang, G., Kan, Q., Zhu, Y.: Rate-dependent cyclic deformation of super-elastic NiTi shape memory alloy: thermo-mechanical coupled and physical mechanism-based constitutive model. Int. J. Plast. 72, 60–90 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2015.05.011
Kan, Q., Yu, C., Kang, G., Li, J., Yan, W.: Mechanics of materials experimental observations on rate-dependent cyclic deformation of super-elastic NiTi shape memory alloy. Mech. Mater. 97, 48–58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2016.02.011
Xie, X., Kan, Q., Kang, G., Lu, F., Chen, K.: Observation on rate-dependent cyclic transformation domain of super-elastic NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 671, 32–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.06.045
Wang, J., Moumni, Z., Zhang, W.: A thermomechanically coupled finite-strain constitutive model for cyclic pseudoelasticity of polycrystalline shape memory alloys. Int. J. Plast. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2017.06.003
Tobushi, H., Takafumi, N., Shimeno, Y., Takahiro, H.: Low-cycle fatigue of TiNi shape memory alloy and formulation of fatigue life. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. ASME 122(2), 186–191 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.482785
Eggeler, G., Hornbogen, E., Yawny, A., Heckmann, A., Wagner, M.: Structural and functional fatigue of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 378(1–2), 24–33 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.327
Matsui, R., Tobushi, H., Furuichi, Y., Horikawa, H.: Tensile deformation and rotating–bending fatigue properties of a highelastic thin wire, a superelastic thin wire, and a superelastic thin tube of NiTi alloys. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 126(4), 384 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1789952
Wagner, M., Sawaguchi, T., Kausträter, G., Höffken, D., Eggeler, G.: Structural fatigue of pseudoelastic NiTi shape memory wires. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 378(1–2), 105–109 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.11.058
Zhang, Y., Zhu, J., Moumni, Z., Zhang, W.: Energy-based fatigue model for shape memory alloys including thermomechanical coupling. Smart Mater. Struct. 25(3), 035042 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/25/3/035042
Zhang, Y., You, Y., Moumni, Z., Anlas, G., Zhu, J., Zhang, W.: Experimental and theoretical investigation of the frequency effect on low cycle fatigue of shape memory alloys. Int. J. Plast. 90, 1–30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2016.11.012
Hornbogen, E.: Review thermo-mechanical fatigue of shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 39(2), 385–399 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000011492.88523.d3
Zheng, L., He, Y., Moumni, Z.: Lüders-like band front motion and fatigue life of pseudoelastic polycrystalline NiTi shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 123, 46–50 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.05.042
Zheng, L., He, Y., Moumni, Z.: Investigation on fatigue behaviors of NiTi polycrystalline strips under stress-controlled tension via in-situ macro-band observation. Int. J. Plast. 90, 116–145 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2016.12.008
Chang, B.-C., Shaw, J.A., Iadicola, M.A.: Thermodynamics of shape memory alloy wire: modeling, experiments, and application. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 18(1), 83–118 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-006-0022-9
Cisse, C., Zaki, W., Zineb, T.B.: A review of constitutive models and modeling techniques for shape memory alloys. Int. J. Plast. 76, 244–284 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2015.08.006
Haller, L., Nedjar, B., Moumni, Z., Vedinaş, I., Trană, E.: A thermomechanical model accounting for the behavior of shape memory alloys in finite deformations. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 28(4), 957–975 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-015-0431-8
Soldatos, D., Triantafyllou, S.P., Panoskaltsis, V.P.: Thermomechanical couplings in shape memory alloy materials. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 29(3), 805–834 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-017-0559-9
Rosakis, P., Rosakis, A.J., Ravichandran, G.: A thermodynamic internal variable model for the partition of plastic work into heat and stored energy in metals. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48, 581–607 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5096(99)00048-4
Moumni, Z., Van Herpen, A., Riberty, P.: Fatigue analysis of shape memory alloys: energy approach. Smart Mater. Struct. 14(5), S287 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/14/5/017
Zaki, W., Moumni, Z.: A 3D model of the cyclic thermomechanical behavior of shape memory alloys. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55(11), 2427–2454 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2007.03.011
Gu, X., Zhang, W., Zaki, W., Moumni, Z.: An extended thermomechanically coupled 3D rate-dependent model for pseudoelastic smas under cyclic loading. Smart Mater. Struct. 26(9), 095047 (2017)
Wang, J., Moumni, Z., Zhang, W.: A thermomechanically coupled finite-strain constitutive model for cyclic pseudoelasticity of polycrystalline shape memory alloys. Int. J. Plast. 97(Supplement C), 194–221 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2017.06.003
He, Y., Sun, Q.: Rate-dependent domain spacing in a stretched NiTi strip. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47(20), 2775–2783 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.06.006
Zhang, S., He, Y.: Fatigue resistance of branching phase-transformation fronts in pseudoelastic NiTi polycrystalline strips. Int. J. Solids Struct. 135, 233–244 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.11.023
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Research and Development Program of China (2017YFB1102800) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (11620101002, 51761145111, 51790171). Ziad Moumni would like to acknowledge SAFEA (State Administration of Foreign Expert of China) for their financial support (WQ20116100007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Andreas Öchsner.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Moumni, Z., You, Y. et al. Energy-based analysis of temperature oscillation at the shakedown state in shape memory alloys. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 31, 1387–1399 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-019-00751-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-019-00751-9