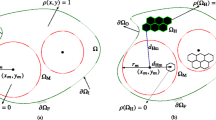
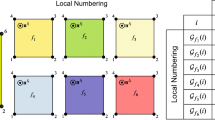
Abstract
The geometric shape of an element plays a key role in computational methods. Triangular and quadrilateral shaped elements are utilized by standard finite element methods. The pioneering work of Wachspress laid the foundation for polygonal interpolants which introduced polygonal elements. Tessellations may be considered as the next stage of element shape evolution. In this work, we investigate the topology optimization of tessellations as a means to coalesce art and engineering. We mainly focus on M.C. Escher’s tessellations using recognizable figures. To solve the state equation, we utilize a Mimetic Finite Difference inspired approach, known as the Virtual Element Method. In this approach, the stiffness matrix is constructed in such a way that the displacement patch test is passed exactly in order to ensure optimum numerical convergence rates. Prior to exploring the artistic aspects of topology optimization designs, numerical verification studies such as the displacement patch test and shear loaded cantilever beam bending problem are conducted to demonstrate the accuracy of the present approach in two-dimensions.























Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Escher MC The official website. http://www.mcescher.com/
Almeida SRM, Paulino GH, Silva ECN (2010) Layout and material gradation in topology optimization of functionally graded structures: A global-local approach. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42(6):855–868
Arroyo M, Ortiz M (2006) Local maximum-entropy approximation schemes: a seamless bridge between finite elements and meshfree methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65(13):2167– 2202
Barber JR (2010) Elasticity, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Beghini LL, Beghini A, Katz N, Baker WF, Paulino GH (2014) Connecting architecture and engineering through structural topology optimization. Eng Struct 59:716–726
Beirão Da Veiga L, Brezzi F, Cangiani A, Manzini G, Marini LD, Russo A (2013a) Basic principles of virtual element methods. Math Model Methods in Appl Sci 23(1):199–214
Beirão Da Veiga L, Brezzi F, Marini LD (2013b) Virtual elements for linear elasticity problems. SIAM J Numer Anal 51(2):794–812
Beirão Da Veiga L, Brezzi F, Marini LD, Russo A (2013c) The hitchhiker guide to the virtual element Method. Math Model Methods in Appl Sci:1–32
Beirão Da Veiga L, Manzini G (2013) A virtual element method with arbitrary regularity. IMA J Numer Anal:1–23. doi:10.1093/imanum/drt018
Belikov VV, Ivanov VD, Kontorovich VK, Korytnik SA, Semenov AY (1997) The Non-sibsonian interpolation: A new method of interpolation of the values of a function on an arbitrary set of points. Comput Math Math Phys 37(1):9–15
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1:193–202
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization - Theory, methods and applications. Springer, New York
Bishop JE (2009) Simulating the pervasive fracture of materials and structures using randomly close packed Voronoi tessellations. Comput Mech 44(4):455–471
Bolander JE, Saito S (1998) Fracture analysis using spring networks with random geometry. Eng Fract Mech 61:569–591
Bolander JE, Sukumar N (2005) Irregular lattice model for quasistatic crack propagation. Phys Rev B- Condens Matter Mater Phys 71(9). art. no. 094106
Bool FH, Kist JR, Wierda F, Locher JL (1992) M.C. Escher: His life and complete graphic work. Harry N. Abrams, Inc, New York
Brezzi F, Marini LD (2013) Virtual Element Methods for plate bending problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 253:455–462
Christ NH, Friedberg R, Lee TD (1982) Weights of links and plaquettes in a random lattice. Nucl Phys B 210(3):337–346
Christensen PW, Klarbring A (2008) An introduction to structural optimization. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Cook RD, Malkus DS, Plesha ME, Witt RJ (2002) Concepts and applications of finite element analysis. John Wiley and Sons, Inc, New Jersey
Emmer M, Schattschneider D (eds) (2005) M.C. Escher’s legacy: A centennial celebration. In: Emmer M, Schattschneider D (eds). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Fathauer R (2010) Designing and drawing tessellations. Tessellations
Fathauer R (2011) Fractal trees. Tarquin Publications
Floater MS (2003) Mean value coordinates. Comput Aided Geom Des 20(1):19–27
Floater MS, Hormann K, Kòs G (2004) A general construction of barycentric coordinates over convex polygons. Adv Comput Math 24(1-4):311–331
Floater MS, Kòs G, Reimers M (2005) Mean value coordinates in 3D. Comput Aided Geom Des 22(7):623–631
Gain AL, Paulino GH (2012) Phase-field based topology optimization with polygonal elements: A finite volume approach for the evolution equation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46(3):327– 342
Gain AL, Paulino GH, Leonardo D, Menezes IFM (2013) Topology optimization using polytopes. Submitted. arXiv:1312.7016
Gain AL, Talischi C, Paulino GH (2014) On the virtual element method for three-dimensional elasticity problems on arbitrary polyhedral meshes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. In press. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2014.05.005
Ghosh S (2011) Micromechanical analysis and multi-scale modelling using the voronoi cell finite element method. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Groenwold AA, Etman LFP (2008) On the equivalence of optimality criterion and sequential approximate optimization methods in the classical topology layout problem. Int J Numer Methods Eng 73(3):297–316
Hassani B, Hinton E (1999) Homogenization and structural topology optimization: Theory, practice and software. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Hiyoshi H, Sugihara K (1999) Two generalizations of an interpolant based on Voronoi diagrams. Int J Shape Model 5(2):219–231
Hormann K, Sukumar N (2008) Maximum entropy coordinates for arbitrary polytopes In: Eurographics symposium on geometry processing, vol 27, pp 1513–1520
Hormann K, Tarini M (2004) A quadrilateral rendering primitive In: Proceedings of the siggraph/eurographics workshop on graphics hardware, pp 7–14
Mijar AR, Swan CC, Arora JS, Kosaka I (1998) Continuum topology optimization for concept design of frame bracing systems. J Struct Eng 124(5):541–550
Natarajan S, Bordas S, Mahapatra DR (2009) Numerical integration over arbitrary polygonal domains based on Schwarz-Christoffel conformal mapping. Int J Numer Methods Eng 80(1):103–134
Ohsaki M (2010) Optimization of finite dimensional structures. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Papoulia KD, Vavasis SA, Ganguly P (2006) Spatial convergence of crack nucleation using a cohesive finite-element model on a pinwheel-based mesh. Int J Numer Methods Eng 67(1):1–16
Paulino GH, Park K, Celes W, Espinha R (2010) Adaptive dynamic cohesive fracture simulation using nodal perturbation and edge-swap operators. Int J Numer Methods Eng 84(11):1303–1343
Penrose R (1979a) Pentaplexity a class of non-periodic tilings of the plane. The Math Intell 2(1):32–37
Penrose R (1979b) Set of tiles for covering a surface. U.S. Patent 4133152
Rozvany GIN, Zhou M, Birker T (1992) Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 4(3-4):250–252
Schattschneider D (2004) M.C. Escher: Visions of symmetry, 2nd edn. Harry N. Abrams
Sibson R (1980) A vector identity for the Dirichlet tessellation. Math Proc Camb Philos Soc 87:151–155
Sukumar N (2004) Construction of polygonal interpolants: A maximum entropy approach. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(12):2159–2181
Sukumar N, Malsch EA (2006) Recent advances in the construction of polygonal finite element interpolations. Arch Comput Methods Eng 13(1):129–163
Sukumar N, Moran B, Semenov AY, Belikov VV (2001) Natural neighbor Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50:1–27
Sukumar N, Tabarraei A (2004) Conforming polygonal finite elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(12):2045–2066
Suzuki K, Kikuchi N (1991) A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 93(3):291–318
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotoes - a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Talischi C, Paulino GH, Pereira A, Menezes IFM (2010) Polygonal finite elements for topology optimization: A unifying paradigm. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82:671–698
Talischi C, Paulino GH, Pereira A, Menezes IFM (2012) PolyTop: A matlab implementation of a general topology optimization framework using unstructured polygonal finite element meshes. J Struct Multidiscip Optim 45(3):329–357
Timoshenko SP, Goodier JN (1970) Theory of elasticity, 3rd edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Wachspress EL (1975) A rational finite element basis. Academic Press, New York
Warren J (1996) Barycentric coordinates for convex polytopes. Adv Comput Math 6(1):97–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paulino, G.H., Gain, A.L. Bridging art and engineering using Escher-based virtual elements. Struct Multidisc Optim 51, 867–883 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1179-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1179-7