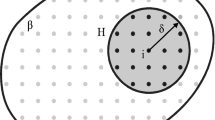
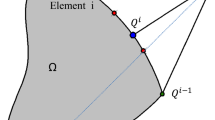
Abstract
Uniform grids have been the common choice of domain discretization in the topology optimization literature. Over-constraining geometrical features of such spatial discretizations can result in mesh-dependent, sub-optimal designs. Thus, in the current work, we employ unstructured polygonal meshes constructed using Voronoi tessellations to conduct structural topology optimization. We utilize the phase-field method, derived from phase transition phenomenon, which makes use of the Allen-Cahn differential equation and sensitivity analysis to update the evolving structural topology. The solution of the Allen-Cahn evolution equation is accomplished by means of a centroidal Voronoi tessellation (CVT) based finite volume approach. The unstructured polygonal meshes not only remove mesh bias but also provide greater flexibility in discretizing complicated (e.g. non-Cartesian) domains. The features of the current approach are demonstrated using various numerical examples for compliance minimization and compliant mechanism problems.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Jouve F (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194:363–393
Allen SM, Cahn JW (1979) A microscopic theory for antiphase boundary motion and its application to antiphase domain coarsening. Acta Metall 27:1085–1095
Aranson IS, Kalatsky VA, Vinokur VM (2000) Continuum field description of crack propagation. Phys Rev Lett 85(1):118–121
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1:193–202
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 69(9–10):635–654
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization—theory, methods and applications. Springer, New York
Bolander JE, Saito S (1998) Fracture analysis using spring networks with random geometry. Eng Fract Mech 61:569–591
Bourdin B (2001) Filters in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(8):2143–2158
Bourdin B, Chambolle A (2003) Design-dependent loads in topology optimization. ESAIM—Control Optim Calc Var 9:19–48
Burger M, Stainko R (2006) Phase-field relaxation of topology optimization with local stress constraints. SIAM J Control Optim 45(4):1447–1466
Caginalp G (1986) An analysis of a phase field model of a free boundary. Arch Ration Mech Anal 92(3):205–245
Cahn JW, Hillard JE (1958) Free energy of a nonuniform system. I. Interfacial energy. J Chem Phys 28:258–267
Céa J, Garreau S, Guillaume P, Masmoudi M (2000) The shape and topological optimizations connection. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 188(4):713–726
Courant R, Friedrichs KO, Lewy H (1928) Über die partiellen Differenzengleichungen der mathematischen Physik. Math Ann 100(1):32–74
Cuthill E, McKee J (1969) Reducing the bandwidth of sparse symmetric matrices. In: Proceedings of the 24th national conference. ACM Press, New York, pp 157–172
Diaz AR, Sigmund O (1995) Checkerboard patterns in layout optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 10(1):40–45
Eschenauer H, Schumacher A (1994) Bubble method for topology and shape optimization of structures. Struct Optim 8(1):42–51
Feng X, Wu H (2008) A posteriori error estimates for finite element approximations of the Cahn–Hilliard equation and the Hele–Shaw flow. J Comput Math 26(6):767–796
Ghosh S (2011) Micromechanical analysis and multi-scale modelling using the Voronoi cell finite element method. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay SN (1991) A two-dimensional automatic mesh generator for finite element analysis for random composites. Comput Struct 41(2):245–256
Guest JK, Prevost JH, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(2):238–254
Kobayashi R (1993) Modeling and numerical simulations of dendritic crystal growth. Phys D: Nonlin Phenom 63(3–4):410–423
Lloyd S (1982) Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 28(2):129–137
March R (1992) Visual reconstructions with discontinuities using variational methods. Image Vis Comput 10:30–38
Martin S, Kaufmann P, Botsch M, Wicke M, Gross M (2008) Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions. Comput Graph Forum 27(5):1521–1529
Nguyen TH, Paulino GH, Song J, Le CH (2010) A computational paradigm for multiresolution topology optimization (MTOP). Struct Multidisc Optim 41(4):525–539
Nguyen TH, Song J, Paulino GH (2011) Single-loop system reliability-based topology optimization considering statistical dependence between limit-states. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 44(5):593–611
Osher S, Fedkiw R (2003) Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces. Springer, New York
Osher S, Sethian JA (1988) Front propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J Comput P 79:12–49
Paulino GH, Menezes IFM, Gattass M, Mukherjee S (1994a) Node and element resequencing using the Laplacian of a finite element graph. Part I: General concepts and algorithm. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37(9):1994
Paulino GH, Menezes IFM, Gattass M, Mukherjee S (1994b) Node and element resequencing using the Laplacian of a finite element graph. Part II: Implementation and numerical results. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37(9):1531–1555
Pendry PD, Schurig D, Smith DR (2006) Controlling electromagnetic fields. Science 312:1780–1782
Pingen G, Waidmann M, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2010) A parametric level-set approach for topology optimization of flow domains. Struct Multidisc Optim 41(1):117–131
Rozvany GIN, Querin OM, Gaspar Z, Pomezanski V (2003) Weight-increasing effect of topology simplification. Struct Multidisc Optim 25(5–6):459–465
Rozvany GIN, Zhou M, Birker T (1992) Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Multidisc Optim 4(3–4):250–252
Sethian JA (1999) Level-set methods and fast marching methods: evolving interfaces in computational geometry, fluid mechanics, computer vision and materials science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Sigmund O, Peterson J (1998) Numerical instabilities in topology optimization: a survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima. Struct Optim 16(1):68–75
Sokolowski J, Zochowski A (1999) On the topological derivatives in shape optimization. SIAM J Control Optim 37:1251–1272
Sukumar N, Tabarraei A (2004) Conforming polygonal finite elements. Int J Numer methods Eng 61(12):2045–2066
Sun Y, Beckermann C (2007) Sharp interface tracking using the phase-field equation. J Comput Phys 220(2):626–653
Sutradhar A, Paulino GH, Miller MJ, Nguyen TH (2010) Topology optimization for designing patient-specific large craniofacial segmental bone replacements. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(30):13222–13227
Suzuki K, Kikuchi N (1991) A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 93(3):291–318
Takezawa A, Nishiwaki S, Kitamura M (2010) Shape and topology optimization based on the phase field method and sensitivity analysis. J Comput Phys 229:2697–2718
Talischi C, Paulino GH, Pereira A, Menezes IFM (2010) Polygonal finite elements for topology optimization: A unifying paradigm. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82:671–698
Talischi C, Paulino GH, Pereira A, Menezes IFM (2011) PolyMesher: A general-purpose mesh generator for polygonal elements written in MATLAB. Struct Multidisc Optim 45(3):309–328
Vasconcellos JFV, Maliska CR (2004) A finite-volume method based on Voronoi discretization for fluid flow problems. Numer Heat Transf B 45:319–342
Wallin M, Ristinmaa M, Askfelt H (2012) Optimal topologies derived from a phase-field method. Struct Multidisc Optim 45(2):171–183
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level-set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:227–246
Wang MY, Zhou S (2004a) Phase field: A variational method for structural topology optimization. Comput Model Eng Sci 6(6):547–566
Wang MY, Zhou S (2004b) Synthesis of shape and topology of multi-material structures with a phase-field method. J Comput-Aided Mater Des 11:117–138
Warren JA, Kobayashi R, Lobkovsky AE, Carter WC (2003) Extending phase field models of solidification to polycrystalline materials. Acta Mater 51(20):6035–6058
Wicke M, Botsch M, Gross M (2007) A finite element method on convex polyhedra. Comput Graph Forum 26(3):355–364
Yip M, Mohle J, Bolander JE (2005) Automated modeling of three-dimensional structural components using irregular lattices. Comput-Aided Civil Infrastruct Eng 20(6):393–407
Zhou S, Wang MY (2007) Multimaterial structural topology optimization with generalized Cahn-Hilliard model of multiphase transitions. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 33:89–111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gain, A.L., Paulino, G.H. Phase-field based topology optimization with polygonal elements: a finite volume approach for the evolution equation. Struct Multidisc Optim 46, 327–342 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0781-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0781-9