Abstract
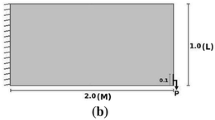
This paper presents and applies a novel shape optimization approach based on the level set description of the geometry and the extended finite element method (X-FEM). The method benefits from the fixed mesh work using X-FEM and from the curves smoothness of the level set description. Design variables are shape parameters of basic geometric features that are described with a level set representation. The number of design variables of this formulation remains small, whereas global (i.e. compliance) and local constraints (i.e. stresses) can be considered. To illustrate the capability of the method to handle stress constraints, numerical applications revisit the minimization of stress concentration in a 2D filet in tension, which has been previously studied in Pedersen (2003). Our results illustrate the great interest of using X-FEM and level set description together. A special attention is also paid to stress computation and accuracy with the X-FEM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Maillot H (2004) Topology optimization for minimum stress design with the homogenization method. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 28(2-3):87–98
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Belytschko T, Moës N, Usui S, Parimi C (2001) Arbitrary discontinuities in finite elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50:993–1013
Belytschko T, Parimi C, Moës N, Sukumar N, Usui S (2003) Structured extended finite element methods for solids defined by implicit surfaces. Int J Numer Methods Eng 56:609–635
Belytschko T, Xiao SP, Parimi C (2003) Topology optimization with implicit functions and regularization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 57:1177–1196
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Bennet JA, Botkin E (1985) Structural shape optimization with geometric description and adaptive mesh refinement. AIAA J 23(3):458–464
Braibant V, Fleury C (1984) Shape optimal design using b-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 44:247–267
Chessa J, Belytschko T (2003) An extended finite element method for two-phase fluids. J Appl Mech 70:10–17
Dankova J, Haslinger J (1996) Numerical realization of a fictitious domain approach used in shape optimization. Part I distributed controls. Appl Math 41:123–147
Daux C, Moës N, Dolbow J, Sukumar N, Belytschko T (2000) Arbitrary branched and intersecting cracks with the extended finite element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 48:1741–1760
Ding Y (1986) Shape optimization of structures: a literature survey. Comput Struct 24(4):985–1004
Duysinx P, Bendsøe MP (1998) Control of local stresses in topology optimization of continuum structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 43:1453–1478
Duysinx P, Van Miegroet L, Jacobs T, Fleury C (2006) Generalized shape optimization using X-FEM and level set methods. IUTAM Symposium on Topological Design, Optimization of Structures, Machines and Materials. Springer, Berlin Hiedelberg New York, pp 23–32
Fleury C (1989) Conlin: an efficient dual optimizer based on convex approximation concepts. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 1:81–89
Guétari Y, Le Corre S, Moës N (2005) Étude des possibilités de la méthode X-FEM pour la simulation numérique de la coupe. Mécanique et Industries 6:315–319
Haftka R, Grandhi R (1986) Structural shape optimization — a survey. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 57:91–106
Kim H, Querin OM, Steven GP, Xie YM (2002) Improving efficiency of evolutionary structural optimization by implementing fixed grid mesh. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 24:441–448
Moës N, Dolbow J, Belytschko T (1999) A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing. Int J Numer Methods Eng 46:131–150
Moës N, Gravouil A, Belytschko T (2002) Non-planar 3d crack growth by the extended finite element and level sets — part i: mechanical model. Int J Numer Methods Eng 53:2549–2568
Moës N, Cloirec M, Cartraud P, Remacle JF (2003) A computational approach to handle complex microstructure geometries. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:3163–3177
Norato J, Haber R, Tortorelli D, Bendsøe MP (2004) A geometry projection method for shape optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 60:2289–2312
Novotny AA, Feijoo RA, Taroco E, Padra C (2003) Topological sensitivity analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:803–829
Osher S, Sethian JA (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79:12–49
Pedersen P (2000) On optimal shapes in materials and structures. Struct Optim 19(3):169–182
Pedersen P (2003) Optimal designs — structures and materials - problems and tools. ISBN 87-90416-06-6. http://www.fam.web.mek.dtu.dk/pp.html
Pedersen P, Laursen C (1983) Design for minimum stress concentration by finite element and linear programming. J Struct Mech 10(4):375–391
Pereira J, Fancello E, Barcellos D (2004) Topology optimization of continuum structures with material failure constraints. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 26(1-2):50–66
Peterson RE (1953) Stress concentration design factors. Wiley, New York
Rozvany GIN (1996) Some shortcomings in Michell’s truss theory. Struct Optim 12: 44–250
Sokolowski J, Zochowski A (1999) On the topological derivative in shape optimization. SIAM J Control Optim 37(4):1251–1272
Sukumar N, Chopp DL, Moes N, Belytschko T (2001) Modeling holes and inclusions by level sets in the extended finite-element method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190:6183–6200
Van Miegroet L, Moës N, Fleury C, Duysinx P (2005) Generalized shape optimization based on the level set method. In: Herskowitz J (ed) Proceedings of the 6th World Congress of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Van Miegroet L, Lemaire E, Jacobs T, Dusyinx P (2006) Stress constrained optimization using X-FEM and level set description. In: Mota Soares CA (ed)Proceeding of 3rd European Conference on Computational Mechanics. Shape and topological sensitivity analysis: theory and applications. Lisbon, Portugal
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:227–246
Zhang S, Belegundu AD (1992) A systematic approach for generating velocity fields in shape optimization. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 5(1-2)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Miegroet, L., Duysinx, P. Stress concentration minimization of 2D filets using X-FEM and level set description. Struct Multidisc Optim 33, 425–438 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0091-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0091-1