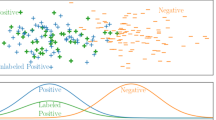
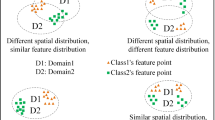
Abstract
Source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) uses models trained from source domains to solve similar tasks in unlabeled domains, without accessing source domain data. Existing SFDA methods have not been able to learn spatial and semantic structural information of target domains simultaneously, making them insufficient and inefficient for target domain exploration. To fully explore the target domain structural information, we propose a novel representation learning framework, called structural information enhancement (SIE). SIE has a two-stage approach that, in the first stage, clusters local neighbors and pushes away global non-neighbors in the feature space to obtain spatial structural information. In the second stage, SIE fine-tunes the clustered model using a semantic structure consistency strategy that exploits semantic structural information by mutual learning interpolated sample pairs. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method, and our method can serve as a strong baseline for future SFDA research.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sriperumbudur, B.K., Gretton, A., Fukumizu, K., Schölkopf, B., Lanckriet, G.R.: Hilbert space embeddings and metrics on probability measures. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11, 1517–1561 (2010)
Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K.M., Rasch, M.J., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.: A kernel two-sample test. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13(1), 723–773 (2012)
Redko, I., Morvant, E., Habrard, A., Sebban, M., Bennani, Y.: A survey on domain adaptation theory: learning bounds and theoretical guarantees. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.11829 (2020)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Zhang, N., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Deep domain confusion: maximizing for domain invariance. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3474 (2014)
Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 97–105 (2015). PMLR
Long, M., Cao, Y., Cao, Z., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Transferable representation learning with deep adaptation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(12), 3071–3085 (2018)
Ganin, Y., Lempitsky, V.: Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1180–1189 (2015). PMLR
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P., Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., Marchand, M., Lempitsky, V.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 2096 (2016)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7167–7176 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Tang, H., Jia, K., Tan, M.: Domain-symmetric networks for adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5031–5040 (2019)
Yang, S., Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S., et al.: Exploiting the intrinsic neighborhood structure for source-free domain adaptation. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 29393–29405 (2021)
Yang, S., Wang, Y., Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S.: Generalized source-free domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 8978–8987 (2021)
Li, R., Jiao, Q., Cao, W., Wong, H.S., Wu, S.: Model adaptation: unsupervised domain adaptation without source data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9641–9650 (2020)
Xia, H., Zhao, H., Ding, Z.: Adaptive adversarial network for source-free domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9010–9019 (2021)
Saenko, K., Kulis, B., Fritz, M., Darrell, T.: Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 213–226 (2010). Springer
Venkateswara, H., Eusebio, J., Chakraborty, S., Panchanathan, S.: Deep hashing network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5018–5027 (2017)
Peng, X., Usman, B., Kaushik, N., Hoffman, J., Wang, D., Saenko, K.: Visda: The visual domain adaptation challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.06924 (2017)
Kundu, J.N., Kulkarni, A.R., Bhambri, S., Mehta, D., Kulkarni, S.A., Jampani, V., Radhakrishnan, V.B.: Balancing discriminability and transferability for source-free domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 11710–11728 (2022). PMLR
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 63(11), 139–144 (2020)
Long, M., Cao, Z., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Conditional adversarial domain adaptation. Advances in neural information processing systems 31 (2018)
Saito, K., Watanabe, K., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T.: Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3723–3732 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Liu, T., Long, M., Jordan, M.: Bridging theory and algorithm for domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 7404–7413 (2019). PMLR
Liang, J., Hu, D., Feng, J.: Do we really need to access the source data? source hypothesis transfer for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6028–6039 (2020). PMLR
Liang, J., Hu, D., Wang, Y., He, R., Feng, J.: Source data-absent unsupervised domain adaptation through hypothesis transfer and labeling transfer. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2021)
Yang, S., Wang, Y., Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S.: Unsupervised domain adaptation without source data by casting a bait. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.12427 1(2), 5 (2020)
Huang, J., Guan, D., Xiao, A., Lu, S.: Model adaptation: historical contrastive learning for unsupervised domain adaptation without source data. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 34, 3635–3649 (2021)
Wu, Z., Xiong, Y., Yu, S.X., Lin, D.: Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimination. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3733–3742 (2018)
Yang, S., Wang, Y., Wang, K., Jui, S., et al.: Attracting and dispersing: A simple approach for source-free domain adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2022)
Wang, F., Han, Z., Gong, Y., Yin, Y.: Exploring domain-invariant parameters for source free domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7151–7160 (2022)
Zhang, H., Cisse, M., Dauphin, Y.N., Lopez-Paz, D.: mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.09412 (2017)
Kim, J.H., Choo, W., Jeong, H., Song, H.O.: Co-mixup: Saliency guided joint mixup with supermodular diversity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.03065 (2021)
Chou, H.P., Chang, S.C., Pan, J.Y., Wei, W., Juan, D.C.: Remix: rebalanced mixup. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 95–110 (2020). Springer
Na, J., Jung, H., Chang, H.J., Hwang, W.: Fixbi: Bridging domain spaces for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1094–1103 (2021)
Wang, X., Li, L., Ye, W., Long, M., Wang, J.: Transferable attention for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 5345–5352 (2019)
Cui, S., Wang, S., Zhuo, J., Su, C., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Gradually vanishing bridge for adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12455–12464 (2020)
Tang, H., Chen, K., Jia, K.: Unsupervised domain adaptation via structurally regularized deep clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8725–8735 (2020)
Lee, C.Y., Batra, T., Baig, M.H., Ulbricht, D.: Sliced wasserstein discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10285–10295 (2019)
Jin, Y., Wang, X., Long, M., Wang, J.: Minimum class confusion for versatile domain adaptation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 464–480 (2020). Springer
Lu, Z., Yang, Y., Zhu, X., Liu, C., Song, Y.Z., Xiang, T.: Stochastic classifiers for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9111–9120 (2020)
Xu, R., Liu, P., Wang, L., Chen, C., Wang, J.: Reliable weighted optimal transport for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4394–4403 (2020)
Xu, R., Li, G., Yang, J., Lin, L.: Larger norm more transferable: An adaptive feature norm approach for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1426–1435 (2019)
Chang, W.G., You, T., Seo, S., Kwak, S., Han, B.: Domain-specific batch normalization for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7354–7362 (2019)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very indebted to the anonymous referees for their critical comments and suggestions for the improvement of this paper. This work was supported by National Key Research and development Program of China (2021YFA1000102), and in part by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62376285, 62272375, 61673396), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (No. ZR2022MF260).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Shao, M., Zhang, L. et al. Two-stage structural information enhancement for source-free domain adaptation. Machine Vision and Applications 34, 121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01472-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01472-5